Supply and Demand Curves
... Demand, in economic terms, shows how much of a product consumers are willing to purchase, at different price points, during a certain time period. After all, we all have limited resources, and we all have to decide what we're willing and able to purchase - and at what price. As an example, let's loo ...
... Demand, in economic terms, shows how much of a product consumers are willing to purchase, at different price points, during a certain time period. After all, we all have limited resources, and we all have to decide what we're willing and able to purchase - and at what price. As an example, let's loo ...
Competition
... IMPLICATION: Firm & Market have different elasticities. Separate Firm and Market graphs needed ...
... IMPLICATION: Firm & Market have different elasticities. Separate Firm and Market graphs needed ...
Ch. 5: EFFICIENCY AND EQUITY
... units of the good where MB>P • The MB curve will be identical to the consumer’s demand curve. • Market demand curve is summation of individual MB curves ...
... units of the good where MB>P • The MB curve will be identical to the consumer’s demand curve. • Market demand curve is summation of individual MB curves ...
Civics and Economics
... Students will review economic vocabulary by creating their own Word Wall terms. Evaluation Students will take an Economic Systems test. Closure Students will complete their classroom exit cards and answer the following questions: What did I learn? What did I not understand? What do I need to review? ...
... Students will review economic vocabulary by creating their own Word Wall terms. Evaluation Students will take an Economic Systems test. Closure Students will complete their classroom exit cards and answer the following questions: What did I learn? What did I not understand? What do I need to review? ...
Microeconomics I
... c. The marginal rate of technical substitution equals the relative prices d. The difference between fixed and variable costs is equal zero. ...
... c. The marginal rate of technical substitution equals the relative prices d. The difference between fixed and variable costs is equal zero. ...
Exam 1 Spring 2004
... By how much would the poultry tax reduce consumer surplus + producer surplus? (2 points) An alternative to the excise tax is for the buyers and sellers to simply pay the government money. How much money would buyers and sellers as a group be willing to pay instead of having the tax? (1 point) The lo ...
... By how much would the poultry tax reduce consumer surplus + producer surplus? (2 points) An alternative to the excise tax is for the buyers and sellers to simply pay the government money. How much money would buyers and sellers as a group be willing to pay instead of having the tax? (1 point) The lo ...
Concordia University
... (ii) Then, take into account the case of Fidel. What is the opportunity cost of packing one brat for Fidel? And what is the opportunity cost of packing one pizza for Fidel? (2 marks) If Fidel packs 75 brats in a given hour, then he would have missed the chance of packing 75 pizzas in that same hour. ...
... (ii) Then, take into account the case of Fidel. What is the opportunity cost of packing one brat for Fidel? And what is the opportunity cost of packing one pizza for Fidel? (2 marks) If Fidel packs 75 brats in a given hour, then he would have missed the chance of packing 75 pizzas in that same hour. ...
THE OPERATION OF HIGHLY COMPETITIVE INDUSTRIES
... But now suppose that something causes the supply curve to shift right—perhaps wages fall or productivity grows. As before, the old equilibrium of $7 and 325 is no longer where the demand curve D and the new supply curve (S1) intersect. In particular, at the old price of $7 we now have a surplus. At ...
... But now suppose that something causes the supply curve to shift right—perhaps wages fall or productivity grows. As before, the old equilibrium of $7 and 325 is no longer where the demand curve D and the new supply curve (S1) intersect. In particular, at the old price of $7 we now have a surplus. At ...
Ethics in the Marketplace
... markets attract resources when demand is high and drives them away when demand is low, so resources are allocated efficiently. • Perfectly competitive markets encourage firms to use resources efficiently to keep costs low and profits high. • Perfectly competitive markets let consumers buy the most s ...
... markets attract resources when demand is high and drives them away when demand is low, so resources are allocated efficiently. • Perfectly competitive markets encourage firms to use resources efficiently to keep costs low and profits high. • Perfectly competitive markets let consumers buy the most s ...
utils - McGraw Hill Higher Education
... Suppose it must decide whether to buy its own copier or send out to a copy shop such as Kinko’s. – If the business buys a copier, it needs to lay out the upfront cost, as well as for toner and paper. – To make a decision, it needs to know the actual cost of the machine and the price of a copy. – The ...
... Suppose it must decide whether to buy its own copier or send out to a copy shop such as Kinko’s. – If the business buys a copier, it needs to lay out the upfront cost, as well as for toner and paper. – To make a decision, it needs to know the actual cost of the machine and the price of a copy. – The ...
