Regulation
... monopoly): – When a single firm can supply a good or service to an entire market at a smaller cost than could two or more firms • Economies of scale and/or scope over a relevant range of output ...
... monopoly): – When a single firm can supply a good or service to an entire market at a smaller cost than could two or more firms • Economies of scale and/or scope over a relevant range of output ...
Supply & Demand
... • A change in the costs of production • A change in technology Demand • A changes in taxes/subsidies/restrictions • Others (price of other goods; expectations; Quantity size of market ). Qe ...
... • A change in the costs of production • A change in technology Demand • A changes in taxes/subsidies/restrictions • Others (price of other goods; expectations; Quantity size of market ). Qe ...
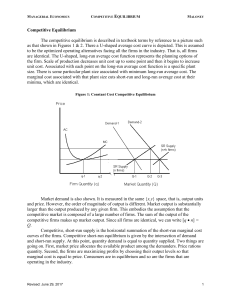
Competitive Equilibrium
... consequence, new firms and new capital will be attracted to the industry. If economic profits are negative, then stockholders receive less than they had expected and to the extent possible capital will move out of the industry. ...
... consequence, new firms and new capital will be attracted to the industry. If economic profits are negative, then stockholders receive less than they had expected and to the extent possible capital will move out of the industry. ...
ECON-1.31-2.1.12 Demand Intro
... at $30, which ticket price brings in more total revenue? If players salaries go up from $300,000 to $325,000 per game what price would you sell your tickets at? The attendance numbers from above still apply. What do you think might cause ticket prices to go up? ...
... at $30, which ticket price brings in more total revenue? If players salaries go up from $300,000 to $325,000 per game what price would you sell your tickets at? The attendance numbers from above still apply. What do you think might cause ticket prices to go up? ...
Supply ch03(CFO)
... to a new relationship between quantity supplied of a good and the price of that good. The shift is brought about by a change in the factors that affect the firm’s cost. price of capital (equipment, building and financing/interest rate costs) price of labor (wage rates, executive compensation, health ...
... to a new relationship between quantity supplied of a good and the price of that good. The shift is brought about by a change in the factors that affect the firm’s cost. price of capital (equipment, building and financing/interest rate costs) price of labor (wage rates, executive compensation, health ...
Chap 014 Micro Colander 8e
... • A perfectly competitive market is a market in which economic forces operate unimpeded • For a market to be perfectly competitive, six conditions must be met: 1. Both buyers and sellers are price takers – a price taker is a firm or individual who takes the price determined by market supply and dema ...
... • A perfectly competitive market is a market in which economic forces operate unimpeded • For a market to be perfectly competitive, six conditions must be met: 1. Both buyers and sellers are price takers – a price taker is a firm or individual who takes the price determined by market supply and dema ...
Chapter 3: Understanding Individual Markets: Demand and Supply
... supply due to change in determinants of supply. Supply and Demand: Market Equilibrium A. Review the text example, Table 3-8, which combines data from supply and demand schedules for corn. B. Have students find the point where quantity supplied equals the quantity demanded, and note this equilibrium ...
... supply due to change in determinants of supply. Supply and Demand: Market Equilibrium A. Review the text example, Table 3-8, which combines data from supply and demand schedules for corn. B. Have students find the point where quantity supplied equals the quantity demanded, and note this equilibrium ...
Exam #2
... C) how sensitive the quantity demanded is to changes in demand. D) the responsiveness of the quantity demanded to changes in price. 2) If a rightward shift of the supply curve causes a 6 percent decrease in the price and a 5 percent increase in the quantity demanded, the price elasticity of demand i ...
... C) how sensitive the quantity demanded is to changes in demand. D) the responsiveness of the quantity demanded to changes in price. 2) If a rightward shift of the supply curve causes a 6 percent decrease in the price and a 5 percent increase in the quantity demanded, the price elasticity of demand i ...
Solutions - UBC Math
... Elasticity of Demand Problems MATH 104 and Math 184 October 18, 2015 1. The current toll for the use of a highway is $2.50. Drivers use this highway because of its convenience even though there are other routes that are free. The provincial government does a study that determines that a toll of p do ...
... Elasticity of Demand Problems MATH 104 and Math 184 October 18, 2015 1. The current toll for the use of a highway is $2.50. Drivers use this highway because of its convenience even though there are other routes that are free. The provincial government does a study that determines that a toll of p do ...
Supply
... available in the market and a person may not necessarily need them in his or her daily life. ...
... available in the market and a person may not necessarily need them in his or her daily life. ...
Lecture Notes: Econ 203 Introductory Microeconomics Lecture 1: 10
... • Accounting profit is revenue less cash outlays; economic profit is revenue less all (explicit and implicit) costs • Production function shows relationship between inputs and output. • Marginal production is the increase in output coming from one additional input. Labor is the most common example. ...
... • Accounting profit is revenue less cash outlays; economic profit is revenue less all (explicit and implicit) costs • Production function shows relationship between inputs and output. • Marginal production is the increase in output coming from one additional input. Labor is the most common example. ...
AP Micro 4-3 Monopolistic Competition
... competitive firm in long-run equilibrium. If this firm were to realize productive efficiency, it would: A) have more economic profit. B) have a loss. C) also achieve allocative efficiency. D) be under producing. E) be in long-run equilibrium. ...
... competitive firm in long-run equilibrium. If this firm were to realize productive efficiency, it would: A) have more economic profit. B) have a loss. C) also achieve allocative efficiency. D) be under producing. E) be in long-run equilibrium. ...
File
... If a product increases in popularity, what effect will that have on the price of the product? Then, what effect will that price change have on the marginal revenue product of workers in that industry, all else equal? 8. Draw a side-by-side graph of a perfectly competitive labor market and firm. Be s ...
... If a product increases in popularity, what effect will that have on the price of the product? Then, what effect will that price change have on the marginal revenue product of workers in that industry, all else equal? 8. Draw a side-by-side graph of a perfectly competitive labor market and firm. Be s ...
Mr. Mayer AP Macroeconomics
... increase and the supply of bananas will decrease – If auto manufacturers can make more money selling SUV’s instead of sedans, then the supply of SUV’s will increase while the supply of sedans will decrease ...
... increase and the supply of bananas will decrease – If auto manufacturers can make more money selling SUV’s instead of sedans, then the supply of SUV’s will increase while the supply of sedans will decrease ...
Economic equilibrium

In economics, economic equilibrium is a state where economic forces such as supply and demand are balanced and in the absence of external influences the (equilibrium) values of economic variables will not change. For example, in the standard text-book model of perfect competition, equilibrium occurs at the point at which quantity demanded and quantity supplied are equal. Market equilibrium in this case refers to a condition where a market price is established through competition such that the amount of goods or services sought by buyers is equal to the amount of goods or services produced by sellers. This price is often called the competitive price or market clearing price and will tend not to change unless demand or supply changes and the quantity is called ""competitive quantity"" or market clearing quantity.