File
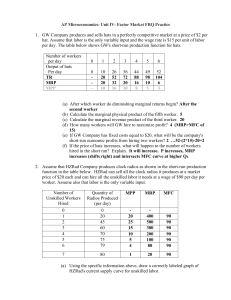
... The table above gives the short-run marginal revenue product of labor per day for a perfectly competitive firm. The firm is currently selling its product at the market price of $5. (a) Calculate the marginal (physical) product of the third worker. 90; 450 = 90 * 5 (RP = MPP * P) (b) Define the law o ...
... The table above gives the short-run marginal revenue product of labor per day for a perfectly competitive firm. The firm is currently selling its product at the market price of $5. (a) Calculate the marginal (physical) product of the third worker. 90; 450 = 90 * 5 (RP = MPP * P) (b) Define the law o ...
Supply and Demand: Demand and Equilibrium
... E. None of the Above You take the slope-weighted average of the two zero quantity prices, 10 and 100. • That means you are 2/9 of the way from one ZQ value to the other • Which one is it? The demanders don’t care much about higher prices, so that means they have less bargaining power—and to the equi ...
... E. None of the Above You take the slope-weighted average of the two zero quantity prices, 10 and 100. • That means you are 2/9 of the way from one ZQ value to the other • Which one is it? The demanders don’t care much about higher prices, so that means they have less bargaining power—and to the equi ...
Parallel Questions
... because as output increases the average total costs falls. There are high fixed costs to producing a newspaper (writing it, including photos and ads, checking copy, and laying out articles). But once the newspaper is written and ready to be printed, these high fixed costs can be spread over a large ...
... because as output increases the average total costs falls. There are high fixed costs to producing a newspaper (writing it, including photos and ads, checking copy, and laying out articles). But once the newspaper is written and ready to be printed, these high fixed costs can be spread over a large ...
PLC unit 1 fall econ
... SSEMI2 The student will explain how the Law of Demand, the Law of Supply, prices, and profits work to determine production and distribution in a market economy. a. Define the Law of Supply and the Law of Demand. b. Describe the role of buyers and sellers in determining market clearing price. c. Illu ...
... SSEMI2 The student will explain how the Law of Demand, the Law of Supply, prices, and profits work to determine production and distribution in a market economy. a. Define the Law of Supply and the Law of Demand. b. Describe the role of buyers and sellers in determining market clearing price. c. Illu ...
IR‐LWHN‐NLH‐008 NLH 2013 Interim Rates Application Page 1 of 1 Q.
... of the quantity demanded of a good or service to a change in its price. The price ...
... of the quantity demanded of a good or service to a change in its price. The price ...
Kinked Demand Curve
... Sweezy’s 1942 contribution. Samuelson immortalized it. The “young” oligopoly case. The industry starts out with price wars and gravitates toward “sticky prices.” ...
... Sweezy’s 1942 contribution. Samuelson immortalized it. The “young” oligopoly case. The industry starts out with price wars and gravitates toward “sticky prices.” ...
Review of Microeconomics
... scarcity, we mean constraints on an individual’s wealth or income, but also on his or her time, knowledge, or information. An economic theory of decision making assumes that individuals act rationally in the sense that they make decisions that best promote their well-being (however that is defined) ...
... scarcity, we mean constraints on an individual’s wealth or income, but also on his or her time, knowledge, or information. An economic theory of decision making assumes that individuals act rationally in the sense that they make decisions that best promote their well-being (however that is defined) ...
PROBLEMS
... If Starbucks doubled its price, while all other firms kept their price the same, their sales would fall by much more than 30 percent. The response would be much larger in this case because there are many substitutes to Starbucks’ coffee. If only Starbucks changed its price, people would switch to su ...
... If Starbucks doubled its price, while all other firms kept their price the same, their sales would fall by much more than 30 percent. The response would be much larger in this case because there are many substitutes to Starbucks’ coffee. If only Starbucks changed its price, people would switch to su ...
Elasticity of Demand Notes
... you of being cheap, explain the Price Elasticity of Demand to them (its not as nerdy as you think) and why chivalry isn’t dead…its just more of an elastic concept and that sometimes fast food can be just as romantic if you just put some thought behind it. P.S. The pizza idea is a registered trademar ...
... you of being cheap, explain the Price Elasticity of Demand to them (its not as nerdy as you think) and why chivalry isn’t dead…its just more of an elastic concept and that sometimes fast food can be just as romantic if you just put some thought behind it. P.S. The pizza idea is a registered trademar ...
Assessment Schedule – 2012
... For any unit before Qe, MR is greater than MC so marginal profits are made so we will produce these units as our profits will rise. For any unit after Qe, MC>MR so marginal losses are made, so we will not be willing to produce these. We maximise profits at Qe where MC = MR. In the long run, the firm ...
... For any unit before Qe, MR is greater than MC so marginal profits are made so we will produce these units as our profits will rise. For any unit after Qe, MC>MR so marginal losses are made, so we will not be willing to produce these. We maximise profits at Qe where MC = MR. In the long run, the firm ...
lec5+tutorial - TCD Maths home
... A plot of P a bQ with a 100 and b 0.5 is shown below. Example The demand function is given by P 100 0.5Q . (a) Find the slope and intercepts of P 100 0.5Q .(b) Plot P 100 0.5Q for 0 Q 220 (c) What is the quantity demanded when(i) P 5 ? (ii) P 20 ? (d) Find an expression ...
... A plot of P a bQ with a 100 and b 0.5 is shown below. Example The demand function is given by P 100 0.5Q . (a) Find the slope and intercepts of P 100 0.5Q .(b) Plot P 100 0.5Q for 0 Q 220 (c) What is the quantity demanded when(i) P 5 ? (ii) P 20 ? (d) Find an expression ...
Chapter 8
... price. • Sum SR supply curves for firms using horizontal summation. • That is: at each possible price, sum up total quantity supplied by each firm. • See Figure 8.9. • (Note that we are assuming that, for each firm, as q es, individual MC curves no .). ...
... price. • Sum SR supply curves for firms using horizontal summation. • That is: at each possible price, sum up total quantity supplied by each firm. • See Figure 8.9. • (Note that we are assuming that, for each firm, as q es, individual MC curves no .). ...
LESSON 6.3 Market Efficiency and Gains from Exchange
... firm produces at the lowest possible cost per unit. Allocative efficiency occurs when firms produce the output that is most valued by consumers. ...
... firm produces at the lowest possible cost per unit. Allocative efficiency occurs when firms produce the output that is most valued by consumers. ...
here
... exceeds the quantity that buyers are willing and able to purchase. The resulting surplus will put downward pressure on the price, pushing it back toward the equilibrium. Likewise, if the price falls below the equilibrium price, the quantity demanded exceeds the quantity supplied. The resulting short ...
... exceeds the quantity that buyers are willing and able to purchase. The resulting surplus will put downward pressure on the price, pushing it back toward the equilibrium. Likewise, if the price falls below the equilibrium price, the quantity demanded exceeds the quantity supplied. The resulting short ...
Economic equilibrium

In economics, economic equilibrium is a state where economic forces such as supply and demand are balanced and in the absence of external influences the (equilibrium) values of economic variables will not change. For example, in the standard text-book model of perfect competition, equilibrium occurs at the point at which quantity demanded and quantity supplied are equal. Market equilibrium in this case refers to a condition where a market price is established through competition such that the amount of goods or services sought by buyers is equal to the amount of goods or services produced by sellers. This price is often called the competitive price or market clearing price and will tend not to change unless demand or supply changes and the quantity is called ""competitive quantity"" or market clearing quantity.























