A change in the price of a good results in a change in the quantity
... an inverse relationship. The change in quantity demanded that results from a change in price is represented by a movement along the demand curve, as shown on the left. The demand curve never shifts when there is a change in one of the variables measured on the axes. If one of the previously constant ...
... an inverse relationship. The change in quantity demanded that results from a change in price is represented by a movement along the demand curve, as shown on the left. The demand curve never shifts when there is a change in one of the variables measured on the axes. If one of the previously constant ...
11extra - U of L Class Index
... B) producing a given output at minimum average cost. C) using the newest available technology. D) increasing market demand. E) external economies. 6) Total efficiency is achieved when 6) _______ A) producers cannot lower the cost of producing a given output. B) all the gains from trade have been rea ...
... B) producing a given output at minimum average cost. C) using the newest available technology. D) increasing market demand. E) external economies. 6) Total efficiency is achieved when 6) _______ A) producers cannot lower the cost of producing a given output. B) all the gains from trade have been rea ...
Unit 2B Overview
... demand curve is downward sloping. The law of diminishing marginal utility states that as more of a good or service is consumed in a given period of time, the additional satisfaction declines. Utility Maximizing Rule: MUx/Px = MUy/Py Consumer surplus equals buyers’ willingness to pay for a good m ...
... demand curve is downward sloping. The law of diminishing marginal utility states that as more of a good or service is consumed in a given period of time, the additional satisfaction declines. Utility Maximizing Rule: MUx/Px = MUy/Py Consumer surplus equals buyers’ willingness to pay for a good m ...
Demand
... The law of demand As the price increases, the quantity demanded decreases, ceteris paribus. This also works in the opposite direction e.g. Price down quantity up ...
... The law of demand As the price increases, the quantity demanded decreases, ceteris paribus. This also works in the opposite direction e.g. Price down quantity up ...
Week 3 – Demand, Market Equilibrium and
... Deadweight loss: the reduction in economic surplus resulting from a market not being in competitive equilibrium. Pareto efficiency – if it is not possible to reallocate resources and make someone better off without making someone else worse off, it maximizes total surplus. Trading all units up un ...
... Deadweight loss: the reduction in economic surplus resulting from a market not being in competitive equilibrium. Pareto efficiency – if it is not possible to reallocate resources and make someone better off without making someone else worse off, it maximizes total surplus. Trading all units up un ...
Ch3
... • Supply is the relationship between the quantity of the good that sellers are willing and able to supply and the price of the good, while other factors affecting quantity supplied are constant. • We can represent supply in a table, a graph, or an equation. Accordingly, we talk about a ...
... • Supply is the relationship between the quantity of the good that sellers are willing and able to supply and the price of the good, while other factors affecting quantity supplied are constant. • We can represent supply in a table, a graph, or an equation. Accordingly, we talk about a ...
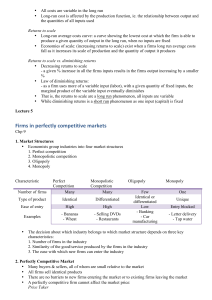
REVIEW FOR UNIT 2/3 MICROECONOMICS EXAMINATION Perfect
... 11. What can be said about fixed costs in the short-run? 12. What can be said about firm’s ability to earn profit in the long run? 13. If the supply curve for a perfectly competitive market is horizontal we can assume that each industry? Monopoly: 14. What is the quantity effect and how does it diff ...
... 11. What can be said about fixed costs in the short-run? 12. What can be said about firm’s ability to earn profit in the long run? 13. If the supply curve for a perfectly competitive market is horizontal we can assume that each industry? Monopoly: 14. What is the quantity effect and how does it diff ...
Questions Assigned for Review Problems and Applications – 2,3,5,8
... notebooks demanded, but not the quantity supplied" is false, in general. As Figure 4-10 shows, the increase in demand for notebooks results in an increased quantity supplied. The only way the statement would be true is if the supply curve were perfectly inelastic, as shown in Figure 4-11. ...
... notebooks demanded, but not the quantity supplied" is false, in general. As Figure 4-10 shows, the increase in demand for notebooks results in an increased quantity supplied. The only way the statement would be true is if the supply curve were perfectly inelastic, as shown in Figure 4-11. ...
Shifting Demand and Supply
... 2. Price of chicken sandwiches (a substitute) increases 3. Price of hamburgers falls from $3 to $1. 4. Price for ground beef triples ...
... 2. Price of chicken sandwiches (a substitute) increases 3. Price of hamburgers falls from $3 to $1. 4. Price for ground beef triples ...
