S3. Effects of Mutations on Proteins – Formative
... d. All three comparisons are likely to show the same degree of sequence similarity 6) The coding DNA sequence (CDS) of a protein is given below. The nucleotides are numbered as shown. What would be the effect on the protein produces by translation of this CDS if a mutation inserted two nucleotides ( ...
... d. All three comparisons are likely to show the same degree of sequence similarity 6) The coding DNA sequence (CDS) of a protein is given below. The nucleotides are numbered as shown. What would be the effect on the protein produces by translation of this CDS if a mutation inserted two nucleotides ( ...
Mutations-Notes guide
... Name: _______________________________ Date: __________________ Hour:______ Mutations Notes (p. 239-240) 1. What are Mutations? ...
... Name: _______________________________ Date: __________________ Hour:______ Mutations Notes (p. 239-240) 1. What are Mutations? ...
Mutations Reading Guide
... Name: _______________________________ Date: __________________ Hour:______ Mutations Notes (p. 239-240) 1. What are Mutations? ...
... Name: _______________________________ Date: __________________ Hour:______ Mutations Notes (p. 239-240) 1. What are Mutations? ...
Evolutionary forces: in small populations
... Evolutionary mechanisms 1. Mutation: the only source of new genetic information. Mutation: any heritable change in the structure or amount of genetic material. Different levels of mutation DNA: point and frame shift mutations (mistakes made during DNA replication) Arrangements of DNA +/- of single ...
... Evolutionary mechanisms 1. Mutation: the only source of new genetic information. Mutation: any heritable change in the structure or amount of genetic material. Different levels of mutation DNA: point and frame shift mutations (mistakes made during DNA replication) Arrangements of DNA +/- of single ...
Evolution and Genetic Engineering Keystone Vocabulary
... 13. A decrease in genetic variation caused by the formation of a new population by a small number of indivuals from a larger population. 14. The addition (insertion mutation) or removal (deletion mutation) of one or more nucleotides that is not indivisible by three, therefore resulting in a complete ...
... 13. A decrease in genetic variation caused by the formation of a new population by a small number of indivuals from a larger population. 14. The addition (insertion mutation) or removal (deletion mutation) of one or more nucleotides that is not indivisible by three, therefore resulting in a complete ...
GENETICS
... Random changes in the sequence of nucleotides in DNA It’s a mistake that’s made during replication or transcription There are 4 types: Base Substitution Base Deletion Base Insertion Jumping Gene ...
... Random changes in the sequence of nucleotides in DNA It’s a mistake that’s made during replication or transcription There are 4 types: Base Substitution Base Deletion Base Insertion Jumping Gene ...
Genetics of AHC - Alternating Hemiplegia of Childhood Foundation
... identified in the following genes:CACNA1A, ATP1A2, SCN1A Associated with FHM, family history of migraines is usually ...
... identified in the following genes:CACNA1A, ATP1A2, SCN1A Associated with FHM, family history of migraines is usually ...
PROTEIN SYNTHESIS QUESTIONS
... 2. The template strand of a gene contains the sequence 3’ TTCAGTCGT 5’. Draw the nontemplate sequence and the mRNA sequence, indicating 5’ and 3’ ends of each. Compare the two sequences. 3. Imagine that the nontemplate sequence in question 2 was traqnscribed instead of the template sequence. Draw th ...
... 2. The template strand of a gene contains the sequence 3’ TTCAGTCGT 5’. Draw the nontemplate sequence and the mRNA sequence, indicating 5’ and 3’ ends of each. Compare the two sequences. 3. Imagine that the nontemplate sequence in question 2 was traqnscribed instead of the template sequence. Draw th ...
1 - gcisd
... b. You need to know the molecules that are involved with Transcription DNA, mRNA, RNA polymerase c. Know where it happens Nucleus d. Understand the products that result from Transcription mRNA e. Understand what happens to the DNA molecule as it is transcribed Unwound and rewound by RNA polymerase 3 ...
