lecture seven - Webster in china
... Consumer lock-in Potential entrants can be deterred if they believe high switching costs will keep them from inducing many consumers to change brands ...
... Consumer lock-in Potential entrants can be deterred if they believe high switching costs will keep them from inducing many consumers to change brands ...
Econ 202 Exercise 4 (Chapters 6-7) 1) Graphically illustrate (using
... 4) Based on your understanding of the aggregate supply and aggregate demand model and the IS-LM model, graphically illustrate and explain what effect a tax increase will have on the economy. In your graphs, clearly illustrate the short-run and medium-run equilibria. 5) Analysis of the macroeconomic ...
... 4) Based on your understanding of the aggregate supply and aggregate demand model and the IS-LM model, graphically illustrate and explain what effect a tax increase will have on the economy. In your graphs, clearly illustrate the short-run and medium-run equilibria. 5) Analysis of the macroeconomic ...
a D
... able to buy at each possible price during a given time period, other things constant – Amounts purchased per period • at each possible price ...
... able to buy at each possible price during a given time period, other things constant – Amounts purchased per period • at each possible price ...
Demand and Marginal Utility
... • The extra satisfaction we get from using additional quantities of product begins to diminish or fade • B/c of DMU people are not willing to pay as much money for a second, third, or fourth product • When you reach the point where the marginal utility is less than the price, you stop buying it ...
... • The extra satisfaction we get from using additional quantities of product begins to diminish or fade • B/c of DMU people are not willing to pay as much money for a second, third, or fourth product • When you reach the point where the marginal utility is less than the price, you stop buying it ...
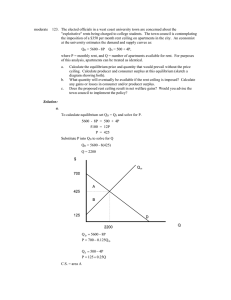
moderate
... Consumer surplus is the area of the triangle between the equilibrium price line 15.28 and the demand curve out to Q = 97.22 Height of triangle is 25 - 15.28 = 9.72 Area = (1/2)(b)(h) = (0.5)(97.22)(9.72) = $472.49 Consumer surplus = $472.49 per year. b. The producer surplus is the area of the triang ...
... Consumer surplus is the area of the triangle between the equilibrium price line 15.28 and the demand curve out to Q = 97.22 Height of triangle is 25 - 15.28 = 9.72 Area = (1/2)(b)(h) = (0.5)(97.22)(9.72) = $472.49 Consumer surplus = $472.49 per year. b. The producer surplus is the area of the triang ...
Market Outcomes - College of Business and Economics
... Identify trends, cycles, and fluctuations and discuss what may have caused them. Specify whether they were demand shifters or supply shifters. I am looking for “likely” reasons for trends, cycles, and “shocks”; not a statistical analysis. Review your understanding of Porter’s Five Forces for this pr ...
... Identify trends, cycles, and fluctuations and discuss what may have caused them. Specify whether they were demand shifters or supply shifters. I am looking for “likely” reasons for trends, cycles, and “shocks”; not a statistical analysis. Review your understanding of Porter’s Five Forces for this pr ...
Monopolistic Competition in the Long Run
... 4. In long-run equilibrium, firms in a monopolistically competitive industry sell at a price greater than marginal cost. 5. They also have excess capacity because they produce less than the minimum-cost output; as a result, they have higher costs than firms in a perfectly competitive industry. ...
... 4. In long-run equilibrium, firms in a monopolistically competitive industry sell at a price greater than marginal cost. 5. They also have excess capacity because they produce less than the minimum-cost output; as a result, they have higher costs than firms in a perfectly competitive industry. ...
Total Revenue Test, Income Elasticity - VCC Library
... 2. When demand is price inelastic, total revenues will increase/decrease/stay the same as the price falls. 3. If Ali’s income increases from $36,000 to $40,000 and the amount of donuts he consumes increases from 52 per year to 86, calculate the income elasticity of demand. What type of goods are don ...
... 2. When demand is price inelastic, total revenues will increase/decrease/stay the same as the price falls. 3. If Ali’s income increases from $36,000 to $40,000 and the amount of donuts he consumes increases from 52 per year to 86, calculate the income elasticity of demand. What type of goods are don ...
ch6
... Double oral auction: A large number of buyers and sellers, each with potentially a different valuation of a good, negotiate with each other, one-on-one, to try to get a better deal ...
... Double oral auction: A large number of buyers and sellers, each with potentially a different valuation of a good, negotiate with each other, one-on-one, to try to get a better deal ...
Econ 101, section 5, S01
... 16. A competitive industry is in zero-profit equilibrium to begin. Then demand shifts permanently to the right. Which of the following will be a feature of the new zero-profit equilibrium that will eventually be reached in the long-run? a. Industry output will be the same as in the original zero-pro ...
... 16. A competitive industry is in zero-profit equilibrium to begin. Then demand shifts permanently to the right. Which of the following will be a feature of the new zero-profit equilibrium that will eventually be reached in the long-run? a. Industry output will be the same as in the original zero-pro ...
Demand & Supply
... influenced by the price of goods in the market. Satisfaction is gained not only from the good itself, but also from being seen to be able to afford it. This may be the case with such prestige items such as paintings, or expensive clothes and cars. ...
... influenced by the price of goods in the market. Satisfaction is gained not only from the good itself, but also from being seen to be able to afford it. This may be the case with such prestige items such as paintings, or expensive clothes and cars. ...
1 - BrainMass
... All firms are price takers. Each firm sets its own price based on its anticipated reaction by its customers. All firms collaborate to establish one price. All firms are free to enter or leave the market. ...
... All firms are price takers. Each firm sets its own price based on its anticipated reaction by its customers. All firms collaborate to establish one price. All firms are free to enter or leave the market. ...
NAME:
... 2. (Third Degree Price Discrimination) Suppose a firm sells to students and others at a single price of $10 per unit. At this price, it sells 10,000 units in total; 2,000 to students and 8,000 to the others (non-students). At the price of $10, demand by students has elasticity -3, while demand by th ...
... 2. (Third Degree Price Discrimination) Suppose a firm sells to students and others at a single price of $10 per unit. At this price, it sells 10,000 units in total; 2,000 to students and 8,000 to the others (non-students). At the price of $10, demand by students has elasticity -3, while demand by th ...
Economic equilibrium

In economics, economic equilibrium is a state where economic forces such as supply and demand are balanced and in the absence of external influences the (equilibrium) values of economic variables will not change. For example, in the standard text-book model of perfect competition, equilibrium occurs at the point at which quantity demanded and quantity supplied are equal. Market equilibrium in this case refers to a condition where a market price is established through competition such that the amount of goods or services sought by buyers is equal to the amount of goods or services produced by sellers. This price is often called the competitive price or market clearing price and will tend not to change unless demand or supply changes and the quantity is called ""competitive quantity"" or market clearing quantity.