Equilibrium Review
... and assist lower-income groups. The laws cause disequilibrium, resulting in a shortage. When rent control is repealed, the prices increase to equilibrium, and lowerincome residents are forced to leave. ...
... and assist lower-income groups. The laws cause disequilibrium, resulting in a shortage. When rent control is repealed, the prices increase to equilibrium, and lowerincome residents are forced to leave. ...
Chapter 2
... d) Normally a price ceiling both raises quantity demanded and lowers quantity supplied. Here, only the first effect is present because the stadium capacity is fixed. ...
... d) Normally a price ceiling both raises quantity demanded and lowers quantity supplied. Here, only the first effect is present because the stadium capacity is fixed. ...
View sample exam
... 6. The Monetarist maintains that the economy is generally at a. full employment because of flexible prices b. less than full employment due to rigid prices c. full employment due to rigid prices d. none of the above ...
... 6. The Monetarist maintains that the economy is generally at a. full employment because of flexible prices b. less than full employment due to rigid prices c. full employment due to rigid prices d. none of the above ...
Chapter 6 and 7
... 2. Why might a producer not be willing to sell at a low price? (assuming the product still made a profit) 2 reasons 3. What does surplus mean? 4. How long does it take to get a price to equilibrium? BONUS What word(s) do stores use to move the price to equilibrium? Most wins ...
... 2. Why might a producer not be willing to sell at a low price? (assuming the product still made a profit) 2 reasons 3. What does surplus mean? 4. How long does it take to get a price to equilibrium? BONUS What word(s) do stores use to move the price to equilibrium? Most wins ...
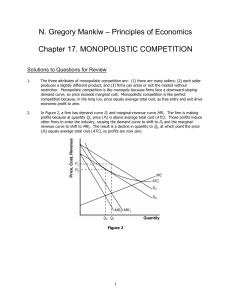
N. Gregory Mankiw – Principles of Economics Chapter 17
... Advertising with no apparent informational content might convey information to consumers if it provides a signal of quality. A firm won't be willing to spend much money advertising a lowquality good, but will be willing to spend significantly more advertising a high-quality good. ...
... Advertising with no apparent informational content might convey information to consumers if it provides a signal of quality. A firm won't be willing to spend much money advertising a lowquality good, but will be willing to spend significantly more advertising a high-quality good. ...
Izmir University of Economics Department of Economics Econ 101
... a. Goods that are more scarce tend to be more expensive. b. When a good or service is less available, people don't consume as much of it; therefore, the price will fall. c. There is an inverse relationship between the price and the quantity demanded of a good or service. d. When demand for a good in ...
... a. Goods that are more scarce tend to be more expensive. b. When a good or service is less available, people don't consume as much of it; therefore, the price will fall. c. There is an inverse relationship between the price and the quantity demanded of a good or service. d. When demand for a good in ...
Where did you go to high school?
... In our previous example: We are told that E=-0.5. We are told that A=( % change in quantity) = –20 We need to solve for B= (% change in price). • Since by definition ...
... In our previous example: We are told that E=-0.5. We are told that A=( % change in quantity) = –20 We need to solve for B= (% change in price). • Since by definition ...
Changes in Quantity Demanded and Quantity Supplied
... •When Price of the good increases, the Quantity Supplied also increases •When Price of the good decreases, the Quantity Supplied also decreases ...
... •When Price of the good increases, the Quantity Supplied also increases •When Price of the good decreases, the Quantity Supplied also decreases ...
opportunity cost
... Figure 1-3: demand and supply curves intersect at the market equilibrium point P*, Q* P* is equilibrium price: price at which the quantity demanded by a good’s buyers precisely equals quantity of that good supplied by sellers ...
... Figure 1-3: demand and supply curves intersect at the market equilibrium point P*, Q* P* is equilibrium price: price at which the quantity demanded by a good’s buyers precisely equals quantity of that good supplied by sellers ...
Overview - Faculty Websites
... Price elasticity of demand = 4 – For each 1% increase in price above $20K there’s a 4% decrease in quantity demanded below 2.0 million – If price rises by 1% to $20.2K, sales drop by 80,000 (4% of 2 million) to 1.92 million ...
... Price elasticity of demand = 4 – For each 1% increase in price above $20K there’s a 4% decrease in quantity demanded below 2.0 million – If price rises by 1% to $20.2K, sales drop by 80,000 (4% of 2 million) to 1.92 million ...
Supply and Demand Together Notes
... Signal that price is too high – people don’t want to buy it ...
... Signal that price is too high – people don’t want to buy it ...
ECO352_Precept_Wk07.pdf
... Thus higher industry output shifts down each firm's cost curves: this is external economy Possible reasons: An industry-wide input produced with economies of scale, or industry-wide know-how spreads more easily to individual firms (silicon valley story). Each firm is small: takes as given the market ...
... Thus higher industry output shifts down each firm's cost curves: this is external economy Possible reasons: An industry-wide input produced with economies of scale, or industry-wide know-how spreads more easily to individual firms (silicon valley story). Each firm is small: takes as given the market ...
The 5 Powers of Economic Thinking (dun dun dun!!!)
... Shifts in Demand and Supply and their effect on Market Price Demand Towards (decreases) ...
... Shifts in Demand and Supply and their effect on Market Price Demand Towards (decreases) ...
Homework 1
... • Suppose that a consumer’s demand is given by – Quantity Demanded (Qd) = 110 – 1*Price ...
... • Suppose that a consumer’s demand is given by – Quantity Demanded (Qd) = 110 – 1*Price ...
HomeworkPacket
... 13) If Oligopolies succeed at perfectly cooperating (collusion) how does the equilibrium profit, price & quantity of their industry differ from a monopolies? a. Explain why do Oligopolies usually fail to achieve a Monopoly outcome? ...
... 13) If Oligopolies succeed at perfectly cooperating (collusion) how does the equilibrium profit, price & quantity of their industry differ from a monopolies? a. Explain why do Oligopolies usually fail to achieve a Monopoly outcome? ...
Federal Urdu University
... a) What is the equilibrium price and quantity? b) If the government imposes a maximum price on that product equals to 1 kg per unit, explain what will happen in this market? Draw a simple graph to explain the maximum price effect. c) If the government imposes a maximum price on that good equal to 4 ...
... a) What is the equilibrium price and quantity? b) If the government imposes a maximum price on that product equals to 1 kg per unit, explain what will happen in this market? Draw a simple graph to explain the maximum price effect. c) If the government imposes a maximum price on that good equal to 4 ...
Economic equilibrium

In economics, economic equilibrium is a state where economic forces such as supply and demand are balanced and in the absence of external influences the (equilibrium) values of economic variables will not change. For example, in the standard text-book model of perfect competition, equilibrium occurs at the point at which quantity demanded and quantity supplied are equal. Market equilibrium in this case refers to a condition where a market price is established through competition such that the amount of goods or services sought by buyers is equal to the amount of goods or services produced by sellers. This price is often called the competitive price or market clearing price and will tend not to change unless demand or supply changes and the quantity is called ""competitive quantity"" or market clearing quantity.