Chapter 3: Supply and Demand
... • The long run is the period of time in which: – New sellers may enter a market – Existing sellers may exit from a market – Existing sellers may adjust fixed factors of ...
... • The long run is the period of time in which: – New sellers may enter a market – Existing sellers may exit from a market – Existing sellers may adjust fixed factors of ...
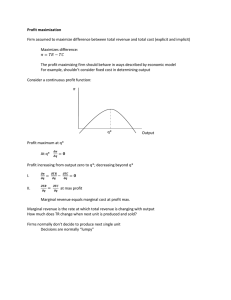
Profit Maximization
... Marginal revenue is the rate at which total revenue is changing with output How much does TR change when next unit is produced and sold? Firms normally don’t decide to produce next single unit Decisions are normally “lumpy” ...
... Marginal revenue is the rate at which total revenue is changing with output How much does TR change when next unit is produced and sold? Firms normally don’t decide to produce next single unit Decisions are normally “lumpy” ...
Homework Quiz 8
... higher prices in the short run, then an increase in production in the long run that would cause price to decline. d. lower prices in the short run because of higher sales, but higher prices in the long run as the inventory of beer is depleted. 6. The characteristics of perfect competition in the lon ...
... higher prices in the short run, then an increase in production in the long run that would cause price to decline. d. lower prices in the short run because of higher sales, but higher prices in the long run as the inventory of beer is depleted. 6. The characteristics of perfect competition in the lon ...
Supply and Demand Infographic Supplemental Activity
... teach it to say “supply and demand.”) The supply and demand infographic highlights basic concepts such as the laws of supply and demand, changes in demand and supply versus changes in the quantity demanded and the quantity supplied, the determinants of demand and supply, and market equilibrium. Supp ...
... teach it to say “supply and demand.”) The supply and demand infographic highlights basic concepts such as the laws of supply and demand, changes in demand and supply versus changes in the quantity demanded and the quantity supplied, the determinants of demand and supply, and market equilibrium. Supp ...
經濟學原理第一次小考
... 13) Consider the market for soft drinks shown in the figure below. Initially the economy is at point a. If people come to expect that the price of a soft drink will increase in the future, there will be a movement to a point such as A) ...
... 13) Consider the market for soft drinks shown in the figure below. Initially the economy is at point a. If people come to expect that the price of a soft drink will increase in the future, there will be a movement to a point such as A) ...
Equilibrium
... So why are prices so important? • Prices are vital in a free market economy. • They help move land, labor and capital into the hands of producers and finished goods into the hands of buyers. • Price is a language both consumers and producers can use to determine value. ...
... So why are prices so important? • Prices are vital in a free market economy. • They help move land, labor and capital into the hands of producers and finished goods into the hands of buyers. • Price is a language both consumers and producers can use to determine value. ...
Economics Holiday Homework - Kendriya Vidyalaya No.1 Devlali
... 11. A consumer consumes only two goods X and Y. State and explains the conditions of consumer’s equilibrium with the help of utility analysis. 12. Explain how the demand for a good is affected by the prices of its related goods. Give examples. 13. Derive the law of demand from the single commodity e ...
... 11. A consumer consumes only two goods X and Y. State and explains the conditions of consumer’s equilibrium with the help of utility analysis. 12. Explain how the demand for a good is affected by the prices of its related goods. Give examples. 13. Derive the law of demand from the single commodity e ...
Chapter 3: Demand, Supply, and Market Equilibrium
... supplied.” • A higher price causes a larger quantity supplied. This is shown here with price increasing from Po to P1, causing quantity supplied to increase from QoA to Q1A, as the producer moves along its supply curve. • We do not say that a higher price causes a larger supply. ...
... supplied.” • A higher price causes a larger quantity supplied. This is shown here with price increasing from Po to P1, causing quantity supplied to increase from QoA to Q1A, as the producer moves along its supply curve. • We do not say that a higher price causes a larger supply. ...
Scarcity and Resource Allocation
... In a laissez faire or free market, they are solved by the interaction of the market forces of demand and supply – known as the price mechanism – setting an equilibrium price and output level. The price mechanism works as consumers and producers are motivated by self-interest and profit- and utility- ...
... In a laissez faire or free market, they are solved by the interaction of the market forces of demand and supply – known as the price mechanism – setting an equilibrium price and output level. The price mechanism works as consumers and producers are motivated by self-interest and profit- and utility- ...
