1 Assignment #5 ANSWERS Answer the questions below by
... 5. Consider two competing car industries: American and Japanese. What would happen to the equilibrium price and quantity of Japanese cars if the prices of American cars go up? Use the following diagram assuming that it represents supply of and demand for Japanese cars. Show on the diagram where the ...
... 5. Consider two competing car industries: American and Japanese. What would happen to the equilibrium price and quantity of Japanese cars if the prices of American cars go up? Use the following diagram assuming that it represents supply of and demand for Japanese cars. Show on the diagram where the ...
Demand and Supply
... • D-1(Q) is the inverse- (or price-) demand curve. It associates a price with every quantity. ...
... • D-1(Q) is the inverse- (or price-) demand curve. It associates a price with every quantity. ...
Perfectly Competitive Market - Directorate of Higher Education, Tripura
... It is important to note that profit in a perfectly competitive market will lead to firms wanting to enter that market If enough firms enter, then the market supply curve will shift to the right. ...
... It is important to note that profit in a perfectly competitive market will lead to firms wanting to enter that market If enough firms enter, then the market supply curve will shift to the right. ...
Demand - Personal.psu.edu
... • Quantity is on the horizontal axis • Since consumers see prices and choose quantities, Q = f(P) • This is opposite of usual graphs in algebra where the dependent variable is on the vertical axis – if you use excel or a graphing calculator you need to make an adjustment ...
... • Quantity is on the horizontal axis • Since consumers see prices and choose quantities, Q = f(P) • This is opposite of usual graphs in algebra where the dependent variable is on the vertical axis – if you use excel or a graphing calculator you need to make an adjustment ...
Review – Goal 8 (Types of Economies, Supply and Demand)
... The demand curve has a ______________ slope. What causes a movement along the demand curve? If quantity demanded does not change with a change in price, the demand is _____. If quantity demanded changes with a change in price, the demand is ____. The amount of goods available. The desire to own some ...
... The demand curve has a ______________ slope. What causes a movement along the demand curve? If quantity demanded does not change with a change in price, the demand is _____. If quantity demanded changes with a change in price, the demand is ____. The amount of goods available. The desire to own some ...
E. Consumers expect the price of soft drinks to rise in the
... b. Income tax revenues should be used to fund education c. If tax rates are reduced then consumer spending will increase. d. Federal income tax rates are higher in most states than state income tax rates. e. all of the above statements are statements of positive economics. 2. Which of the following ...
... b. Income tax revenues should be used to fund education c. If tax rates are reduced then consumer spending will increase. d. Federal income tax rates are higher in most states than state income tax rates. e. all of the above statements are statements of positive economics. 2. Which of the following ...
Answers to Workshop 2
... quantity demanded but a fall in the quantity supplied. If, however, demand exceeds supply in any market (a shortage), the price will rise. This will lead to a fall in the quantity demanded and a rise in the quantity supplied. In either case, the adjustment of price will ensure that demand and supply ...
... quantity demanded but a fall in the quantity supplied. If, however, demand exceeds supply in any market (a shortage), the price will rise. This will lead to a fall in the quantity demanded and a rise in the quantity supplied. In either case, the adjustment of price will ensure that demand and supply ...
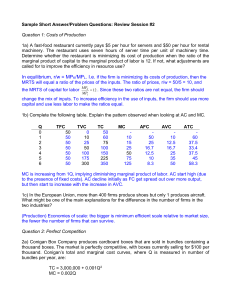
Review Session #2
... is room for only one firm in the market that produces efficiently. In other words, AC are everywhere declining over the relevant range of output (so if we had many firms producing, then each firm would produce less, leading to AC increasing). Monopoly: Slide 15, Chapter 10. Note, the DWL is equal to ...
... is room for only one firm in the market that produces efficiently. In other words, AC are everywhere declining over the relevant range of output (so if we had many firms producing, then each firm would produce less, leading to AC increasing). Monopoly: Slide 15, Chapter 10. Note, the DWL is equal to ...