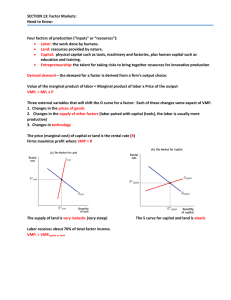
SECTION 13: Factor Markets: Need to Know: Four factors of production (“inputs” or “resources”):
... wage takers ‐ additional cost of hiring the next unit of labor, or marginal factor cost of labor (MFCL) was constant and equal to the wage (supply of labor was a horizontal line at the market wage) Monopsony – a market in which there is only one buyer; in the labor market it must offer higher and ...
... wage takers ‐ additional cost of hiring the next unit of labor, or marginal factor cost of labor (MFCL) was constant and equal to the wage (supply of labor was a horizontal line at the market wage) Monopsony – a market in which there is only one buyer; in the labor market it must offer higher and ...
Learning Area
... The learner will be able to demonstrate knowledge and understanding of the economic cycle within the context of ‘the economic problem’. Assessment Standard We know this when the learner: 1.3: Illustrates by means of a graph and discusses how demand and supply influence prices. Learning Space: Assess ...
... The learner will be able to demonstrate knowledge and understanding of the economic cycle within the context of ‘the economic problem’. Assessment Standard We know this when the learner: 1.3: Illustrates by means of a graph and discusses how demand and supply influence prices. Learning Space: Assess ...
rci.rutgers.edu - Rutgers University
... demanded of hot dogs falls, thus reducing the demand for ketchup, causing both price and quantity of ketchup to fall. Since the quantity of ketchup falls, the demand for tomatoes by ketchup producers falls, so both price and quantity of tomatoes fall. When the price of tomatoes falls, producers of ...
... demanded of hot dogs falls, thus reducing the demand for ketchup, causing both price and quantity of ketchup to fall. Since the quantity of ketchup falls, the demand for tomatoes by ketchup producers falls, so both price and quantity of tomatoes fall. When the price of tomatoes falls, producers of ...
Econ 1102: Principles of Macroeconomics
... b. Calculate your income elasticity of demand as your income increases from $10,000 to $12,000 if (i) the price is $12 (2 Pts.), and (ii) the price is $16. (2 Pts.) ...
... b. Calculate your income elasticity of demand as your income increases from $10,000 to $12,000 if (i) the price is $12 (2 Pts.), and (ii) the price is $16. (2 Pts.) ...
Principles of Economics
... •Indifference curve is a curve that connects all the baskets (combinations) of goods that give the same value of pleasure to a consumer. •Its slope is Marginal rate of substitution MRS which tells what is the amount of good Y a consumer is willing to give up in order to get additional unit of X stay ...
... •Indifference curve is a curve that connects all the baskets (combinations) of goods that give the same value of pleasure to a consumer. •Its slope is Marginal rate of substitution MRS which tells what is the amount of good Y a consumer is willing to give up in order to get additional unit of X stay ...
Basic Need, Merit, or Economic Good
... • Public goods: have a low subtractability and a low excludability • Private goods: have a high market potential because of their high levels of excludability and subtractability ...
... • Public goods: have a low subtractability and a low excludability • Private goods: have a high market potential because of their high levels of excludability and subtractability ...
Microeconomics Ⅱ
... 11. Which of the following is the distinguishing characteristic of oligopoly? a. There is relatively easy entry into and exit from oligopolistic industries. b. There will be no attempt at product differentiation in oligopolies. c. There are a large number of firms in an oligopolistic industry. d. Fi ...
... 11. Which of the following is the distinguishing characteristic of oligopoly? a. There is relatively easy entry into and exit from oligopolistic industries. b. There will be no attempt at product differentiation in oligopolies. c. There are a large number of firms in an oligopolistic industry. d. Fi ...
oligopoly
... undercut this price by a single penny, the total industry profits would change only by a very small amount (since P changes very little, total Q changes very little, which implies that total costs change very little). But the firm that undercut the price would earn all of the industry profits, and n ...
... undercut this price by a single penny, the total industry profits would change only by a very small amount (since P changes very little, total Q changes very little, which implies that total costs change very little). But the firm that undercut the price would earn all of the industry profits, and n ...
The Laws of Supply and Demand - Elizabethtown Area School
... What is “equilibrium”? • Equilibrium is when quantity supplied and quantity demanded are equal – Perfection!!!! ...
... What is “equilibrium”? • Equilibrium is when quantity supplied and quantity demanded are equal – Perfection!!!! ...
Economic equilibrium

In economics, economic equilibrium is a state where economic forces such as supply and demand are balanced and in the absence of external influences the (equilibrium) values of economic variables will not change. For example, in the standard text-book model of perfect competition, equilibrium occurs at the point at which quantity demanded and quantity supplied are equal. Market equilibrium in this case refers to a condition where a market price is established through competition such that the amount of goods or services sought by buyers is equal to the amount of goods or services produced by sellers. This price is often called the competitive price or market clearing price and will tend not to change unless demand or supply changes and the quantity is called ""competitive quantity"" or market clearing quantity.