questions
... QUESTIONS 1. Price inflation is a In the general level of . This means that prices of goods and services over some time, which in turn the value of money, so consumers will be able to buy for the same money. 2. Simple price index is used to measure the change in the price of Composite price index me ...
... QUESTIONS 1. Price inflation is a In the general level of . This means that prices of goods and services over some time, which in turn the value of money, so consumers will be able to buy for the same money. 2. Simple price index is used to measure the change in the price of Composite price index me ...
lecture 3
... ► The market equilibrium will be found at the intersection of demand and supply curves… ► We can distinguish the short-run dynamics and the long-run dynamics: - the short-run refers to the adjustment from a current equilibrium to the new equilibrium through an adjustment of output for existing firms ...
... ► The market equilibrium will be found at the intersection of demand and supply curves… ► We can distinguish the short-run dynamics and the long-run dynamics: - the short-run refers to the adjustment from a current equilibrium to the new equilibrium through an adjustment of output for existing firms ...
Production Behavior-Perfect Competition
... producer’s eggs are perfect substitutes with other egg producers’ eggs. Therefore, the Demand for the individual producer’s eggs is described as a horizontal line at the market equilibrium price P*. ...
... producer’s eggs are perfect substitutes with other egg producers’ eggs. Therefore, the Demand for the individual producer’s eggs is described as a horizontal line at the market equilibrium price P*. ...
Consumer Behavior, Consumption, and Consumers` Surplus
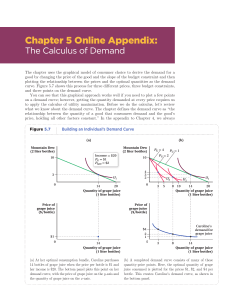
... As shown by Figure 3-1, (see Stigler, G., 1966, chapter three, distributed in class) the downward sloping demand curve summarizes the relationship between the price of a product and the amount purchased by the consumer or household. Divisibility does not prose a problem for the analysis because few ...
... As shown by Figure 3-1, (see Stigler, G., 1966, chapter three, distributed in class) the downward sloping demand curve summarizes the relationship between the price of a product and the amount purchased by the consumer or household. Divisibility does not prose a problem for the analysis because few ...
Case template - GEOCITIES.ws
... o Firm sells 1000 units of a good at home for $20 and 100 abroad for $15 o Price elasticity in both markets is such that a $0.01 reduction in price increases sales by 1 unit o Domestically this price reduction would give marginal revenue of $9.99 Increased revenue : one more unit sold at $19.99 ...
... o Firm sells 1000 units of a good at home for $20 and 100 abroad for $15 o Price elasticity in both markets is such that a $0.01 reduction in price increases sales by 1 unit o Domestically this price reduction would give marginal revenue of $9.99 Increased revenue : one more unit sold at $19.99 ...
3/13-3/20 - David Friedman
... • Imperfect price discrimination may reduce the classical inefficiency – Also may make possible the production of goods that could not cover their cost if all sold at the same price – But if your book might go to an Englishman who values it at $11 instead of an American who values it at $19, which i ...
... • Imperfect price discrimination may reduce the classical inefficiency – Also may make possible the production of goods that could not cover their cost if all sold at the same price – But if your book might go to an Englishman who values it at $11 instead of an American who values it at $19, which i ...
MACROECONOMICS SESSION 2 LECTURE NOTES
... A market is an organized exchange of commodities (including resources, goods, and services) among buyers and sellers, during a given time period. Four important points about markets. 1. Markets are voluntary trades among buyers who want something (the demand side) and sellers who have something (the ...
... A market is an organized exchange of commodities (including resources, goods, and services) among buyers and sellers, during a given time period. Four important points about markets. 1. Markets are voluntary trades among buyers who want something (the demand side) and sellers who have something (the ...
Welfare Analysis of Trade
... their consumption of a good less the amount they have to pay for it. – producers’ surplus is the total revenue received from the sale of a good less its costs of production ...
... their consumption of a good less the amount they have to pay for it. – producers’ surplus is the total revenue received from the sale of a good less its costs of production ...
MANAGING SUPPLY AND DEMAND
... iii. Gamblers/fun travelers. They want a highly popular place where they can gamble, participate in recreation or sport and enjoy a good night lifeand fine dining. They are also concerned about price, the availability of good beaches, sun bathing and good weather. On the other hand, they are less co ...
... iii. Gamblers/fun travelers. They want a highly popular place where they can gamble, participate in recreation or sport and enjoy a good night lifeand fine dining. They are also concerned about price, the availability of good beaches, sun bathing and good weather. On the other hand, they are less co ...
Study all concepts!
... complements. If the prices of cars rise many people may not buy new cars and the demand for petrol will fall and vice versa. Therefore, if the price of a good rises the demand for its complement will fall and ...
... complements. If the prices of cars rise many people may not buy new cars and the demand for petrol will fall and vice versa. Therefore, if the price of a good rises the demand for its complement will fall and ...
competition (new window)
... No individual buyer or seller is large enough to affect the market price. ...
... No individual buyer or seller is large enough to affect the market price. ...
the_firm_Monopolistic_competition - IB-Econ
... Less competition increases demand for this firm’s product, and makes it less elastic (steeper). Demand increases until the firm is ...
... Less competition increases demand for this firm’s product, and makes it less elastic (steeper). Demand increases until the firm is ...
Supply and demand
In microeconomics, supply and demand is an economic model of price determination in a market. It concludes that in a competitive market, the unit price for a particular good, or other traded item such as labor or liquid financial assets, will vary until it settles at a point where the quantity demanded (at the current price) will equal the quantity supplied (at the current price), resulting in an economic equilibrium for price and quantity transacted.The four basic laws of supply and demand are: If demand increases (demand curve shifts to the right) and supply remains unchanged, a shortage occurs, leading to a higher equilibrium price. If demand decreases (demand curve shifts to the left) and supply remains unchanged, a surplus occurs, leading to a lower equilibrium price. If demand remains unchanged and supply increases (supply curve shifts to the right), a surplus occurs, leading to a lower equilibrium price. If demand remains unchanged and supply decreases (supply curve shifts to the left), a shortage occurs, leading to a higher equilibrium price.↑