Macro-Economics
... increasing demand ,that the volume of employment can be increased and unemployment can be removed. PERFEC T COMPETITION : macro economics is based on the assumption of perfect competition under the conditions of perfect competition ,there is no external interference in the determination of prices . ...
... increasing demand ,that the volume of employment can be increased and unemployment can be removed. PERFEC T COMPETITION : macro economics is based on the assumption of perfect competition under the conditions of perfect competition ,there is no external interference in the determination of prices . ...
ECMA04H - UTSC - University of Toronto
... particularly useful to first year students. 1. Keep up: University courses tend to be cumulative, so that not falling behind is critical. If you are up-to-date in your work, my lectures will make more sense and reinforce what you are studying. On the other hand, if you fall behind, the lectures will ...
... particularly useful to first year students. 1. Keep up: University courses tend to be cumulative, so that not falling behind is critical. If you are up-to-date in your work, my lectures will make more sense and reinforce what you are studying. On the other hand, if you fall behind, the lectures will ...
Disentangling goods, labor, and credit market frictions in three European economies
... This paper develops a model of credit, labor, and goods market frictions introduced in a symmetrical way, with matching functions associating, respectively, job seekers and vacancies, financial institutions and “projects,” and “selling firms” and “customers.” The model is kept tractable under a set ...
... This paper develops a model of credit, labor, and goods market frictions introduced in a symmetrical way, with matching functions associating, respectively, job seekers and vacancies, financial institutions and “projects,” and “selling firms” and “customers.” The model is kept tractable under a set ...
I`m a teacher - The Good, the Bad and the Economist
... been allocated to the right areas and consumers are paying the right price for the correct amount of goods.1 Consumer surplus I always enjoy this part of the syllabus in class as it lends itself very easy to students’ own experiences and intuitiveness. I ask you too to imagine walking by a store w ...
... been allocated to the right areas and consumers are paying the right price for the correct amount of goods.1 Consumer surplus I always enjoy this part of the syllabus in class as it lends itself very easy to students’ own experiences and intuitiveness. I ask you too to imagine walking by a store w ...
LECTURE NOTES 3 and 4 EC 403
... than demand for others in that their consumption can be dispensed with or postponed. Demand for necessities is inelastic, their consumption cannot be postponed. Demand for durable goods is more elastic than that of non-durable goods. (3) Proportion of income spent on a commodity. If proportion of in ...
... than demand for others in that their consumption can be dispensed with or postponed. Demand for necessities is inelastic, their consumption cannot be postponed. Demand for durable goods is more elastic than that of non-durable goods. (3) Proportion of income spent on a commodity. If proportion of in ...
Political Risk (1)
... Wall and Rees: International Business, 2nd edition © Pearson Education Limited 2004 ...
... Wall and Rees: International Business, 2nd edition © Pearson Education Limited 2004 ...
Labour Markets and Supply-side Policies
... stabilization. For example, the government may seek to alter the distribution of income, to reduce child poverty, to boost innovation and entrepreneurship, etc. It is nevertheless important for the consequences for employment and inflation of such policies to be examined. In the first section we set ...
... stabilization. For example, the government may seek to alter the distribution of income, to reduce child poverty, to boost innovation and entrepreneurship, etc. It is nevertheless important for the consequences for employment and inflation of such policies to be examined. In the first section we set ...
GREAT Demand PP - iBlog Teacher Websites
... For example, this might be a really hot day, so more people want lemonade ...
... For example, this might be a really hot day, so more people want lemonade ...
Document
... Competition Imperfect competition: market structures between perfect competition and monopoly • more than one seller, but too few to create a perfectly competitive market • often violate other conditions of perfect competition, such as the requirement of a standardized product or free entry and exit ...
... Competition Imperfect competition: market structures between perfect competition and monopoly • more than one seller, but too few to create a perfectly competitive market • often violate other conditions of perfect competition, such as the requirement of a standardized product or free entry and exit ...
Ch13 - OCCC.edu
... 5. Motivation for Firms to Profit Maximize -if they didn’t they would have to face these actions a. Other firms entering the market and selling a similar or same product at a lower price. b. Other firms could take over the existing firm and use their set-up to operate more efficiently and earn great ...
... 5. Motivation for Firms to Profit Maximize -if they didn’t they would have to face these actions a. Other firms entering the market and selling a similar or same product at a lower price. b. Other firms could take over the existing firm and use their set-up to operate more efficiently and earn great ...
PDF
... As illustrated in subsequent sections , the indirect effect may actually dominate the direct effect . ...
... As illustrated in subsequent sections , the indirect effect may actually dominate the direct effect . ...
