price. - Cloudfront.net
... increases the use of the other Price of complement goes up - curve shifts left; Price of complement goes down - curve shifts right Change in Expectations: If you expect something better to come out - curve shifts left; If you expect something to be scarce in the future - curve shifts right Number of ...
... increases the use of the other Price of complement goes up - curve shifts left; Price of complement goes down - curve shifts right Change in Expectations: If you expect something better to come out - curve shifts left; If you expect something to be scarce in the future - curve shifts right Number of ...
Eco 301 Name
... producers would receive. With the tax, the demand curve shifts down by $5 and the amount producers receive is reduced to PP. However, the amount consumers must pay is PC, which is exactly what they would pay without the tax, P*. Hence, the burden on consumers, PC - P*, is zero, while the burden on p ...
... producers would receive. With the tax, the demand curve shifts down by $5 and the amount producers receive is reduced to PP. However, the amount consumers must pay is PC, which is exactly what they would pay without the tax, P*. Hence, the burden on consumers, PC - P*, is zero, while the burden on p ...
problem set 7 - Shepherd Webpages
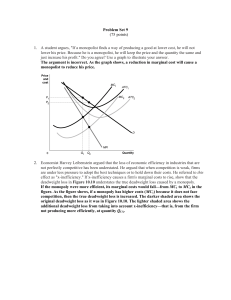
... Draw an average total cost curve in each of the following figures to indicate that the firm in Part (a) is operating with an economic profit greater than zero, the firm in Part (b) is operating with an economic loss, and the firm in Part (c) is “breaking even” (operating with an economic profit equa ...
... Draw an average total cost curve in each of the following figures to indicate that the firm in Part (a) is operating with an economic profit greater than zero, the firm in Part (b) is operating with an economic loss, and the firm in Part (c) is “breaking even” (operating with an economic profit equa ...
Intermediate Microeconomics
... Aggregate surplus and maximization of that surplus, measuring, deadweight loss, ...
... Aggregate surplus and maximization of that surplus, measuring, deadweight loss, ...
FAST ANSWErS 2 Term1 TEST
... Sand is a factor of production of HDB flats (1) . As such when the price of sand increases, P will increase the cost of production (1). This means that government cannot produce as much flats as they used to and will cause the supply curve for HDB flats to shift leftward or upwards from S0 to S1. Fr ...
... Sand is a factor of production of HDB flats (1) . As such when the price of sand increases, P will increase the cost of production (1). This means that government cannot produce as much flats as they used to and will cause the supply curve for HDB flats to shift leftward or upwards from S0 to S1. Fr ...
f04ex2 - Rose
... ___ 15. Suppose demand has increased in a perfectly competitive industry and each firm has moved to its new short-run equilibrium. Then, in the further process of long-run adjustment, the individual firm will face: A. increasing price and increasing profit. B. increasing price and decreasing profit ...
... ___ 15. Suppose demand has increased in a perfectly competitive industry and each firm has moved to its new short-run equilibrium. Then, in the further process of long-run adjustment, the individual firm will face: A. increasing price and increasing profit. B. increasing price and decreasing profit ...
Second Midterm and Answers to Second Midterm
... MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTIONS (4 points each) 11) Luxemburg is a small country in Europe. Before free-trade between Luxemburg and the international market is allowed, the local price of a pound of beef is $4.50 in Luxemburg and $3.50 in the international market. When free-trade is allowed between Luxem ...
... MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTIONS (4 points each) 11) Luxemburg is a small country in Europe. Before free-trade between Luxemburg and the international market is allowed, the local price of a pound of beef is $4.50 in Luxemburg and $3.50 in the international market. When free-trade is allowed between Luxem ...
Chapter 3
... The Demand Side of the Market Demand Schedules and Demand Curves: Demand schedule A table showing the relationship between the price of a product and the quantity of the product demanded. Quantity demanded The amount of a well defined good or service that a consumer is willing and able to purchase ...
