The Apple Market Experiments with Economics
... were able to get higher prices for their apples than others. Some sellers were lucky enough to be o ered a relatively high price by the rst buyer they ran into. Similarly, some buyers were able to nd a seller who would sell cheaply and others could only nd sellers who insisted on a high price. Ev ...
... were able to get higher prices for their apples than others. Some sellers were lucky enough to be o ered a relatively high price by the rst buyer they ran into. Similarly, some buyers were able to nd a seller who would sell cheaply and others could only nd sellers who insisted on a high price. Ev ...
Trade based on economies of scale under monopolistic
... What happens when the two countries start trading with each other and form an integrated market of 2 million autos? At first, it seems that the integration of the markets will not have any effect on the demand directed to the typical US or EU firm. Consider, for example, the case of EU firms. In fa ...
... What happens when the two countries start trading with each other and form an integrated market of 2 million autos? At first, it seems that the integration of the markets will not have any effect on the demand directed to the typical US or EU firm. Consider, for example, the case of EU firms. In fa ...
Assignment Guide
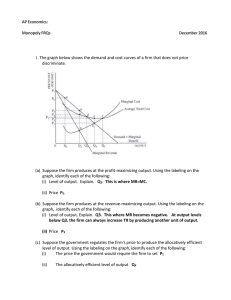
... 2) Explain why the marginal revenue curve for a monopolist lies below the demand curve when plotted on a graph. 3) Calculate marginal revenue from a schedule of output and total revenue, and plot marginal revenue and price. 4) Explain why a monopoly firm should never operate on the inelastic portion ...
... 2) Explain why the marginal revenue curve for a monopolist lies below the demand curve when plotted on a graph. 3) Calculate marginal revenue from a schedule of output and total revenue, and plot marginal revenue and price. 4) Explain why a monopoly firm should never operate on the inelastic portion ...
Worksheet 2 2.1 Economic systems - Liceo Ginnasio Statale «Virgilio
... Firms will allocate resources to the production of the most profitable goods and services There will always be full employment of resources Firms have an incentive to keep their costs of production as low as possible Consumers will only get what they want depending on their willingness and ability t ...
... Firms will allocate resources to the production of the most profitable goods and services There will always be full employment of resources Firms have an incentive to keep their costs of production as low as possible Consumers will only get what they want depending on their willingness and ability t ...
PDF
... The next section presents a brief conceptual background. This section is followed by sections specifying the empirical models, data, and results. Conceptual Background Yearling Supply ...
... The next section presents a brief conceptual background. This section is followed by sections specifying the empirical models, data, and results. Conceptual Background Yearling Supply ...
Chapter 1 - McGraw Hill Higher Education
... supply curve: the quantity demanded = the quantity supplied and no pressure for price to change • At prices above this point the quantity supplied exceeds the quantity demanded (there is excess supply) and prices fall • At prices below this point there is excess demand and prices rise ...
... supply curve: the quantity demanded = the quantity supplied and no pressure for price to change • At prices above this point the quantity supplied exceeds the quantity demanded (there is excess supply) and prices fall • At prices below this point there is excess demand and prices rise ...
Elastic - McGraw Hill Higher Education
... Difficult to adjust quickly to changes in price Supply fluctuates more often and by larger amounts Some oil-producing countries are unstable Speculation about instability ...
... Difficult to adjust quickly to changes in price Supply fluctuates more often and by larger amounts Some oil-producing countries are unstable Speculation about instability ...
L10-producer econ1
... Is this realistic? What happens to the number of cans Harry can get when he has to start competing with Barry and 998 other people laid off by IBM? Many natural resources also fail to increase in supply as the number of ...
... Is this realistic? What happens to the number of cans Harry can get when he has to start competing with Barry and 998 other people laid off by IBM? Many natural resources also fail to increase in supply as the number of ...
Market Equilibrium and Applications
... decrease in Supply (Graph 7) is to increase price and decrease quantity while the result of an increase in Demand (Graph 4) is to increase both price and quantity. Clearly, because the changes in both demand and supply curves cause price to increase, then price will increase. However, each shift has ...
... decrease in Supply (Graph 7) is to increase price and decrease quantity while the result of an increase in Demand (Graph 4) is to increase both price and quantity. Clearly, because the changes in both demand and supply curves cause price to increase, then price will increase. However, each shift has ...
Price discrimination and price sensitivity in the car market
... cars. In the Netherlands sales tax on diesel cars is considerably higher than sales tax on gasoline cars. There is a lump-sum tax difference of 1868 euros compared to an average price difference of 2395 euros, but this still leaves a sizeable price difference of 517 euros. Verboven (2002) finds a s ...
