Chapter 6: Price Elasticity of Demand
... You have $10 to spend. You should spend your money on the product that gives you the most satisfaction per dollar (MU/P). So when the waitress comes to the table what do you buy first on beer or one steak? Since the beer gives you 15 units of satisfaction per dollar and the steak gives you only 8 pe ...
... You have $10 to spend. You should spend your money on the product that gives you the most satisfaction per dollar (MU/P). So when the waitress comes to the table what do you buy first on beer or one steak? Since the beer gives you 15 units of satisfaction per dollar and the steak gives you only 8 pe ...
Perfect Competition in LONG RUN - pm
... If demand increases, what happens in the short-run and how does it return to the long run? ...
... If demand increases, what happens in the short-run and how does it return to the long run? ...
MONOPOLY
... To sell an additional unit of its good, a monopolist needs to lower price. This price reduction both gains revenue and loses revenue for the monopolist. In the exhibit, the revenue gained and revenue lost are shaded and labeled. Marginal revenue is equal to the larger shaded area minus the small ...
... To sell an additional unit of its good, a monopolist needs to lower price. This price reduction both gains revenue and loses revenue for the monopolist. In the exhibit, the revenue gained and revenue lost are shaded and labeled. Marginal revenue is equal to the larger shaded area minus the small ...
Course I
... In our example, It takes a price of 250.000 TL. before there is any incentive to supply chocolate. At a higher prices it becomes increasingly lucrative to supply chocolate bars and there is a corresponding increase in the quantity of bars supplied.Taken together columns (1) and (3) describe the supp ...
... In our example, It takes a price of 250.000 TL. before there is any incentive to supply chocolate. At a higher prices it becomes increasingly lucrative to supply chocolate bars and there is a corresponding increase in the quantity of bars supplied.Taken together columns (1) and (3) describe the supp ...
Chapter 4
... • NOTE: shows only the relationship between the price of this good and the quantity purchased • Price of other goods, income and quality are held constant • This curve shows market demand, individual demand is the same except the numbers are smaller on the horizontal axis. Limits of a Demand Curve • ...
... • NOTE: shows only the relationship between the price of this good and the quantity purchased • Price of other goods, income and quality are held constant • This curve shows market demand, individual demand is the same except the numbers are smaller on the horizontal axis. Limits of a Demand Curve • ...
The Wizard Test Maker
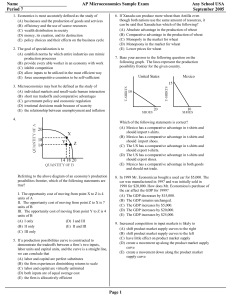
... (B) to secure a resource that has perfectly inelastic supply (C) to secure a resource that has perfectly elastic supply (D) to employ a worker who is new to the labor force (E) to change production from one output to another 55. When too little of a product is being produced at the market price, the ...
... (B) to secure a resource that has perfectly inelastic supply (C) to secure a resource that has perfectly elastic supply (D) to employ a worker who is new to the labor force (E) to change production from one output to another 55. When too little of a product is being produced at the market price, the ...
exercisesch12
... much greater than the quantity demanded of 250,000 at $11.60. Price would fall, so $11.60 can’t be the market price. If price were to equal $7.50, people would be willing to buy about 375,000 cassettes, but each firm would only be willing to produce a little less than 300 or 300,000 in total. Quant ...
... much greater than the quantity demanded of 250,000 at $11.60. Price would fall, so $11.60 can’t be the market price. If price were to equal $7.50, people would be willing to buy about 375,000 cassettes, but each firm would only be willing to produce a little less than 300 or 300,000 in total. Quant ...
Demand - anuppstu
... In the figure (4.1) the quantity demanded of shirts in plotted on horizontal axis OX and price is measured on vertical axis OY. Each price quantity combination is plotted as a point on this graph. If we join the price quantity points a, b, c, d, e and f, we get the individual demand curve for shir ...
... In the figure (4.1) the quantity demanded of shirts in plotted on horizontal axis OX and price is measured on vertical axis OY. Each price quantity combination is plotted as a point on this graph. If we join the price quantity points a, b, c, d, e and f, we get the individual demand curve for shir ...
chapter 5 consumer choice answers to online review questions
... 4. a. Recall that the market demand curve is simply the horizontal sum (summed over quantities at each price) of the individual demand curves. In this case, then, the market demand schedule is: ...
