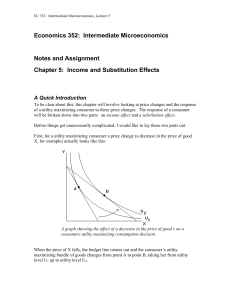
Chapter 5: Income and Substitution Effects
... price of X will be an increase in the quantity of X consumed, even if the income effect reduces the quantity of X consumed. There is a bizarre, but theoretically possible case where the income effect outweighs the substitution effect. This is called a Giffen good, which the textbook describes under ...
... price of X will be an increase in the quantity of X consumed, even if the income effect reduces the quantity of X consumed. There is a bizarre, but theoretically possible case where the income effect outweighs the substitution effect. This is called a Giffen good, which the textbook describes under ...
Chapter 5: Supply
... supply to decrease, shifting the curve to the left. In the real world, sellers are entering the market and leaving the market all the time. Some economic analysts believe that, at least initially, the development of the Internet will result in larger numbers entering the market than in leaving. They ...
... supply to decrease, shifting the curve to the left. In the real world, sellers are entering the market and leaving the market all the time. Some economic analysts believe that, at least initially, the development of the Internet will result in larger numbers entering the market than in leaving. They ...
Four Market Models
... and the industry in which it operates. Which of the following is correct? 1. The diagrams portray neither long-run nor short-run equilibrium. 2. The diagrams portray both long-run and short-run equilibrium. 3. The diagrams portray short-run equilibrium, but not long-run equilibrium. 4. The diagrams ...
... and the industry in which it operates. Which of the following is correct? 1. The diagrams portray neither long-run nor short-run equilibrium. 2. The diagrams portray both long-run and short-run equilibrium. 3. The diagrams portray short-run equilibrium, but not long-run equilibrium. 4. The diagrams ...
The Art and Science of Economics
... production is lower than the rate that would be associated with the lowest average cost Alternatively, excess capacity means that each producer could easily produce more and in the process would lower the average cost the marginal value of increased output would exceed its marginal cost greater ...
... production is lower than the rate that would be associated with the lowest average cost Alternatively, excess capacity means that each producer could easily produce more and in the process would lower the average cost the marginal value of increased output would exceed its marginal cost greater ...
Innovation - grata international
... Quotation period established by the contract for goods (works, services) sale shall not be subject to any changes during twelve months after the establishment thereof. Quotation period, for the purposes of this Law, must be specified according to the terms and conditions of the contract within the t ...
... Quotation period established by the contract for goods (works, services) sale shall not be subject to any changes during twelve months after the establishment thereof. Quotation period, for the purposes of this Law, must be specified according to the terms and conditions of the contract within the t ...
M Cheaper Oil Will nOt hurt the eCOnOmy
... percent at the world level now lie in shale. For a given production of other goods, more oil can now be produced, and much of it comes from formations that were not previously exploitable. The easiest way to understand the shift in the production frontier is ...
... percent at the world level now lie in shale. For a given production of other goods, more oil can now be produced, and much of it comes from formations that were not previously exploitable. The easiest way to understand the shift in the production frontier is ...
Essay Questions Chap 19 - Weber State University
... contractions). Interest rates do not affect velocity in Friedman’s theory, since the relative returns on money and other assets are predicted to remain relatively constant. 4. In the liquidity trap the demand for money becomes horizontal. Depict this graphically. Demonstrate and explain why increase ...
... contractions). Interest rates do not affect velocity in Friedman’s theory, since the relative returns on money and other assets are predicted to remain relatively constant. 4. In the liquidity trap the demand for money becomes horizontal. Depict this graphically. Demonstrate and explain why increase ...
Total Product of Labor
... 1. Draw a total product of labor curve holding capital constant. Underneath draw an average product of labor curve and a marginal product of labor curve. Explain the peak points for MPL and APL, as well as the point where MPL is zero. 2. Explain the firms hiring decision. What quantity of labor shou ...
... 1. Draw a total product of labor curve holding capital constant. Underneath draw an average product of labor curve and a marginal product of labor curve. Explain the peak points for MPL and APL, as well as the point where MPL is zero. 2. Explain the firms hiring decision. What quantity of labor shou ...
Ch05_lec
... Casual restaurants use first-come, first served to allocate tables. Supermarkets also uses first-come, first-served at checkout. First-come, first-served works best when scarce resources can serves just one person at a time in a ...
... Casual restaurants use first-come, first served to allocate tables. Supermarkets also uses first-come, first-served at checkout. First-come, first-served works best when scarce resources can serves just one person at a time in a ...
Market Models
... price to all consumers. In many cases, however, monopolist will use PRICE DISCRIMINATION, or sell the same good to different customers for different prices This practice is not possible in competitive markets where there are many firms selling the same product at competitive prices. ...
... price to all consumers. In many cases, however, monopolist will use PRICE DISCRIMINATION, or sell the same good to different customers for different prices This practice is not possible in competitive markets where there are many firms selling the same product at competitive prices. ...
section2powerpoint
... –A diminishing marginal rate of substitution is the key assumption of consumer theory. –A diminishing marginal rate of substitution is a general tendency for a person to be willing to give up less of good y to get one more unit of good x, and at the same time remain indifferent, as the quantity of g ...
... –A diminishing marginal rate of substitution is the key assumption of consumer theory. –A diminishing marginal rate of substitution is a general tendency for a person to be willing to give up less of good y to get one more unit of good x, and at the same time remain indifferent, as the quantity of g ...
Ch06 Govt actions in markets
... Everything you earn and most things you buy are taxed. Who really pays these taxes? Income tax and the social insurance taxes are deducted from your pay, and provincial sales tax and GST are added to the price of the most of the things you buy, so isn’t it obvious that you pay these taxes? Isn’t ...
... Everything you earn and most things you buy are taxed. Who really pays these taxes? Income tax and the social insurance taxes are deducted from your pay, and provincial sales tax and GST are added to the price of the most of the things you buy, so isn’t it obvious that you pay these taxes? Isn’t ...
Chapter 12
... What Happens to Profits in the Long Run? Is Zero Economic Profit Inevitable in the Long Run? A firm’s profits will be eliminated in the long run only if a firm stands still and fails to find new ways of differentiating its product or fails to find new ways of lowering the cost of producing its prod ...
... What Happens to Profits in the Long Run? Is Zero Economic Profit Inevitable in the Long Run? A firm’s profits will be eliminated in the long run only if a firm stands still and fails to find new ways of differentiating its product or fails to find new ways of lowering the cost of producing its prod ...
Supply and demand
In microeconomics, supply and demand is an economic model of price determination in a market. It concludes that in a competitive market, the unit price for a particular good, or other traded item such as labor or liquid financial assets, will vary until it settles at a point where the quantity demanded (at the current price) will equal the quantity supplied (at the current price), resulting in an economic equilibrium for price and quantity transacted.The four basic laws of supply and demand are: If demand increases (demand curve shifts to the right) and supply remains unchanged, a shortage occurs, leading to a higher equilibrium price. If demand decreases (demand curve shifts to the left) and supply remains unchanged, a surplus occurs, leading to a lower equilibrium price. If demand remains unchanged and supply increases (supply curve shifts to the right), a surplus occurs, leading to a lower equilibrium price. If demand remains unchanged and supply decreases (supply curve shifts to the left), a shortage occurs, leading to a higher equilibrium price.↑























