Econ 201 Lecture 12 A Note on the Firm`s Shut
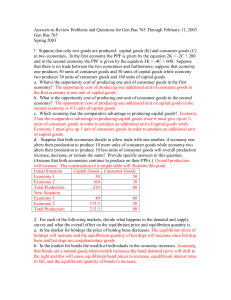
... It might seem that a firm that can sell as much output as it wishes at a constant market price would always do best in the short run by producing and selling the output level for which price equals marginal cost. But there are exceptions to this rule. Suppose, for example, that the market price of t ...
... It might seem that a firm that can sell as much output as it wishes at a constant market price would always do best in the short run by producing and selling the output level for which price equals marginal cost. But there are exceptions to this rule. Suppose, for example, that the market price of t ...
Chapter 8
... – Start with modest concessions and make them smaller as you proceed – Avoid making concessions early in the negotiation – Do not give up anything without something in return ...
... – Start with modest concessions and make them smaller as you proceed – Avoid making concessions early in the negotiation – Do not give up anything without something in return ...
chapter overview
... 1. Other things being equal, as price increases, the corresponding quantity demanded falls. 2. Restated, there is an inverse relationship between price and quantity demanded. 3. Note the “other-things-equal” assumption refers to consumer income and tastes, prices of related goods, and other things b ...
... 1. Other things being equal, as price increases, the corresponding quantity demanded falls. 2. Restated, there is an inverse relationship between price and quantity demanded. 3. Note the “other-things-equal” assumption refers to consumer income and tastes, prices of related goods, and other things b ...
Micro: Demand and Supply VIDEL LECTURE
... each possible price, other things constant Law of supply states that the quantity supplied is usually directly related to its price, other things constant The lower the price, the smaller the quantity supplied Conversely, the higher the price, the greater the quantity ...
... each possible price, other things constant Law of supply states that the quantity supplied is usually directly related to its price, other things constant The lower the price, the smaller the quantity supplied Conversely, the higher the price, the greater the quantity ...
Natural-Resource-Economics-10th-Edition-Tietenberg
... D. The private market equilibrium will be at a point where too much steel is being produced. The price of steel will be too low. Too much pollution is being produced. This is illustrated in text Figure 2.5. It is simplest to assume that marginal private benefits are equal to marginal social benefits ...
... D. The private market equilibrium will be at a point where too much steel is being produced. The price of steel will be too low. Too much pollution is being produced. This is illustrated in text Figure 2.5. It is simplest to assume that marginal private benefits are equal to marginal social benefits ...
Market Structure and Pricing Decisions
... In an oligopolistic market there are small number of firms so that sellers are conscious of their interdependence. The competition is not perfect, yet the rivalry among firms is high. Given that there are large number of possible reactions of competitors, the behavior of firms may assume various for ...
... In an oligopolistic market there are small number of firms so that sellers are conscious of their interdependence. The competition is not perfect, yet the rivalry among firms is high. Given that there are large number of possible reactions of competitors, the behavior of firms may assume various for ...
Chapter 4: Demand for Labor in Short Run
... Curve for Labor • Shows relationship between wage rate and firm’s desired employment level holding all other relevant factors (including other inputs) fixed (like K). • Firm’s SR demand curve for labor IS the downward portion of the MRPL curve. • Ignore upward sloped portion because at any price or ...
... Curve for Labor • Shows relationship between wage rate and firm’s desired employment level holding all other relevant factors (including other inputs) fixed (like K). • Firm’s SR demand curve for labor IS the downward portion of the MRPL curve. • Ignore upward sloped portion because at any price or ...
Oligopoly - ILM.COM.PK
... monopoly price can be above or below average total costs. Thus, the monopolist need not always make a profit. In the long run, of course, unprofitable monopolists will either stop production or raise the price further above marginal cost until it covers average total costs. The monopolist will alw ...
... monopoly price can be above or below average total costs. Thus, the monopolist need not always make a profit. In the long run, of course, unprofitable monopolists will either stop production or raise the price further above marginal cost until it covers average total costs. The monopolist will alw ...
ANSWER - Harper College
... ANSWER: Allocative Efficiency – they were not producing what consumers wanted. They were producing film and most consumers wanted to take digital pictures. ...
... ANSWER: Allocative Efficiency – they were not producing what consumers wanted. They were producing film and most consumers wanted to take digital pictures. ...
Answers to Practice Questions and Problems 1
... c. In the market for computers technology improves while simultaneously the wages of software engineers increase. The supply curve will shift to the right due to the technological change and it will shift to the left due to the increase in wages. We do not know whether the equilibrium price and qua ...
... c. In the market for computers technology improves while simultaneously the wages of software engineers increase. The supply curve will shift to the right due to the technological change and it will shift to the left due to the increase in wages. We do not know whether the equilibrium price and qua ...
Oligopoly
... 1. How much can it get away with without inciting retaliation 2. If it’s rivals do retaliate and a price war ensues, whether it will be able to ‘see off’ some or all of its rivals while surviving itself. It is not unreasonable to compare rival firms in an oligopoly to the players in a game. They wil ...
... 1. How much can it get away with without inciting retaliation 2. If it’s rivals do retaliate and a price war ensues, whether it will be able to ‘see off’ some or all of its rivals while surviving itself. It is not unreasonable to compare rival firms in an oligopoly to the players in a game. They wil ...
A Firm in a Compeitive Market
... quantities of a good a producer is willing and able to sell (produce) at alternative prices in a given time period, ceteris paribus. ...
... quantities of a good a producer is willing and able to sell (produce) at alternative prices in a given time period, ceteris paribus. ...
PPT_Mic9e_one_click_ch03
... Demand in Product/Output Markets Changes in Quantity Demanded versus Changes in Demand Price and Quantity Demanded: The Law of Demand Other Determinants of Household Demand Shift of Demand versus Movement Along the Demand Curve From Household Demand to Market Demand Supply in Product/Output Markets ...
... Demand in Product/Output Markets Changes in Quantity Demanded versus Changes in Demand Price and Quantity Demanded: The Law of Demand Other Determinants of Household Demand Shift of Demand versus Movement Along the Demand Curve From Household Demand to Market Demand Supply in Product/Output Markets ...
Lysine Case
... after periods (sample sizes) Prices were seasonal? Before prices should be oligopoly based? ...
... after periods (sample sizes) Prices were seasonal? Before prices should be oligopoly based? ...
Supply and demand
In microeconomics, supply and demand is an economic model of price determination in a market. It concludes that in a competitive market, the unit price for a particular good, or other traded item such as labor or liquid financial assets, will vary until it settles at a point where the quantity demanded (at the current price) will equal the quantity supplied (at the current price), resulting in an economic equilibrium for price and quantity transacted.The four basic laws of supply and demand are: If demand increases (demand curve shifts to the right) and supply remains unchanged, a shortage occurs, leading to a higher equilibrium price. If demand decreases (demand curve shifts to the left) and supply remains unchanged, a surplus occurs, leading to a lower equilibrium price. If demand remains unchanged and supply increases (supply curve shifts to the right), a surplus occurs, leading to a lower equilibrium price. If demand remains unchanged and supply decreases (supply curve shifts to the left), a shortage occurs, leading to a higher equilibrium price.↑