... The Demand Side of the Market Demand Schedules and Demand Curves: Demand schedule A table showing the relationship between the price of a product and the quantity of the product demanded. Quantity demanded The amount of a well defined good or service that a consumer is willing and able to purchase ...
Chapter 3
... The Demand Side of the Market Demand Schedules and Demand Curves: Demand schedule A table showing the relationship between the price of a product and the quantity of the product demanded. Quantity demanded The amount of a well defined good or service that a consumer is willing and able to purchase ...
... The Demand Side of the Market Demand Schedules and Demand Curves: Demand schedule A table showing the relationship between the price of a product and the quantity of the product demanded. Quantity demanded The amount of a well defined good or service that a consumer is willing and able to purchase ...
P 1 - Arcada
... As more firms join the market, the industry supply curve shifts to the right, and market price falls. ...
... As more firms join the market, the industry supply curve shifts to the right, and market price falls. ...
Chapter 2 - Test Bank
... The demand for grapefruit juice increases as the price of orange juice increases because grapefruit juice is a substitute. As the demand for grapefruit juice increases, the equilibrium price and quantity of grapefruit juice increase. ...
... The demand for grapefruit juice increases as the price of orange juice increases because grapefruit juice is a substitute. As the demand for grapefruit juice increases, the equilibrium price and quantity of grapefruit juice increase. ...
See graph - personal.kent.edu
... e. Who has the higher tax incidence of this tax? Explain what we mean by tax incidence. Consumers have the higher tax incidence. Their price goes from $.80 with no tax to $1.20 with the tax, an increase of $0.40. Supply price goes from $.80 with no tax to $.60 with the tax (consumer pays $1.20 and . ...
... e. Who has the higher tax incidence of this tax? Explain what we mean by tax incidence. Consumers have the higher tax incidence. Their price goes from $.80 with no tax to $1.20 with the tax, an increase of $0.40. Supply price goes from $.80 with no tax to $.60 with the tax (consumer pays $1.20 and . ...
Q d
... What factors affect sellers’ supply of goods? How do supply and demand determine the price of a good and the quantity sold? ...
... What factors affect sellers’ supply of goods? How do supply and demand determine the price of a good and the quantity sold? ...
here
... DemandShifts_SR&LR. This sheet shows the effect of a shift in the demand curve in the short run and in the long run. In the short run, the supply curve is relatively inelastic (steeper). In the long run, sellers have more time to adjust to the price change. Part of this adjustment might be new selle ...
... DemandShifts_SR&LR. This sheet shows the effect of a shift in the demand curve in the short run and in the long run. In the short run, the supply curve is relatively inelastic (steeper). In the long run, sellers have more time to adjust to the price change. Part of this adjustment might be new selle ...
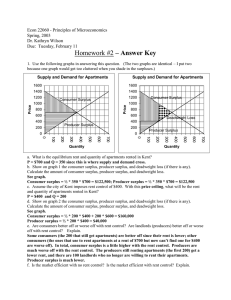
Supply and demand
In microeconomics, supply and demand is an economic model of price determination in a market. It concludes that in a competitive market, the unit price for a particular good, or other traded item such as labor or liquid financial assets, will vary until it settles at a point where the quantity demanded (at the current price) will equal the quantity supplied (at the current price), resulting in an economic equilibrium for price and quantity transacted.The four basic laws of supply and demand are: If demand increases (demand curve shifts to the right) and supply remains unchanged, a shortage occurs, leading to a higher equilibrium price. If demand decreases (demand curve shifts to the left) and supply remains unchanged, a surplus occurs, leading to a lower equilibrium price. If demand remains unchanged and supply increases (supply curve shifts to the right), a surplus occurs, leading to a lower equilibrium price. If demand remains unchanged and supply decreases (supply curve shifts to the left), a shortage occurs, leading to a higher equilibrium price.↑