... 4. a. Recall that the market demand curve is simply the horizontal sum (summed over quantities at each price) of the individual demand curves. In this case, then, the market demand schedule is: ...
unit5problemset
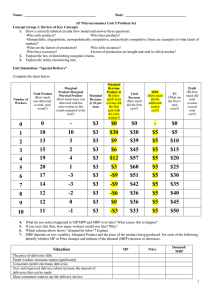
... 12. Use the graph. If the government requires workers to obtain a license in this industry, what will happen to the wage and quantity of workers hired by the firm? A. The wage will stay the same, but the MRP would increase so quantity would increase B. The wage would fall and the quantity would decr ...
... 12. Use the graph. If the government requires workers to obtain a license in this industry, what will happen to the wage and quantity of workers hired by the firm? A. The wage will stay the same, but the MRP would increase so quantity would increase B. The wage would fall and the quantity would decr ...
Chapter 12
... Revenue for the Monopolist As price falls, total revenue for the monopolist does not rise linearly with output. – Instead, it reaches a maximum value at the quantity corresponding to the midpoint of the demand curve (ϵp=1)after which it again begins to fall. – Total revenue (TR) reaches its maximu ...
... Revenue for the Monopolist As price falls, total revenue for the monopolist does not rise linearly with output. – Instead, it reaches a maximum value at the quantity corresponding to the midpoint of the demand curve (ϵp=1)after which it again begins to fall. – Total revenue (TR) reaches its maximu ...
Forecasting Prices in Electricity Markets Electricity is one of the most
... the particularities of how these prices are brought into being. The process of price formation in electricity markets follows in essence the basic rule of microeconomic theory (Law of Supply and Demand) by which the price of the underlying commodity in a competitive market should reflect the relativ ...
... the particularities of how these prices are brought into being. The process of price formation in electricity markets follows in essence the basic rule of microeconomic theory (Law of Supply and Demand) by which the price of the underlying commodity in a competitive market should reflect the relativ ...
Monopoly and Monopsony Labor Market Behavior
... doesn’t change with production). Their marginal productivity of labor is constant at 10 (Q(L) = 10L), and labor is the only factor of production. They face a labor supply curve equal to Ls = 8w − 32. Find the optimal amount of labor hired and the wage in the market. ...
... doesn’t change with production). Their marginal productivity of labor is constant at 10 (Q(L) = 10L), and labor is the only factor of production. They face a labor supply curve equal to Ls = 8w − 32. Find the optimal amount of labor hired and the wage in the market. ...
macyellow1answersfall2011
... B. upsloping because successive units of a specific product yield less and less extra utility. C. downsloping because of increasing marginal opportunity costs. D. downsloping because successive units of a specific product yield less and less extra utility. 10. The output of MP3 players should be: A. ...
... B. upsloping because successive units of a specific product yield less and less extra utility. C. downsloping because of increasing marginal opportunity costs. D. downsloping because successive units of a specific product yield less and less extra utility. 10. The output of MP3 players should be: A. ...
PPT_Econ_standardch03
... Demand in Product/Output Markets Changes in Quantity Demanded versus Changes in Demand Price and Quantity Demanded: The Law of Demand Other Determinants of Household Demand Shift of Demand versus Movement Along the Demand Curve From Household Demand to Market Demand Supply in Product/Output Markets ...
... Demand in Product/Output Markets Changes in Quantity Demanded versus Changes in Demand Price and Quantity Demanded: The Law of Demand Other Determinants of Household Demand Shift of Demand versus Movement Along the Demand Curve From Household Demand to Market Demand Supply in Product/Output Markets ...
Joffe - Post Keynesian Study Group
... • price setting is thus highly dependent on what information is available • commonly this is trend extrapolation ...
... • price setting is thus highly dependent on what information is available • commonly this is trend extrapolation ...
Supply and demand
In microeconomics, supply and demand is an economic model of price determination in a market. It concludes that in a competitive market, the unit price for a particular good, or other traded item such as labor or liquid financial assets, will vary until it settles at a point where the quantity demanded (at the current price) will equal the quantity supplied (at the current price), resulting in an economic equilibrium for price and quantity transacted.The four basic laws of supply and demand are: If demand increases (demand curve shifts to the right) and supply remains unchanged, a shortage occurs, leading to a higher equilibrium price. If demand decreases (demand curve shifts to the left) and supply remains unchanged, a surplus occurs, leading to a lower equilibrium price. If demand remains unchanged and supply increases (supply curve shifts to the right), a surplus occurs, leading to a lower equilibrium price. If demand remains unchanged and supply decreases (supply curve shifts to the left), a shortage occurs, leading to a higher equilibrium price.↑