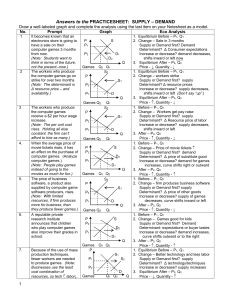
Supply and Demand Practice Sheet Answers
... buyers, so per unit costs rise. All else constant they can’t produce as much.) The manufacturer of the computer games raises the price on the games. (Note: This is the trick question. Since the price of games changes, there is Δ Quantity Demanded and Supplied, not Δ Demand.) The popularity of the co ...
... buyers, so per unit costs rise. All else constant they can’t produce as much.) The manufacturer of the computer games raises the price on the games. (Note: This is the trick question. Since the price of games changes, there is Δ Quantity Demanded and Supplied, not Δ Demand.) The popularity of the co ...
Lecture_02.4 Elasticity
... • Economist use the (own) price elasticity of demand to summarize how responsive quantity demanded is to price • Own-price (product’s price) • Cross-price (related goods – substitutes, complements) • Income • Demand curves are not always linear; and responsiveness can change with price ...
... • Economist use the (own) price elasticity of demand to summarize how responsive quantity demanded is to price • Own-price (product’s price) • Cross-price (related goods – substitutes, complements) • Income • Demand curves are not always linear; and responsiveness can change with price ...
Supply & Demand
... reduce the demand to 300 from 500 at a price of £5. Suppliers do not have the information or time to adjust supply immediately and still offer 600 for sale at £5. This results in a market surplus (S > D D) ...
... reduce the demand to 300 from 500 at a price of £5. Suppliers do not have the information or time to adjust supply immediately and still offer 600 for sale at £5. This results in a market surplus (S > D D) ...
Answer to Quiz #2 (updated 3:25 p.m. Tuesday, May 31, 2011)
... 1000 – Q while the supply curve for corn is given by the equation P = 3Q where P is the price per unit of corn and Q is units of corn. a. (2 points) What is the equilibrium price and quantity in the corn market? The equilibrium price in this market is $750 and the equilibrium quantity is 250 units. ...
... 1000 – Q while the supply curve for corn is given by the equation P = 3Q where P is the price per unit of corn and Q is units of corn. a. (2 points) What is the equilibrium price and quantity in the corn market? The equilibrium price in this market is $750 and the equilibrium quantity is 250 units. ...
File
... Supply= The amount of a product offered for sale at all possible prices in the market. Law of Supply= As supply increases, price increases. ...
... Supply= The amount of a product offered for sale at all possible prices in the market. Law of Supply= As supply increases, price increases. ...
- Franklin High School
... 12. Alligator shoes went on sale and the quantity demand for this stylish footwear went up. The proprietor, being a shrewd businesswoman, also had available alligator belts, alligator purses, and alligator vests to go with the shoes. Although these other items were not priced at sale prices, the dem ...
... 12. Alligator shoes went on sale and the quantity demand for this stylish footwear went up. The proprietor, being a shrewd businesswoman, also had available alligator belts, alligator purses, and alligator vests to go with the shoes. Although these other items were not priced at sale prices, the dem ...
Study Guide
... industry. (supply curves in left hand graph above…) b. Hint: Why is there a difference between these 2 supply curves? ______________________________________________________________________________________________________ _______________________________________________________________________________ ...
... industry. (supply curves in left hand graph above…) b. Hint: Why is there a difference between these 2 supply curves? ______________________________________________________________________________________________________ _______________________________________________________________________________ ...
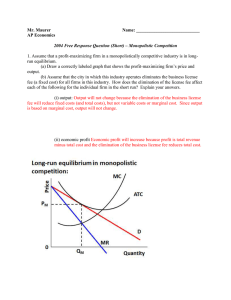
Mr. Maurer Name: AP Economics 2004 Free Response Question
... curve, so total revenue increases as price decreases. (c) Given the information in part (a), what happens to the demand curve for the typical firm in the long-run? Explain. If a monopolistically competitive firm is earning economic profit, in the long run, the demand curve for the typical firm will ...
... curve, so total revenue increases as price decreases. (c) Given the information in part (a), what happens to the demand curve for the typical firm in the long-run? Explain. If a monopolistically competitive firm is earning economic profit, in the long run, the demand curve for the typical firm will ...
Economic equilibrium

In economics, economic equilibrium is a state where economic forces such as supply and demand are balanced and in the absence of external influences the (equilibrium) values of economic variables will not change. For example, in the standard text-book model of perfect competition, equilibrium occurs at the point at which quantity demanded and quantity supplied are equal. Market equilibrium in this case refers to a condition where a market price is established through competition such that the amount of goods or services sought by buyers is equal to the amount of goods or services produced by sellers. This price is often called the competitive price or market clearing price and will tend not to change unless demand or supply changes and the quantity is called ""competitive quantity"" or market clearing quantity.