AP Economics
... 2) Have clear tastes & choose 3) Have limited means & choose 4) Must choose from options B. Utility Maximization Rule (UMR) > explains how consumers spend their $ so that the last dollar spent on each product yields the same MU. The consumer is in equilibrium in amount spent and quantity purchased o ...
... 2) Have clear tastes & choose 3) Have limited means & choose 4) Must choose from options B. Utility Maximization Rule (UMR) > explains how consumers spend their $ so that the last dollar spent on each product yields the same MU. The consumer is in equilibrium in amount spent and quantity purchased o ...
Chapter 2
... frequently. Ask about the importance of price until someone volunteers that income is important and the prices of substitute goods are important. Expectations of price change (e.g., clearance sales) can also be discussed. Few students will mention complementary goods, and most will reject the idea o ...
... frequently. Ask about the importance of price until someone volunteers that income is important and the prices of substitute goods are important. Expectations of price change (e.g., clearance sales) can also be discussed. Few students will mention complementary goods, and most will reject the idea o ...
supply and demand exercises
... c) a decrease in the opportunity cost associated with growing wheat; d) a leftward shift in the supply curve for wheat. ...
... c) a decrease in the opportunity cost associated with growing wheat; d) a leftward shift in the supply curve for wheat. ...
Supply and Demand
... Law of demand: Consumers buy more of a good when its price decreases and less when its price increases. Would you buy a slice of pizza for lunch if it cost $1? (Would you buy more than one?) Would you buy a slice of pizza for lunch if it cost $5? As the price of pizza gets higher fewer of us are wil ...
... Law of demand: Consumers buy more of a good when its price decreases and less when its price increases. Would you buy a slice of pizza for lunch if it cost $1? (Would you buy more than one?) Would you buy a slice of pizza for lunch if it cost $5? As the price of pizza gets higher fewer of us are wil ...
1 Price Ali Ayşe Arda Ada Market demand $0.00 20 16 4 8 0.50 18
... a. a rightward shift of the demand curve. b. an upward left movement along the demand curve. c. a leftward shift of the demand curve. d. a right downward movement along the demand curve. 5. If Murat’s income decreases, Murat’s demand for a. each good he purchases will decrease. b. luxury goods will ...
... a. a rightward shift of the demand curve. b. an upward left movement along the demand curve. c. a leftward shift of the demand curve. d. a right downward movement along the demand curve. 5. If Murat’s income decreases, Murat’s demand for a. each good he purchases will decrease. b. luxury goods will ...
Chapter 6 Equilibrium
... ceiling, the maximum price that can be legally charged for a good or service. Rent control is a prime example of a price ceiling. In other cases, the government can create a price floor, or a minimum price for a good or service. Minimum wage is a prime example of a price floor, as are agricultural ...
... ceiling, the maximum price that can be legally charged for a good or service. Rent control is a prime example of a price ceiling. In other cases, the government can create a price floor, or a minimum price for a good or service. Minimum wage is a prime example of a price floor, as are agricultural ...
Module 1 Vocabulary Glossary Term Definition Basic economic
... Total amount of a good or service available for purchase. Supply is the whole curve,‖ supply for goods and services at all prices. ...
... Total amount of a good or service available for purchase. Supply is the whole curve,‖ supply for goods and services at all prices. ...
Chapter 6 Notes
... -prices need to change to solve problems of surplus or shortage -supply shock…sudden shortage of a good -rising prices are the easiest way to solve -Price system is free -distribution based on decisions of consumers Wide choice of goods -allows consumers to choose from similar goods -rationing + sho ...
... -prices need to change to solve problems of surplus or shortage -supply shock…sudden shortage of a good -rising prices are the easiest way to solve -Price system is free -distribution based on decisions of consumers Wide choice of goods -allows consumers to choose from similar goods -rationing + sho ...
Economic equilibrium

In economics, economic equilibrium is a state where economic forces such as supply and demand are balanced and in the absence of external influences the (equilibrium) values of economic variables will not change. For example, in the standard text-book model of perfect competition, equilibrium occurs at the point at which quantity demanded and quantity supplied are equal. Market equilibrium in this case refers to a condition where a market price is established through competition such that the amount of goods or services sought by buyers is equal to the amount of goods or services produced by sellers. This price is often called the competitive price or market clearing price and will tend not to change unless demand or supply changes and the quantity is called ""competitive quantity"" or market clearing quantity.