Worksheet on Elasticity
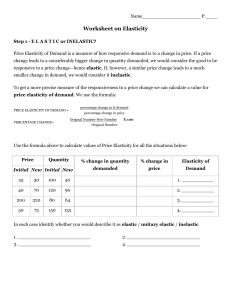
... Worksheet on Elasticity Step 1 - E L A S T I C or INELASTIC? Price Elasticity of Demand is a measure of how responsive demand is to a change in price. If a price change leads to a considerably bigger change in quantity demanded, we would consider the good to be responsive to a price change—hence ela ...
... Worksheet on Elasticity Step 1 - E L A S T I C or INELASTIC? Price Elasticity of Demand is a measure of how responsive demand is to a change in price. If a price change leads to a considerably bigger change in quantity demanded, we would consider the good to be responsive to a price change—hence ela ...
Free Sample
... inferior goods. Good examples of inferior goods are second-hand clothing and food such as Spam, ramen noodles, macaroni and cheese, and peanut butter and jelly. The example used in the text is a tooth extraction. Ask the students to come up with other examples of inferior goods as they have better a ...
... inferior goods. Good examples of inferior goods are second-hand clothing and food such as Spam, ramen noodles, macaroni and cheese, and peanut butter and jelly. The example used in the text is a tooth extraction. Ask the students to come up with other examples of inferior goods as they have better a ...
Downlaod File
... The law of supply is a fundamental principal of economic theory, which is that quantities respond in the same direction as price changes. In other words, the law of supply states that (all other things unchanged) an increase in price results in an increase in quantity supplied. This means that produ ...
... The law of supply is a fundamental principal of economic theory, which is that quantities respond in the same direction as price changes. In other words, the law of supply states that (all other things unchanged) an increase in price results in an increase in quantity supplied. This means that produ ...
Lecture 26: The Labour Market
... horizontal axis... • ... and total Costs total and total revenues on the vertical axis. • Let us assume we are in a short period with fixed costs equal to 5, and the wage fixed at 1 per unit. ...
... horizontal axis... • ... and total Costs total and total revenues on the vertical axis. • Let us assume we are in a short period with fixed costs equal to 5, and the wage fixed at 1 per unit. ...
Question 1 Economists tend to focus on one structural aspect of
... have stayed about the same for most firms. have become razor thin for many producers. are not important since this industry is in the nonprofit sector. 4 points Question 8 Using the linear approximation system to estimate the profit maximizing price requires that the managers know the costs of produ ...
... have stayed about the same for most firms. have become razor thin for many producers. are not important since this industry is in the nonprofit sector. 4 points Question 8 Using the linear approximation system to estimate the profit maximizing price requires that the managers know the costs of produ ...
ECON 203 - Baton Rouge Community College
... 2. Use demand and supply to describe the allocative function of prices and markets; 3. Explain macroeconomic goals, economic measurement and problems created by the business cycle; 4. Define aggregate demand, supply and the causes of changes in macroeconomic equilibrium; 5. Explain monetary and fisc ...
... 2. Use demand and supply to describe the allocative function of prices and markets; 3. Explain macroeconomic goals, economic measurement and problems created by the business cycle; 4. Define aggregate demand, supply and the causes of changes in macroeconomic equilibrium; 5. Explain monetary and fisc ...
ECONOMICS SOLUT IONS
... than goods that are necessities. For example the demand for maize is inelastic because maize is a necessity and the quantity that people buy is not very much dependent on its price. Tickets for a concert are a luxury, so the demand for concert tickets is much more elastic than the demand for maize. ...
... than goods that are necessities. For example the demand for maize is inelastic because maize is a necessity and the quantity that people buy is not very much dependent on its price. Tickets for a concert are a luxury, so the demand for concert tickets is much more elastic than the demand for maize. ...
Price
... price rises and sellers’ costs do not, profit per unit rises, and they want to produce and sell more if price falls and sellers’ costs do not, profit per unit falls, and they want to produce and sell less ...
... price rises and sellers’ costs do not, profit per unit rises, and they want to produce and sell more if price falls and sellers’ costs do not, profit per unit falls, and they want to produce and sell less ...
Managerial Economics in a Global Economy
... QdX = quantity demanded of commodity X by an individual per time period PX = price per unit of commodity X I = consumer’s income PY = price of related (substitute or complementary) commodity T = tastes of the consumer ...
... QdX = quantity demanded of commodity X by an individual per time period PX = price per unit of commodity X I = consumer’s income PY = price of related (substitute or complementary) commodity T = tastes of the consumer ...
Workshop 5
... To which of the above four categories do the following apply to the member firms? (There can be more than one market category in each case.) (a) Firms face a downward sloping demand curve. ..................................................................... (b) New firms can freely enter the indust ...
... To which of the above four categories do the following apply to the member firms? (There can be more than one market category in each case.) (a) Firms face a downward sloping demand curve. ..................................................................... (b) New firms can freely enter the indust ...
Ch. 7 Market Structures
... demand set the equilibrium price, and each firm sets a level of output that will maximize its profits at that price. • Imperfect competition refers to market structures that lack one or more of the five conditions of perfect competition ...
... demand set the equilibrium price, and each firm sets a level of output that will maximize its profits at that price. • Imperfect competition refers to market structures that lack one or more of the five conditions of perfect competition ...
Chapter 1: The Labor Market
... • Describe re-equilibrating process by changing C.P. factor: – Increase in income causes increase in demand (shift D rightward) – At old P, Qd greater than Qs: so individuals bid up price till reach new ...
... • Describe re-equilibrating process by changing C.P. factor: – Increase in income causes increase in demand (shift D rightward) – At old P, Qd greater than Qs: so individuals bid up price till reach new ...
Chapter 8
... What is So Perfect about Perfect Competition? MC is cost of producing the marginal (last) unit. P is value to buyers of the marginal (last) unit. ...
... What is So Perfect about Perfect Competition? MC is cost of producing the marginal (last) unit. P is value to buyers of the marginal (last) unit. ...
Practice Quiz
... Topic: Perfect competition, Difficulty: D, Type: RE, Answer: d If a firm has no ability to select the price of its product, it: a. will go out of business due to losses. b. is a price-maker. c. cannot maximize profit. d. has a horizontal individual demand curve. Topic: Price taker, Difficulty: D, Ty ...
... Topic: Perfect competition, Difficulty: D, Type: RE, Answer: d If a firm has no ability to select the price of its product, it: a. will go out of business due to losses. b. is a price-maker. c. cannot maximize profit. d. has a horizontal individual demand curve. Topic: Price taker, Difficulty: D, Ty ...
Economic equilibrium

In economics, economic equilibrium is a state where economic forces such as supply and demand are balanced and in the absence of external influences the (equilibrium) values of economic variables will not change. For example, in the standard text-book model of perfect competition, equilibrium occurs at the point at which quantity demanded and quantity supplied are equal. Market equilibrium in this case refers to a condition where a market price is established through competition such that the amount of goods or services sought by buyers is equal to the amount of goods or services produced by sellers. This price is often called the competitive price or market clearing price and will tend not to change unless demand or supply changes and the quantity is called ""competitive quantity"" or market clearing quantity.