Consumer Choice
... A. If Hurley spends all his income on fish, how many fish does he buy? B. If Hurley spends all his income on mangos, how many mangos does he buy? C. If Hurley buys 100 fish, how many mangos can he buy? D. Plot each of the bundles from parts A – C on a graph that measures fish on the horizontal axis ...
... A. If Hurley spends all his income on fish, how many fish does he buy? B. If Hurley spends all his income on mangos, how many mangos does he buy? C. If Hurley buys 100 fish, how many mangos can he buy? D. Plot each of the bundles from parts A – C on a graph that measures fish on the horizontal axis ...
20083210498134
... Elasticity: Supply • For an upward-sloping S curve, Es > 0. • For a horizontal S curve, Es = 0. • Since S curve may be down-sloping (not often happens), Es < 0 is possible. • Elastic supply: |Es| > 1 • Elastic supply: |Es| < 1 ...
... Elasticity: Supply • For an upward-sloping S curve, Es > 0. • For a horizontal S curve, Es = 0. • Since S curve may be down-sloping (not often happens), Es < 0 is possible. • Elastic supply: |Es| > 1 • Elastic supply: |Es| < 1 ...
On the (in)efficiency of production taxes and firms` organizational
... (Grossman and Hart [7], Hart and Moore [9], Hart and Holmstrom [8]) and particularly the theory of managerial firms by Legros and Newman [10]. The latter assumes each firm is composed by operational units run by managers that choose the organizational setting in order to maximize their payoff rather ...
... (Grossman and Hart [7], Hart and Moore [9], Hart and Holmstrom [8]) and particularly the theory of managerial firms by Legros and Newman [10]. The latter assumes each firm is composed by operational units run by managers that choose the organizational setting in order to maximize their payoff rather ...
Law of Demand
... For each of the headlines listed on the front side, draw the appropriate change in demand on the graph. Remember, an Increase means the line moves to the right, a Decrease means the line moves to the left, and No Change means the line stays the same. ...
... For each of the headlines listed on the front side, draw the appropriate change in demand on the graph. Remember, an Increase means the line moves to the right, a Decrease means the line moves to the left, and No Change means the line stays the same. ...
PDF
... The joint estimation of empirical specifications of equations (1) and (4) allows us to measure the degree of oligopsony power in a particular market. As specified, however, data on the quantities of nonspecialized inputs (i.e., inputs other than x1 ) are necessary to estimate the degree of oligopson ...
... The joint estimation of empirical specifications of equations (1) and (4) allows us to measure the degree of oligopsony power in a particular market. As specified, however, data on the quantities of nonspecialized inputs (i.e., inputs other than x1 ) are necessary to estimate the degree of oligopson ...
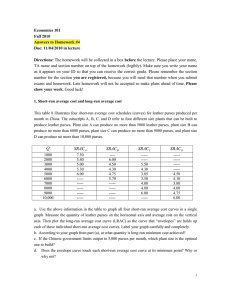
Economics 101 Fall 2010 Answers to Homework #4 Due: 11/04/2010 in lecture
... Guam and Hawaii initially both operate as closed economies, which means that they had consumed only domestically produced goods. Madison Coke Company (MCC) made an agreement with the government of Guam and Hawaii respectively to exclusively provide coke to the market in these two economies. Before o ...
... Guam and Hawaii initially both operate as closed economies, which means that they had consumed only domestically produced goods. Madison Coke Company (MCC) made an agreement with the government of Guam and Hawaii respectively to exclusively provide coke to the market in these two economies. Before o ...
PDF
... the much more limited variety available 30 years ago? A conservative estimate of the value of extra variety and convenience might be 10 percent for food consumed at home other than produce, 20 percent for produce where the increased variety in winter (as well as summer farmers' markets) has been so ...
... the much more limited variety available 30 years ago? A conservative estimate of the value of extra variety and convenience might be 10 percent for food consumed at home other than produce, 20 percent for produce where the increased variety in winter (as well as summer farmers' markets) has been so ...
Economic equilibrium

In economics, economic equilibrium is a state where economic forces such as supply and demand are balanced and in the absence of external influences the (equilibrium) values of economic variables will not change. For example, in the standard text-book model of perfect competition, equilibrium occurs at the point at which quantity demanded and quantity supplied are equal. Market equilibrium in this case refers to a condition where a market price is established through competition such that the amount of goods or services sought by buyers is equal to the amount of goods or services produced by sellers. This price is often called the competitive price or market clearing price and will tend not to change unless demand or supply changes and the quantity is called ""competitive quantity"" or market clearing quantity.