The Individual Demand Curve
... Combining consumer surplus with the aggregate profits that producers obtain we can evaluate: 1) Costs and benefits of different market structures 2) Public policies that alter the behavior of consumers and firms ...
... Combining consumer surplus with the aggregate profits that producers obtain we can evaluate: 1) Costs and benefits of different market structures 2) Public policies that alter the behavior of consumers and firms ...
Chapter 6 SUPPLY AND EQUILIBRIUM
... The Determinants of Supply As with the demand curve, we move along the supply curve, from one point to another on the same line, if the price of the product changes. We shift the line if anything else changes. Those factors that will cause the shifts in supply are called the determinants of supply. ...
... The Determinants of Supply As with the demand curve, we move along the supply curve, from one point to another on the same line, if the price of the product changes. We shift the line if anything else changes. Those factors that will cause the shifts in supply are called the determinants of supply. ...
Market Failure Stakeholder Analysis (Who Wins, Loses) Monopoly
... Net Social Benefit Accounting Change in CS: P2ABP* (loss) Government Spending: P2ACP* (gain) Gain because society gets it back ...
... Net Social Benefit Accounting Change in CS: P2ABP* (loss) Government Spending: P2ACP* (gain) Gain because society gets it back ...
Chapter 1
... Break-even quantity: The output at which total revenue = total cost. Break-even point: The corresponding ordered pair (x, p). ...
... Break-even quantity: The output at which total revenue = total cost. Break-even point: The corresponding ordered pair (x, p). ...
lecture notes - Livingston Public Schools
... 1. The market period is so short that elasticity of supply is inelastic; it could be almost perfectly inelastic or vertical. In this situation, it is virtually impossible for producers to adjust their resources and change the quantity supplied. (Think of adjustments on a farm once the crop has been ...
... 1. The market period is so short that elasticity of supply is inelastic; it could be almost perfectly inelastic or vertical. In this situation, it is virtually impossible for producers to adjust their resources and change the quantity supplied. (Think of adjustments on a farm once the crop has been ...
Lecture Slide 01
... Topic 1(a): Review of Consumer Theory By the same logic, the area under the demand curve as we increase Q from 1 to 2 units tells us the maximum willingness to pay for the second unit. In this case, that area equals $7. Indeed, the area under a D curve between any two quantities tells us the maximu ...
... Topic 1(a): Review of Consumer Theory By the same logic, the area under the demand curve as we increase Q from 1 to 2 units tells us the maximum willingness to pay for the second unit. In this case, that area equals $7. Indeed, the area under a D curve between any two quantities tells us the maximu ...
Test questions - December, 2000
... Indicate whether the statements below are true or false (or uncertain) and explain briefly (but clearly) why you believe they are true, false or uncertain. Most of the marks are given for your explanation. You may use diagrams, words and/or algebra in your answers. Answer the questions in the space ...
... Indicate whether the statements below are true or false (or uncertain) and explain briefly (but clearly) why you believe they are true, false or uncertain. Most of the marks are given for your explanation. You may use diagrams, words and/or algebra in your answers. Answer the questions in the space ...
Fall 2006 - University at Albany
... 2. Draw demand and supply curves showing how individuals and firms respond to prices and illustrate how various factors influence the shape and position of the curves. 3. Explain the concept of an equilibrium price. 4. Illustrate how market prices allocate resources and how attempts to repeal the la ...
... 2. Draw demand and supply curves showing how individuals and firms respond to prices and illustrate how various factors influence the shape and position of the curves. 3. Explain the concept of an equilibrium price. 4. Illustrate how market prices allocate resources and how attempts to repeal the la ...
CPI (Consumer Price Index) and Inflation
... Consumer Price Index (CPI) • 80,000 of the most commonly bought consumer goods ...
... Consumer Price Index (CPI) • 80,000 of the most commonly bought consumer goods ...
pe_pset1_soln - University of Victoria
... Rearranging, we get P=120-Q (this is the usual slope-intercept form that allows you to draw the equation easily—remember y=mx+b from high school algebra?). Since MB and P are both measured on the vertical axis, we can express this as MB=120-Q. Now just set P=MB, or 100=120-Q to solve for where the p ...
... Rearranging, we get P=120-Q (this is the usual slope-intercept form that allows you to draw the equation easily—remember y=mx+b from high school algebra?). Since MB and P are both measured on the vertical axis, we can express this as MB=120-Q. Now just set P=MB, or 100=120-Q to solve for where the p ...
monopoly
... A monopoly is an industry with a single firm in which the entry of new firms is blocked. An oligopoly is an industry in which there is a small number of firms, each large enough so that its presence affects prices. Firms that differentiate their products in industries with many producers and free en ...
