Consumer surplus
... from participating in a market. • Consumer surplus can be computed by finding the area below the demand curve and above the price. Copyright © 2004 South-Western ...
... from participating in a market. • Consumer surplus can be computed by finding the area below the demand curve and above the price. Copyright © 2004 South-Western ...
Supply and Demand Analysis
... • I almost decided not to buy it! • They tried to squeeze the very last cent from me! • Total amount paid is close to total value. • Consumer surplus is low. Michael R. Baye, Managerial Economics and Business Strategy, 3e. ©The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. , ...
... • I almost decided not to buy it! • They tried to squeeze the very last cent from me! • Total amount paid is close to total value. • Consumer surplus is low. Michael R. Baye, Managerial Economics and Business Strategy, 3e. ©The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. , ...
Market Disturbances
... as the total revenues of the firm minus the total costs of the firm. The amount of product that any firm is willing to sell depends on two things: the price of the product and the firm’s costs. Due to the special conditions of the perfectly competitive model the firm considers the price of the produ ...
... as the total revenues of the firm minus the total costs of the firm. The amount of product that any firm is willing to sell depends on two things: the price of the product and the firm’s costs. Due to the special conditions of the perfectly competitive model the firm considers the price of the produ ...
sample final exam
... 1. David has an income (Y) of $50 with which he can purchase DVDs (D) at $10 each and haircuts (H) at $20 each. Which one of the following represents Guy's budget line? a) Y = 10QD - 20QH b) 50 = QD + QH c) Y = 50 + QD + QH d) 50 = 10QD + 20QH 2. Real income in terms of a good is defined as a) incom ...
... 1. David has an income (Y) of $50 with which he can purchase DVDs (D) at $10 each and haircuts (H) at $20 each. Which one of the following represents Guy's budget line? a) Y = 10QD - 20QH b) 50 = QD + QH c) Y = 50 + QD + QH d) 50 = 10QD + 20QH 2. Real income in terms of a good is defined as a) incom ...
Lab 12: Perfectly Competitive Market
... c. Due to entry and exit, the long-run equilibrium market price is at the level equal to the minimum point of firm’s ATC curve. See graph below. All the firms in a perfectly competitive market earn economic profit equal to zero. (Since economic profit is the profit after accounting for the implicit ...
... c. Due to entry and exit, the long-run equilibrium market price is at the level equal to the minimum point of firm’s ATC curve. See graph below. All the firms in a perfectly competitive market earn economic profit equal to zero. (Since economic profit is the profit after accounting for the implicit ...
Micro Lecture 6: Elasticity Applications
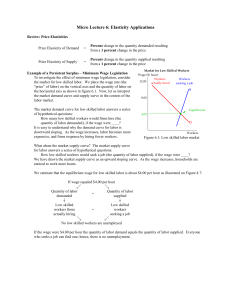
... Currently, the Federal minimum wage is $7.25 per hour. That is, by law the wage paid by employers cannot fall below $7.25 per hour. In Massachusetts it is $8.00 per hour. That is, in Massachusetts all low skilled labor must be paid at least $8.00 per hour. While there may be some dispute about the p ...
... Currently, the Federal minimum wage is $7.25 per hour. That is, by law the wage paid by employers cannot fall below $7.25 per hour. In Massachusetts it is $8.00 per hour. That is, in Massachusetts all low skilled labor must be paid at least $8.00 per hour. While there may be some dispute about the p ...
CFO11e_econ_ch05_GE
... The Importance of Being Unimportant When an item represents a relatively small part of our total budget, we tend to pay little attention to its price. ...
... The Importance of Being Unimportant When an item represents a relatively small part of our total budget, we tend to pay little attention to its price. ...
Derived Demand and MRP
... Demand is the different quantities of workers that businesses are willing and able to hire at different wages. What is the Law of Demand for Labor? There is an INVERSE relationship between wage and quantity of labor demanded. What is Supply for Labor? Supply is the different quantities of individual ...
... Demand is the different quantities of workers that businesses are willing and able to hire at different wages. What is the Law of Demand for Labor? There is an INVERSE relationship between wage and quantity of labor demanded. What is Supply for Labor? Supply is the different quantities of individual ...
Profit-Maximization by a monopolist
... Imagine there is some sort of monopoly over a product of software, like Microsoft. In columns 1 and 2 of Table 11.a.1 we can see the demand schedule for this particular monopoly. From this you can see that as the quantity increases the price decreases, representing the downward sloping demand curve ...
... Imagine there is some sort of monopoly over a product of software, like Microsoft. In columns 1 and 2 of Table 11.a.1 we can see the demand schedule for this particular monopoly. From this you can see that as the quantity increases the price decreases, representing the downward sloping demand curve ...
Chapter 1 end of chapter key
... Contrast how a market system and a command economy try to cope with economic scarcity. A market system allows for the private ownership of resources and coordinates economic activity through market prices. Participants act in their own self-interest and seek to maximize satisfaction or profit throug ...
... Contrast how a market system and a command economy try to cope with economic scarcity. A market system allows for the private ownership of resources and coordinates economic activity through market prices. Participants act in their own self-interest and seek to maximize satisfaction or profit throug ...
Price Controls
... • The incidence of a tax refers to who bears the burden of a tax. • The incidence of a tax does not depend on whether the tax is levied on buyers or sellers. • The incidence of the tax depends on the price elasticities of supply and demand. • The burden tends to fall on the side of the market that i ...
... • The incidence of a tax refers to who bears the burden of a tax. • The incidence of a tax does not depend on whether the tax is levied on buyers or sellers. • The incidence of the tax depends on the price elasticities of supply and demand. • The burden tends to fall on the side of the market that i ...
Slide 1
... drawn, there is a natural duopoly—a market with two firms. – How would answer change if demand increases? ...
... drawn, there is a natural duopoly—a market with two firms. – How would answer change if demand increases? ...
Supply and demand
In microeconomics, supply and demand is an economic model of price determination in a market. It concludes that in a competitive market, the unit price for a particular good, or other traded item such as labor or liquid financial assets, will vary until it settles at a point where the quantity demanded (at the current price) will equal the quantity supplied (at the current price), resulting in an economic equilibrium for price and quantity transacted.The four basic laws of supply and demand are: If demand increases (demand curve shifts to the right) and supply remains unchanged, a shortage occurs, leading to a higher equilibrium price. If demand decreases (demand curve shifts to the left) and supply remains unchanged, a surplus occurs, leading to a lower equilibrium price. If demand remains unchanged and supply increases (supply curve shifts to the right), a surplus occurs, leading to a lower equilibrium price. If demand remains unchanged and supply decreases (supply curve shifts to the left), a shortage occurs, leading to a higher equilibrium price.↑