15A.H Supply and Demand
... Have students complete the attached Supply and Demand Worksheet. Evaluate each student’s work using the Social Science Rubric as follows, and add the scores to determine the ...
... Have students complete the attached Supply and Demand Worksheet. Evaluate each student’s work using the Social Science Rubric as follows, and add the scores to determine the ...
Document
... • As P rises, firms with lower costs enter the market before those with higher costs. • Further increases in P make it worthwhile for higher-cost firms to enter the market, which increases market quantity supplied. • Hence, LR market supply curve slopes upward. • At any P, ...
... • As P rises, firms with lower costs enter the market before those with higher costs. • Further increases in P make it worthwhile for higher-cost firms to enter the market, which increases market quantity supplied. • Hence, LR market supply curve slopes upward. • At any P, ...
Chapter 1
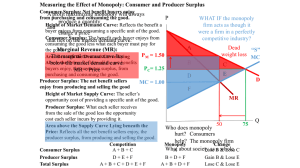
... One seller (but many buyers), one product (no substitutes), there are barriers to entry and price maker The monopolist is the supply-side of the market and has complete control over the amount offered for sale. Monopolist controls price but must consider consumer demand Profits will be maxim ...
... One seller (but many buyers), one product (no substitutes), there are barriers to entry and price maker The monopolist is the supply-side of the market and has complete control over the amount offered for sale. Monopolist controls price but must consider consumer demand Profits will be maxim ...
Ch06 Govt actions in markets
... Everything you earn and most things you buy are taxed. Who really pays these taxes? Income tax and the social insurance taxes are deducted from your pay, and provincial sales tax and GST are added to the price of the most of the things you buy, so isn’t it obvious that you pay these taxes? Isn’t ...
... Everything you earn and most things you buy are taxed. Who really pays these taxes? Income tax and the social insurance taxes are deducted from your pay, and provincial sales tax and GST are added to the price of the most of the things you buy, so isn’t it obvious that you pay these taxes? Isn’t ...
Monopolisitic Competition PP
... a. downward-sloping; are a few b. upward-sloping; are many c. vertical; are a few d. downward-sloping; are many e. downward-sloping; one or two ...
... a. downward-sloping; are a few b. upward-sloping; are many c. vertical; are a few d. downward-sloping; are many e. downward-sloping; one or two ...
Marginal Revenue
... from a one unit change in production Intuition: We can reduce the firm’s total costs without reducing the total quantity of output produced by shifting production from the high marginal cost plant to the low marginal cost plant. Question: Can this go on indefinitely? ...
... from a one unit change in production Intuition: We can reduce the firm’s total costs without reducing the total quantity of output produced by shifting production from the high marginal cost plant to the low marginal cost plant. Question: Can this go on indefinitely? ...
Pure Exchange Economy
... In the Edgeworth box, we simply find the point on one agent’s indifference curve where the other agent reaches the highest utility. Figure 5 about here. Pareto efficient points are characterized by a tangency condition: the marginal rate of substitution must be the same for each agent. The set of Pa ...
... In the Edgeworth box, we simply find the point on one agent’s indifference curve where the other agent reaches the highest utility. Figure 5 about here. Pareto efficient points are characterized by a tangency condition: the marginal rate of substitution must be the same for each agent. The set of Pa ...
exam one -- summer 2001 - Portland State University
... E. None of the above are correct. 20. Which of the following statements is not true for a perfectly competitive firm? A. A firm’s demand curve is horizontal B. The firm can influence its demand curve by advertising its product C. The firm’s demand curve is perfectly elastic D. The market demand and ...
... E. None of the above are correct. 20. Which of the following statements is not true for a perfectly competitive firm? A. A firm’s demand curve is horizontal B. The firm can influence its demand curve by advertising its product C. The firm’s demand curve is perfectly elastic D. The market demand and ...
Competitive Firms File - Faculty of Business and Economics Courses
... Quantity Quantity (firm) (market) This entry shifts the short-run supply curve to the right from S1 to S2, as shown in panel (c). In the new long-run equilibrium, point C, price has returned to P1 but the quantity sold has increased to Q3. Profits are again zero, and price is back to the minimum of ...
... Quantity Quantity (firm) (market) This entry shifts the short-run supply curve to the right from S1 to S2, as shown in panel (c). In the new long-run equilibrium, point C, price has returned to P1 but the quantity sold has increased to Q3. Profits are again zero, and price is back to the minimum of ...
Lecture slides File - Faculty of Business and Economics Courses
... Quantity Quantity (firm) (market) This entry shifts the short-run supply curve to the right from S1 to S2, as shown in panel (c). In the new long-run equilibrium, point C, price has returned to P1 but the quantity sold has increased to Q3. Profits are again zero, and price is back to the minimum of ...
... Quantity Quantity (firm) (market) This entry shifts the short-run supply curve to the right from S1 to S2, as shown in panel (c). In the new long-run equilibrium, point C, price has returned to P1 but the quantity sold has increased to Q3. Profits are again zero, and price is back to the minimum of ...
MASTER CARDS UNIT II (MICRO ECONOMICS)
... 8- Explain how rise in the income of the consumer affect the demand of a good. Give example. Ans;- Due to increase in income there would increase in demand for the good if it is normal and demand curve shift rightward.(use rightward shift in demand curve). 9- Explain the various degrees of price ela ...
... 8- Explain how rise in the income of the consumer affect the demand of a good. Give example. Ans;- Due to increase in income there would increase in demand for the good if it is normal and demand curve shift rightward.(use rightward shift in demand curve). 9- Explain the various degrees of price ela ...
Firms will demand labor until the marginal revenue
... The MPL falls as the amount of labor employed increases. The optimum demand for labor falls where the real wage rate (w/P) is equal to the MPL. ...
... The MPL falls as the amount of labor employed increases. The optimum demand for labor falls where the real wage rate (w/P) is equal to the MPL. ...
Economic equilibrium

In economics, economic equilibrium is a state where economic forces such as supply and demand are balanced and in the absence of external influences the (equilibrium) values of economic variables will not change. For example, in the standard text-book model of perfect competition, equilibrium occurs at the point at which quantity demanded and quantity supplied are equal. Market equilibrium in this case refers to a condition where a market price is established through competition such that the amount of goods or services sought by buyers is equal to the amount of goods or services produced by sellers. This price is often called the competitive price or market clearing price and will tend not to change unless demand or supply changes and the quantity is called ""competitive quantity"" or market clearing quantity.
![2008_FRQ_[Form_B]](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/008213058_1-3bae458f2d6d341bdc2c12b0ab692eb5-300x300.png)