X-Linked
... autosomal dominant disorders with no abnormal clinical features Probably results from a combination of genetic and environmental factors Need to be taken into account when interpret family history information for autosomal dominant disorders ...
... autosomal dominant disorders with no abnormal clinical features Probably results from a combination of genetic and environmental factors Need to be taken into account when interpret family history information for autosomal dominant disorders ...
SBI4U Molecular genetics UNIT_AK
... ___ 6.A base-pair substitution can be classified as all of the following, except: a. nonsense mutation c. silent mutation b. frameshift mutation d. missense mutation ___ 7.Which of the following genes is not under the control of the lac operator? a. LacI c. LacZ b. Lac X ...
... ___ 6.A base-pair substitution can be classified as all of the following, except: a. nonsense mutation c. silent mutation b. frameshift mutation d. missense mutation ___ 7.Which of the following genes is not under the control of the lac operator? a. LacI c. LacZ b. Lac X ...
Y-Linked Autosomal Dominant Inheritance Autosomal Dominant
... autosomal dominant disorders with no abnormal clinical features Probably results from a combination of genetic and environmental factors Need to be taken into account when interpret family history information for autosomal dominant disorders ...
... autosomal dominant disorders with no abnormal clinical features Probably results from a combination of genetic and environmental factors Need to be taken into account when interpret family history information for autosomal dominant disorders ...
Lecture 7 Mutation and its consequences CAMPBELL BIOLOGY
... e.g. auxotrophic mutants of Neurospora crassa. Wild-type can grow on minimal medium but mutants require nutritional supplements. 2. Homeotic Mutants These are mutants that show developmental defects i.e. They may for example have body parts in the wrong location e.g. the Drosophila antennapedia muta ...
... e.g. auxotrophic mutants of Neurospora crassa. Wild-type can grow on minimal medium but mutants require nutritional supplements. 2. Homeotic Mutants These are mutants that show developmental defects i.e. They may for example have body parts in the wrong location e.g. the Drosophila antennapedia muta ...
MCB 421 Exam #1 (A)
... analysis showed that codon 64, which is normally a tyrosine, is replaced by an amber codon. Next, you introduce a copy of the supD amber suppressor (inserts Serine) and find that the strain is still a proline auxotroph. A). (1 point). What is the likely explanation for this result? [Replacement of t ...
... analysis showed that codon 64, which is normally a tyrosine, is replaced by an amber codon. Next, you introduce a copy of the supD amber suppressor (inserts Serine) and find that the strain is still a proline auxotroph. A). (1 point). What is the likely explanation for this result? [Replacement of t ...
RC 2 Student Notes
... Nucleic acid that uses genetic information from DNA to produce proteins Structure is single stranded Sugar is ribose Proteins Proteins are chains of amino acids Amino acids are determined by codons A codon is a sequence of 3 nucleotides (like AAA or CGG) from the mRNA (which was set from the DNA) ...
... Nucleic acid that uses genetic information from DNA to produce proteins Structure is single stranded Sugar is ribose Proteins Proteins are chains of amino acids Amino acids are determined by codons A codon is a sequence of 3 nucleotides (like AAA or CGG) from the mRNA (which was set from the DNA) ...
Biology Chapter 6 Advanced Genetics The Continuity of Life: Part II
... sex-limited characteristic: a trait expressed in only one sex even though the genes are present in the autosomes of both sexes example - brightly colored feathers of roosters humans: body hair, beard, breast development, and milk production Gene Mutations gene mutation: ...
... sex-limited characteristic: a trait expressed in only one sex even though the genes are present in the autosomes of both sexes example - brightly colored feathers of roosters humans: body hair, beard, breast development, and milk production Gene Mutations gene mutation: ...