... A monopoly is an industry with a single firm in which the entry of new firms is blocked. An oligopoly is an industry in which there is a small number of firms, each large enough so that its presence affects prices. Firms that differentiate their products in industries with many producers and free en ...
Unit 2 Question Solutions
... 9. The market is in equilibrium when there are 1,500 units of housing offered at the price of $2,000 per month, so 1,200 is not an efficient level of housing. The price ceiling forces consumers to reduce their consumption of the good from the efficient level. In the first sketch below, the housing ...
... 9. The market is in equilibrium when there are 1,500 units of housing offered at the price of $2,000 per month, so 1,200 is not an efficient level of housing. The price ceiling forces consumers to reduce their consumption of the good from the efficient level. In the first sketch below, the housing ...
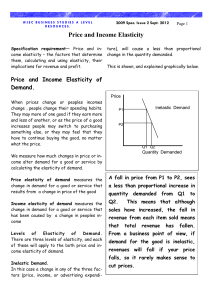
Price and Income Elasticity
... the three factors (price, income, or advertising expenditure), will cause a more than proportional change in the quantity demanded. This is shown, and explained graphically below. ...
... the three factors (price, income, or advertising expenditure), will cause a more than proportional change in the quantity demanded. This is shown, and explained graphically below. ...
Ch 3 Insert C
... 3. What effect will each of the following have on the demand for small automobiles such as the Mini-Cooper and Smart car? LO1 a. Small automobiles become more fashionable. b. The price of large automobiles rises (with the price of small autos remaining the same). c. Income declines and small autos a ...
... 3. What effect will each of the following have on the demand for small automobiles such as the Mini-Cooper and Smart car? LO1 a. Small automobiles become more fashionable. b. The price of large automobiles rises (with the price of small autos remaining the same). c. Income declines and small autos a ...
Name
... a. (____/8) Assume excessively large SUVs include spillover costs that are not borne by the initial consumer but rather society as a whole. i. Explain two negative externalities associated with SUVs. Who pays the external costs? ii. Use a supply and demand graph to illustrate a negative externality. ...
... a. (____/8) Assume excessively large SUVs include spillover costs that are not borne by the initial consumer but rather society as a whole. i. Explain two negative externalities associated with SUVs. Who pays the external costs? ii. Use a supply and demand graph to illustrate a negative externality. ...
Oligopoly and Monopolistic Competition
... B) a slope equal to zero, but its demand curve has a negative slope ...
... B) a slope equal to zero, but its demand curve has a negative slope ...
Document
... Exercising first-degree price discrimination is usually difficult (why?). However, the firm may know which groups of consumers are likely to be more willing to pay than others. Firms use two approaches to divide consumers into groups: - Directly based on observable characteristics • Age, gender, ...
... Exercising first-degree price discrimination is usually difficult (why?). However, the firm may know which groups of consumers are likely to be more willing to pay than others. Firms use two approaches to divide consumers into groups: - Directly based on observable characteristics • Age, gender, ...
AP Microeconomics – Chapter 4 Outline Sarver I - jb
... the legal prohibitions might make drug use more socially acceptable and shift demand to the right. III. Price Elasticity of Supply A. The concept of price elasticity also applies to supply. The elasticity formula is the same as that for demand, but we must substitute the word “supplied” for the word ...
... the legal prohibitions might make drug use more socially acceptable and shift demand to the right. III. Price Elasticity of Supply A. The concept of price elasticity also applies to supply. The elasticity formula is the same as that for demand, but we must substitute the word “supplied” for the word ...
Supply and demand
In microeconomics, supply and demand is an economic model of price determination in a market. It concludes that in a competitive market, the unit price for a particular good, or other traded item such as labor or liquid financial assets, will vary until it settles at a point where the quantity demanded (at the current price) will equal the quantity supplied (at the current price), resulting in an economic equilibrium for price and quantity transacted.The four basic laws of supply and demand are: If demand increases (demand curve shifts to the right) and supply remains unchanged, a shortage occurs, leading to a higher equilibrium price. If demand decreases (demand curve shifts to the left) and supply remains unchanged, a surplus occurs, leading to a lower equilibrium price. If demand remains unchanged and supply increases (supply curve shifts to the right), a surplus occurs, leading to a lower equilibrium price. If demand remains unchanged and supply decreases (supply curve shifts to the left), a shortage occurs, leading to a higher equilibrium price.↑