Quiz 6
... ice cream and yogurt. Therefore, Susan’s demand for ice cream is more elastic than Carol’s demand for ice cream. _____2) For the elasticity of demand, if we increase the amount of response time, elasticity increases. _____3) Suppose cell phones have an income elasticity of demand (Yd) equal to 3.25. ...
... ice cream and yogurt. Therefore, Susan’s demand for ice cream is more elastic than Carol’s demand for ice cream. _____2) For the elasticity of demand, if we increase the amount of response time, elasticity increases. _____3) Suppose cell phones have an income elasticity of demand (Yd) equal to 3.25. ...
S 11 Practice MC Test
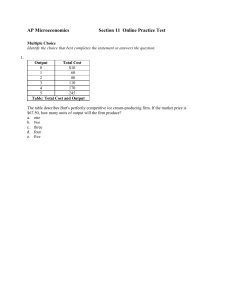
... a. minimize its losses by shutting down. b. minimize its losses by continuing to produce. c. break even. d. earn an economic profit. e. exit the market in the long run. ...
... a. minimize its losses by shutting down. b. minimize its losses by continuing to produce. c. break even. d. earn an economic profit. e. exit the market in the long run. ...
Microeconomics: Supply and Demand
... quantity demanded. There are two types: Elastic and Inelastic Demand Elastic- when a small change in a good’s price causes a major, opposite change in the quantity demanded Inelastic- when a change in a good’s price has little impact on the quantity demanded ...
... quantity demanded. There are two types: Elastic and Inelastic Demand Elastic- when a small change in a good’s price causes a major, opposite change in the quantity demanded Inelastic- when a change in a good’s price has little impact on the quantity demanded ...
Problem Set 1
... a. Suppose the government imposes a binding price floor in the cheese market. Use a supply-anddemand diagram to show the effect of this policy on the price of cheese and the quantity of cheese sold. Is there a shortage or surplus of cheese? (Answer: you can do it by yourself). b. Farmers complain th ...
... a. Suppose the government imposes a binding price floor in the cheese market. Use a supply-anddemand diagram to show the effect of this policy on the price of cheese and the quantity of cheese sold. Is there a shortage or surplus of cheese? (Answer: you can do it by yourself). b. Farmers complain th ...
Microeconomics Review 1
... 5. Rule: No monopoly will produce where the demand for a good is inelastic 6. Monopolies will price discriminate if they know the elasticity of demand for their customers. Cournot Model: each firm takes the other firm’s output as fixed. Bertrand Model: each firm takes the other firms prices as fixed ...
... 5. Rule: No monopoly will produce where the demand for a good is inelastic 6. Monopolies will price discriminate if they know the elasticity of demand for their customers. Cournot Model: each firm takes the other firm’s output as fixed. Bertrand Model: each firm takes the other firms prices as fixed ...
Economics 101 L
... a) Is a firm in a competitive industry considered a price taker or a price setter? Explain what this means. Price taker. This means that the firm does not have any power to set the price for the good in the market. Whatever price the market determines is the price that the firm must charge. b) Is a ...
... a) Is a firm in a competitive industry considered a price taker or a price setter? Explain what this means. Price taker. This means that the firm does not have any power to set the price for the good in the market. Whatever price the market determines is the price that the firm must charge. b) Is a ...
Price Elasticity of Supply
... demand - supply will be elastic. Conversely when stocks are low, dwindling supplies force prices higher because of scarcity (3) The ease and cost of factor substitution/mobility: If both capital and labour are occupationally mobile then the elasticity of supply for a product is higher than if capita ...
... demand - supply will be elastic. Conversely when stocks are low, dwindling supplies force prices higher because of scarcity (3) The ease and cost of factor substitution/mobility: If both capital and labour are occupationally mobile then the elasticity of supply for a product is higher than if capita ...
HW #2 Solutions
... The explanation is most easily achieved with the aid of a graph such as Figure 3.3, which shows two indifference curves intersecting at point A. We know from the definition of an indifference curve that a consumer has the same level of utility along any given curve. In this case, the consumer is ind ...
... The explanation is most easily achieved with the aid of a graph such as Figure 3.3, which shows two indifference curves intersecting at point A. We know from the definition of an indifference curve that a consumer has the same level of utility along any given curve. In this case, the consumer is ind ...
Answers to First Midterm
... a. The economic incidence of the tax will fall solely on producers of this good and the deadweight loss due to this tax will be equal to zero. b. The economic incidence of the tax will fall solely on consumers of this good and the deadweight loss due to this tax will be equal to zero. c. The economi ...
... a. The economic incidence of the tax will fall solely on producers of this good and the deadweight loss due to this tax will be equal to zero. b. The economic incidence of the tax will fall solely on consumers of this good and the deadweight loss due to this tax will be equal to zero. c. The economi ...
Markets Exercise #5 Answers
... Suppose instead that the government wanted to make sure that farmers had enough income by controlling the quantity produced. Given the original equilibrium price and quantity, would it select an imposed quantity of 890 or 850? 850. Why? Lower production means a higher price and since demand is inela ...
... Suppose instead that the government wanted to make sure that farmers had enough income by controlling the quantity produced. Given the original equilibrium price and quantity, would it select an imposed quantity of 890 or 850? 850. Why? Lower production means a higher price and since demand is inela ...
Answer the following 20 multiple choice questions. Each question is
... (c) Microland has recently experienced some type of technological breakthrough. (d) Microland has overcome the problem of scarcity. 3. A society can produce two goods: bread and cookies. The society's production possibility frontier is negatively sloped and "bowed outward" from the origin. As this s ...
... (c) Microland has recently experienced some type of technological breakthrough. (d) Microland has overcome the problem of scarcity. 3. A society can produce two goods: bread and cookies. The society's production possibility frontier is negatively sloped and "bowed outward" from the origin. As this s ...
Elasticity of Demand
... product even at the higher price while some customers will stop buying the product. A decrease in price leads to no change in total revenue as your current customers will now be paying a lower price, but this will be offset by the new customers you will gain who will start buying your product. ...
... product even at the higher price while some customers will stop buying the product. A decrease in price leads to no change in total revenue as your current customers will now be paying a lower price, but this will be offset by the new customers you will gain who will start buying your product. ...
Supply - Cobb Learning
... A fall in input prices makes production more profitable at each output price, so firms supply a larger quantity at each price, and the S curve shifts to the right. ...
... A fall in input prices makes production more profitable at each output price, so firms supply a larger quantity at each price, and the S curve shifts to the right. ...
Mr. Maurer Name: ____________________________ AP Economics
... The John Lamb Company, a profit-maximizing firm producing widgets, is in a perfectly competitive widget market. Assume John Lamb employs a fixed number of employees and rents a machine for a variable number of hours from a perfectly competitive market. (a) Using correctly labeled side-by-side graphs ...
... The John Lamb Company, a profit-maximizing firm producing widgets, is in a perfectly competitive widget market. Assume John Lamb employs a fixed number of employees and rents a machine for a variable number of hours from a perfectly competitive market. (a) Using correctly labeled side-by-side graphs ...
Economic equilibrium

In economics, economic equilibrium is a state where economic forces such as supply and demand are balanced and in the absence of external influences the (equilibrium) values of economic variables will not change. For example, in the standard text-book model of perfect competition, equilibrium occurs at the point at which quantity demanded and quantity supplied are equal. Market equilibrium in this case refers to a condition where a market price is established through competition such that the amount of goods or services sought by buyers is equal to the amount of goods or services produced by sellers. This price is often called the competitive price or market clearing price and will tend not to change unless demand or supply changes and the quantity is called ""competitive quantity"" or market clearing quantity.