Example of computing a competitive equilibrium in an
... (we will use pb = 1 later) such that: (i) given the prices, consumers maximize their utility at the allocation (fA ; fB ; bA ; bB ) (i.e., these quantities are their consumer demands given the prices and the endowments) (ii) markets clear, i.e. demand equals supply for each good: ...
... (we will use pb = 1 later) such that: (i) given the prices, consumers maximize their utility at the allocation (fA ; fB ; bA ; bB ) (i.e., these quantities are their consumer demands given the prices and the endowments) (ii) markets clear, i.e. demand equals supply for each good: ...
Document
... 1. Which of the following will not change the demand for oranges? a. A change in consumers’ incomes b. A change in the price of grapefruits, a substitute for oranges c. A change in the price of oranges d. A change in consumers’ taste for oranges e. An expectation that the price of oranges will chang ...
... 1. Which of the following will not change the demand for oranges? a. A change in consumers’ incomes b. A change in the price of grapefruits, a substitute for oranges c. A change in the price of oranges d. A change in consumers’ taste for oranges e. An expectation that the price of oranges will chang ...
File
... the price is high and more of it if the price is low 12) Law of Supply: The principle that suppliers will normally offer more for sale at higher prices and less at lower prices 13) Marginal Utility: Additional use that is derived from each unit acquired ...
... the price is high and more of it if the price is low 12) Law of Supply: The principle that suppliers will normally offer more for sale at higher prices and less at lower prices 13) Marginal Utility: Additional use that is derived from each unit acquired ...
Chapter 11: Perfect Competition
... c. As with (b), the demand curve facing a single firm in a competitive market is horizontal instead of downward sloping. Secondly, the profit maximizing level of output is not where MC = AVC, but where MC = P = MR. Third, the MC curve should go through the minimum point of the ATC curve. It currentl ...
... c. As with (b), the demand curve facing a single firm in a competitive market is horizontal instead of downward sloping. Secondly, the profit maximizing level of output is not where MC = AVC, but where MC = P = MR. Third, the MC curve should go through the minimum point of the ATC curve. It currentl ...
Microeconomic Concepts Describe how households, businesses
... b. Explain the role of profit as an incentive for entrepreneurs. Entrepreneurs are willing to risk their resources in order to sell them for financial gain or profit, and are successful when providing goods and services valued by consumers. Successful entrepreneurs are willing to assume risk, have u ...
... b. Explain the role of profit as an incentive for entrepreneurs. Entrepreneurs are willing to risk their resources in order to sell them for financial gain or profit, and are successful when providing goods and services valued by consumers. Successful entrepreneurs are willing to assume risk, have u ...
EOCT Study Guide
... b. Explain the role of profit as an incentive for entrepreneurs. Entrepreneurs are willing to risk their resources in order to sell them for financial gain or profit, and are successful when providing goods and services valued by consumers. Successful entrepreneurs are willing to assume risk, have u ...
... b. Explain the role of profit as an incentive for entrepreneurs. Entrepreneurs are willing to risk their resources in order to sell them for financial gain or profit, and are successful when providing goods and services valued by consumers. Successful entrepreneurs are willing to assume risk, have u ...
Chapter_4_Section_2
... change in the quantity of a product purchased in response to a change in price Figure 4.3 on pg. 96 ...
... change in the quantity of a product purchased in response to a change in price Figure 4.3 on pg. 96 ...
Economic equilibrium

In economics, economic equilibrium is a state where economic forces such as supply and demand are balanced and in the absence of external influences the (equilibrium) values of economic variables will not change. For example, in the standard text-book model of perfect competition, equilibrium occurs at the point at which quantity demanded and quantity supplied are equal. Market equilibrium in this case refers to a condition where a market price is established through competition such that the amount of goods or services sought by buyers is equal to the amount of goods or services produced by sellers. This price is often called the competitive price or market clearing price and will tend not to change unless demand or supply changes and the quantity is called ""competitive quantity"" or market clearing quantity.