... b. You need to know the molecules that are involved with Transcription DNA, mRNA, RNA polymerase c. Know where it happens Nucleus d. Understand the products that result from Transcription mRNA e. Understand what happens to the DNA molecule as it is transcribed Unwound and rewound by RNA polymerase 3 ...
What Can BRCA Mutations Tell Us About Ancestry?
... *Some categories include family members of mutation carriers who have not yet been diagnosed with breast cancer. The sample number does not include these data. ...
... *Some categories include family members of mutation carriers who have not yet been diagnosed with breast cancer. The sample number does not include these data. ...
WEBQUEST – DNA and Protein Synthesis
... PART 2: Fireflies Go back to Molecules of Inheritance and click on What Makes a Firefly Glow? 6. What does the LUC gene specify? ___________________ 7. a. The RNA polymerase makes a copy of the LUC gene in what form? _____________ b. Once transcription is complete, where does the mRNA go next? ____ ...
... PART 2: Fireflies Go back to Molecules of Inheritance and click on What Makes a Firefly Glow? 6. What does the LUC gene specify? ___________________ 7. a. The RNA polymerase makes a copy of the LUC gene in what form? _____________ b. Once transcription is complete, where does the mRNA go next? ____ ...
Unit 4 Review
... Answer the following questions using as many key terms as possible. Cross out key terms once you have used them at least once. Revise your answers until all key terms are crossed out. Write in complete sentences. ...
... Answer the following questions using as many key terms as possible. Cross out key terms once you have used them at least once. Revise your answers until all key terms are crossed out. Write in complete sentences. ...
Microevolution: Unique Gene Pools
... • When antibiotics are applied to a population of microorganisms to treat an infection, some of the microorganisms may be naturally immune to the drug. • Why? A random mutation occurred in the genetic code of the ...
... • When antibiotics are applied to a population of microorganisms to treat an infection, some of the microorganisms may be naturally immune to the drug. • Why? A random mutation occurred in the genetic code of the ...
Chapter 15 - Advances in Molecular Genetics
... 27. What is a frameshift mutation? 28. What test is given to every child born in the US at birth? Why? What is the nature of the disorder being tested? 29.Describe three different chromosome arrangements and in the space below, draw representative samples of them. 30. What is the biggest danger in s ...
... 27. What is a frameshift mutation? 28. What test is given to every child born in the US at birth? Why? What is the nature of the disorder being tested? 29.Describe three different chromosome arrangements and in the space below, draw representative samples of them. 30. What is the biggest danger in s ...
RevShtFinalBio160
... trait, crossing over, synapsis, zygote, genotype, phenotype Describe the similarities and differences of a pair of homologous chromosomes Diagram and solve an X-linked trait problem with hemophilia or colorblindness Descriptions and names of types of non-Mendelian inheritance patterns Similarities a ...
... trait, crossing over, synapsis, zygote, genotype, phenotype Describe the similarities and differences of a pair of homologous chromosomes Diagram and solve an X-linked trait problem with hemophilia or colorblindness Descriptions and names of types of non-Mendelian inheritance patterns Similarities a ...
Branchio-oto-renal syndrome (BOR)
... of any relevant family history and full contact details for the referring clinician ...
... of any relevant family history and full contact details for the referring clinician ...
11.1 Intro Evo and Mutations
... In darker areas (such as the forest), this would decrease fitness because these bears would stand out. They would not be able to live as long and then they would reproduce less. When would this not change fitness? If the bear was in an area where it did not need to hide, it may not change fitnes ...
... In darker areas (such as the forest), this would decrease fitness because these bears would stand out. They would not be able to live as long and then they would reproduce less. When would this not change fitness? If the bear was in an area where it did not need to hide, it may not change fitnes ...
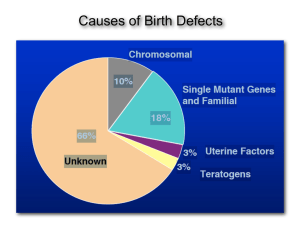
Causes of Birth Defects
... pleiotropy: refers to the multiple structures effected by one gene or one mutant gene. Haploinsufficiency occurs when a diploid organism only has a single functional copy of a gene (with the other copy inactivated by mutation) and the single functional copy of the gene does not produce enough of a g ...
