TIP Translation - dna
... ____ 6. Nitrogenous bases are held to the sides of the DNA ladder by a. helix bonds. c. hydrogen bonds. b. covalent bonds. d. ionic bonds. ____ 7. The first step in making a protein is a. amino acids linked together. b. transfer RNA matching mRNA. ...
... ____ 6. Nitrogenous bases are held to the sides of the DNA ladder by a. helix bonds. c. hydrogen bonds. b. covalent bonds. d. ionic bonds. ____ 7. The first step in making a protein is a. amino acids linked together. b. transfer RNA matching mRNA. ...
Dioxyribose Nucleic Acid
... code from the nucleus to the ribosomes in the cytoplasm. – When the ribosomes get the code, they can start making proteins. ...
... code from the nucleus to the ribosomes in the cytoplasm. – When the ribosomes get the code, they can start making proteins. ...
Ch. 19 – Eukaryotic Genomes
... Silencers – act like prok repressors, probably modify chromatin Coordinately controlled genes – collections of genes, that are related, are usually all expressed or all repressed, and are all transcribed together, even if they are not near on the chromosome. ...
... Silencers – act like prok repressors, probably modify chromatin Coordinately controlled genes – collections of genes, that are related, are usually all expressed or all repressed, and are all transcribed together, even if they are not near on the chromosome. ...
Ch 16 Genetics Review
... genetic code. • These chemicals act as the cell's memory, instructing it on how to synthesize enzymes and other proteins. These four nucleotides encode everything an organism needs to live and protects this information with incredible accuracy. ...
... genetic code. • These chemicals act as the cell's memory, instructing it on how to synthesize enzymes and other proteins. These four nucleotides encode everything an organism needs to live and protects this information with incredible accuracy. ...
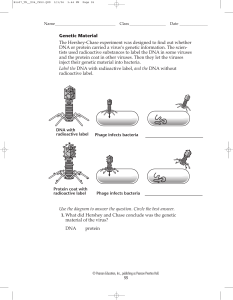
Genetic Material The Hershey-Chase experiment was designed to
... Label the DNA with radioactive label, and the DNA without radioactive label. ...
... Label the DNA with radioactive label, and the DNA without radioactive label. ...
DNA Strand 1 - Duncanville ISD
... 1. The process of making an exact copy of DNA is called _________________. 2. DNA is made of units called _________________________________. 3. The process of making a copy of RNA is called _______________________. 4. What is the function of mRNA? ...
... 1. The process of making an exact copy of DNA is called _________________. 2. DNA is made of units called _________________________________. 3. The process of making a copy of RNA is called _______________________. 4. What is the function of mRNA? ...
Microbial Genetics
... restricted to narrower temperature range • Drug resistance or sensitivity: permeability, degradation, or site of action • Morphology: change in capsule or other feature leads to change in colony • Catabolic: loss of a degradative enzyme leads to, for example, inability to ferment a carbohydrate • Vi ...
... restricted to narrower temperature range • Drug resistance or sensitivity: permeability, degradation, or site of action • Morphology: change in capsule or other feature leads to change in colony • Catabolic: loss of a degradative enzyme leads to, for example, inability to ferment a carbohydrate • Vi ...
DNA PPT - McKinney ISD Staff Sites
... two strands open at the hydrogen bonds. • The DNA molecule separates into two strands • DNA Polymerase “pastes” matching nucleotides on each half of the “unzipped” DNA. ...
... two strands open at the hydrogen bonds. • The DNA molecule separates into two strands • DNA Polymerase “pastes” matching nucleotides on each half of the “unzipped” DNA. ...
Variation exists within individuals, within populations, and among
... Examples of types of questions are given in italics Basic terminology – review terms in genetics (Hardy-Weinberg, Mendel, molecular genetics); you should not only be able to define the terms, but understand the concepts behind them Define F1, homozygote, allele, reciprocal cross, dominance A syndrom ...
... Examples of types of questions are given in italics Basic terminology – review terms in genetics (Hardy-Weinberg, Mendel, molecular genetics); you should not only be able to define the terms, but understand the concepts behind them Define F1, homozygote, allele, reciprocal cross, dominance A syndrom ...
DNA mutations 11.3 notes
... If the DNA is mutated, what will happen to the mRNA? It will take the changed info into the cytoplasm and the tRNA will bring the wrong amino acid to the rRNA. The protein will be based on the mutated ...
... If the DNA is mutated, what will happen to the mRNA? It will take the changed info into the cytoplasm and the tRNA will bring the wrong amino acid to the rRNA. The protein will be based on the mutated ...
Genetics Study Guide
... 1. What is a plant that has two dominant genes or two recessive genes called? homozygous 2. The “rungs” of the DNA ladder are made up of a pair of bases. 3. What is heredity? Traits passing from parents to offspring 4. How are sex cells different from other human cells? Sex cells have half as many c ...
... 1. What is a plant that has two dominant genes or two recessive genes called? homozygous 2. The “rungs” of the DNA ladder are made up of a pair of bases. 3. What is heredity? Traits passing from parents to offspring 4. How are sex cells different from other human cells? Sex cells have half as many c ...
Slide 1
... Restriction enzymes cleave specific DNA sequences, many of them produce ‘sticky ends” ...
... Restriction enzymes cleave specific DNA sequences, many of them produce ‘sticky ends” ...
Themes in the Development of DNA Science
... Linus Pauling uses X-ray crystallography to deduce the structure of ...
... Linus Pauling uses X-ray crystallography to deduce the structure of ...
Slide 1 - Brookwood High School
... Used to study how a trait is passed from one generation to the next Often used to track diseases or genetic disorders in a family ...
... Used to study how a trait is passed from one generation to the next Often used to track diseases or genetic disorders in a family ...
Genetic Exchange - Pennsylvania State University
... Self-replicative recombination •Transposon or IS self-replicates copy to splice into DNA at a specific target sequences. • Endonuclease activity cuts target sequence, leaving single strand overhanging ends. •Transposon is ligated to ends. • Gaps are filled by DNA polymerase to yield a target sequen ...
... Self-replicative recombination •Transposon or IS self-replicates copy to splice into DNA at a specific target sequences. • Endonuclease activity cuts target sequence, leaving single strand overhanging ends. •Transposon is ligated to ends. • Gaps are filled by DNA polymerase to yield a target sequen ...
Genetics
... Relate the concept of the gene to the sequences of nucleotides in DNA Sequence the steps involving protein synthesis Categorize the different kinds of mutations that can occur in DNA Compare the effects of different kinds of mutations on cells and organisms. ...
... Relate the concept of the gene to the sequences of nucleotides in DNA Sequence the steps involving protein synthesis Categorize the different kinds of mutations that can occur in DNA Compare the effects of different kinds of mutations on cells and organisms. ...
15 Guided Reading
... Read the assigned pages in the order that they are assigned and answer each question as you go. 15.1 Selective Breeding: Read Pages 419-420 ...
... Read the assigned pages in the order that they are assigned and answer each question as you go. 15.1 Selective Breeding: Read Pages 419-420 ...
S-strain (virulent)
... Nucleic Acids and Protein Synthesis Griffith took the 1st steps in answering whether genes are made of DNA or Protein. Used bacteria to help solve this problem. ...
... Nucleic Acids and Protein Synthesis Griffith took the 1st steps in answering whether genes are made of DNA or Protein. Used bacteria to help solve this problem. ...