... cars. In the Netherlands sales tax on diesel cars is considerably higher than sales tax on gasoline cars. There is a lump-sum tax difference of 1868 euros compared to an average price difference of 2395 euros, but this still leaves a sizeable price difference of 517 euros. Verboven (2002) finds a s ...
A partial equilibrium approach to estimating the potential payoffs of
... transaction costs, most bulky commodities such as cereals are only semitradables, thus the general conclusions from a closed-economy model, such as this one, should be similar in terms of the general direction, if not the magnitude. Another assumption is that producers form rational expectations abo ...
... transaction costs, most bulky commodities such as cereals are only semitradables, thus the general conclusions from a closed-economy model, such as this one, should be similar in terms of the general direction, if not the magnitude. Another assumption is that producers form rational expectations abo ...
Chapter 3 - Demand, Supply, and Market Equilibrium
... Demand is a schedule or a curve that shows the various amounts of a product that consumers will purchase at each of several possible prices during a specified period of time.1 The table in Figure 3.1 is a hypothetical demand schedule for a single consumer purchasing a particular product, in this cas ...
... Demand is a schedule or a curve that shows the various amounts of a product that consumers will purchase at each of several possible prices during a specified period of time.1 The table in Figure 3.1 is a hypothetical demand schedule for a single consumer purchasing a particular product, in this cas ...
File
... – Free of entry and exit into the market – not as easy as perfect competition because of the existence of product differentiation. – Role of non-price competition is significant – various methods used to attract the customers to buy a particular brand. – Selling cost – different types of expenditure ...
... – Free of entry and exit into the market – not as easy as perfect competition because of the existence of product differentiation. – Role of non-price competition is significant – various methods used to attract the customers to buy a particular brand. – Selling cost – different types of expenditure ...
why a demand curve may not be downward sloping?
... price of any commodity rises or falls by the proportion of the number of buyer and sellers.......that which regulates the price... [of goods] is nothing else but their quantity in proportion to their rent’ (Locke, 1691). Here, by quantity he probably meant supply and rent as the basis for demand. La ...
... price of any commodity rises or falls by the proportion of the number of buyer and sellers.......that which regulates the price... [of goods] is nothing else but their quantity in proportion to their rent’ (Locke, 1691). Here, by quantity he probably meant supply and rent as the basis for demand. La ...
Competition Policy
... In practice the EC and the European Court of justice follow this approach (useful to increase legal certainty and reduce the cost of investigations) ...
... In practice the EC and the European Court of justice follow this approach (useful to increase legal certainty and reduce the cost of investigations) ...
CHAPTER 11
... Internet allows firms to enter and leave markets at will making them closer to a purely competitive market. Applying the Tools: The Broader Importance of the MR = MC Equilibrium Condition The MR = MC equilibrium condition is simple, but it is enormously powerful. Understanding this condition is to ...
... Internet allows firms to enter and leave markets at will making them closer to a purely competitive market. Applying the Tools: The Broader Importance of the MR = MC Equilibrium Condition The MR = MC equilibrium condition is simple, but it is enormously powerful. Understanding this condition is to ...
Lecture 6
... - few substitutes + small share of budget … inelastic - many substitutes + large share of budget … elastic. • Graphical trick for Own Price elasticity: • Where is the larger elasticity, point C or D? • Total Revenue and Elasticity. Consider the following demand curve: Price: 10 Quantity: 0 Total Rev ...
... - few substitutes + small share of budget … inelastic - many substitutes + large share of budget … elastic. • Graphical trick for Own Price elasticity: • Where is the larger elasticity, point C or D? • Total Revenue and Elasticity. Consider the following demand curve: Price: 10 Quantity: 0 Total Rev ...
Supply and demand
In microeconomics, supply and demand is an economic model of price determination in a market. It concludes that in a competitive market, the unit price for a particular good, or other traded item such as labor or liquid financial assets, will vary until it settles at a point where the quantity demanded (at the current price) will equal the quantity supplied (at the current price), resulting in an economic equilibrium for price and quantity transacted.The four basic laws of supply and demand are: If demand increases (demand curve shifts to the right) and supply remains unchanged, a shortage occurs, leading to a higher equilibrium price. If demand decreases (demand curve shifts to the left) and supply remains unchanged, a surplus occurs, leading to a lower equilibrium price. If demand remains unchanged and supply increases (supply curve shifts to the right), a surplus occurs, leading to a lower equilibrium price. If demand remains unchanged and supply decreases (supply curve shifts to the left), a shortage occurs, leading to a higher equilibrium price.↑