... pleiotropy: refers to the multiple structures effected by one gene or one mutant gene. Haploinsufficiency occurs when a diploid organism only has a single functional copy of a gene (with the other copy inactivated by mutation) and the single functional copy of the gene does not produce enough of a g ...
Molecular Genetics - Lake Travis Independent School District
... The “language” of mRNA is sometimes called the genetic code. The genetic code is read 3 letters (or bases) at a time, called codons. A codon is made up of 3 nucleotides that specify for a single amino acid Amino acids are strung together to form proteins (polypeptides) ...
... The “language” of mRNA is sometimes called the genetic code. The genetic code is read 3 letters (or bases) at a time, called codons. A codon is made up of 3 nucleotides that specify for a single amino acid Amino acids are strung together to form proteins (polypeptides) ...
Discovering the material for heredity: DNA
... redundancy of the genetic code. Example: The mutation that changes AUU to AUC still codes for the same amino acid, isoleucine. Thus, the polypeptide created would be identical to that made by the un-mutated form of the gene. ...
... redundancy of the genetic code. Example: The mutation that changes AUU to AUC still codes for the same amino acid, isoleucine. Thus, the polypeptide created would be identical to that made by the un-mutated form of the gene. ...
GSLC Protein Synthesis Computer Activity (word)
... Think about your building analogy in questions 2 to 4. How would adding or removing base pairs affect the construction of the building? ...
... Think about your building analogy in questions 2 to 4. How would adding or removing base pairs affect the construction of the building? ...
Genetic Disorders - West Lake Eagles
... from a parent or acquired. A hereditary mutation is a mistake that is present in the DNA of virtually all body cells. Hereditary mutations are also called germ line mutations because the gene change exists in the reproductive cells and can be passed from generation to generation, from parent to newb ...
... from a parent or acquired. A hereditary mutation is a mistake that is present in the DNA of virtually all body cells. Hereditary mutations are also called germ line mutations because the gene change exists in the reproductive cells and can be passed from generation to generation, from parent to newb ...
Genetic Mutations Notes
... are no diseases caused by silent mutations, because the protein made is same one called for in the original codon. Silent mutations have NO effect on the organism—no change occurs. EQ: Define a frameshift mutation, and describe its effects. Frameshift Mutation – The addition or deletion of a nucleot ...
... are no diseases caused by silent mutations, because the protein made is same one called for in the original codon. Silent mutations have NO effect on the organism—no change occurs. EQ: Define a frameshift mutation, and describe its effects. Frameshift Mutation – The addition or deletion of a nucleot ...
Frameshift mutation

A frameshift mutation (also called a framing error or a reading frame shift) is a genetic mutation caused by indels (insertions or deletions) of a number of nucleotides in a DNA sequence that is not divisible by three. Due to the triplet nature of gene expression by codons, the insertion or deletion can change the reading frame (the grouping of the codons), resulting in a completely different translation from the original. The earlier in the sequence the deletion or insertion occurs, the more altered the protein. A frameshift mutation is not the same as a single-nucleotide polymorphism in which a nucleotide is replaced, rather than inserted or deleted. A frameshift mutation will in general cause the reading of the codons after the mutation to code for different amino acids. The frameshift mutation will also alter the first stop codon (""UAA"", ""UGA"" or ""UAG"") encountered in the sequence. The polypeptide being created could be abnormally short or abnormally long, and will most likely not be functional.Frameshift mutations are apparent in severe genetic diseases such as Tay-Sachs disease and Cystic Fibrosis; they increase susceptibility to certain cancers and classes of familial hypercholesterolaemia; in 1997, a frameshift mutation was linked to resistance to infection by the HIV retrovirus. Frameshift mutations have been proposed as a source of biological novelty, as with the alleged creation of nylonase, however, this interpretation is controversial. A study by Negoro et al (2006) found that a frameshift mutation was unlikely to have been the cause and that rather a two amino acid substitution in the catalytic cleft of an ancestral esterase amplified Ald-hydrolytic activity.