A. Incomplete Penetrance D. Pleiotropy B. Variable Expressivity
... thinning all over their head. 9. Neurofibromatosis is a disease caused by mutations in the neurofibromin gene (OMIM, 2008b). These mutations can cause the Schwann cells in an affected individual's nervous system to grow into tumors called neurofibromas, which appear as café-au-lait colored spots or ...
... thinning all over their head. 9. Neurofibromatosis is a disease caused by mutations in the neurofibromin gene (OMIM, 2008b). These mutations can cause the Schwann cells in an affected individual's nervous system to grow into tumors called neurofibromas, which appear as café-au-lait colored spots or ...
What happens in a Genetics Laboratory
... without consent from the patient. As new improved tests are developed, laboratories may perform these tests on stored samples (if for example initial testing did not provide any results), if consent has been given. In this way both patients and clinicians can ...
... without consent from the patient. As new improved tests are developed, laboratories may perform these tests on stored samples (if for example initial testing did not provide any results), if consent has been given. In this way both patients and clinicians can ...
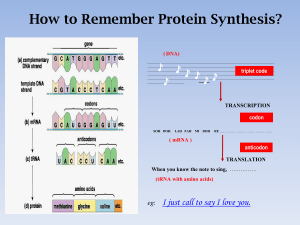
How to remember Protein Synthesis
... • DNA in the nucleus contains a triplet code; each group of three bases stands for one amino acid. • During transcription, an mRNA copy of the DNA template is made. • The mRNA is processed before leaving the nucleus. • The mRNA joins with a ribosome, where tRNA carries the amino acids into position ...
... • DNA in the nucleus contains a triplet code; each group of three bases stands for one amino acid. • During transcription, an mRNA copy of the DNA template is made. • The mRNA is processed before leaving the nucleus. • The mRNA joins with a ribosome, where tRNA carries the amino acids into position ...
Hereditary Hyperferritinemia-Cataract Syndrome: Two Novel
... µg/L. The proband herself had had previous surgical extraction of cataracts, and there were premature cataracts in 8 other family members. The son of the proband required cataract extraction at 5 years old. Hyperferritinemia was confirmed only in family members with cataract. Analysis of genomic DNA ...
... µg/L. The proband herself had had previous surgical extraction of cataracts, and there were premature cataracts in 8 other family members. The son of the proband required cataract extraction at 5 years old. Hyperferritinemia was confirmed only in family members with cataract. Analysis of genomic DNA ...
Computationally Focusing the Directed Evolution of Proteins
... Fig. 1. The optimal DNA mutation rate as determined from a statistical model, similar to a spin-glass, that captures the effect of interactions between amino acids [Voigt et al., 2001]. The genetic code is included in the model. The data is for a N 50 protein and 1,000 mutants are screened. The ®t ...
... Fig. 1. The optimal DNA mutation rate as determined from a statistical model, similar to a spin-glass, that captures the effect of interactions between amino acids [Voigt et al., 2001]. The genetic code is included in the model. The data is for a N 50 protein and 1,000 mutants are screened. The ®t ...
TRANSCRIPTION AND TRANSLATION
... the third nucleotide has changed, both codons code for tyrosine, so the final protein is the same. Sometimes point mutations result in a frame-shift mutation. In this case, a single nucleotide is added or deleted to the DNA sequence. This causes a shift in what is called the reading frame. Because DN ...
... the third nucleotide has changed, both codons code for tyrosine, so the final protein is the same. Sometimes point mutations result in a frame-shift mutation. In this case, a single nucleotide is added or deleted to the DNA sequence. This causes a shift in what is called the reading frame. Because DN ...
CONNECTIVE TISSUE LABORATORY Center for Medical Genetics
... (elastin) and Von Kossa (calcium) staining methods. If a clinical diagnosis of PXE is suspected, an initial molecular analysis of exons 18, 24, 28 and 29 of the ABCC6 gene is performed and the presence of the frequent 23-29 multi-exon deletion is verified. This set of exons contains 80% of the mutat ...
... (elastin) and Von Kossa (calcium) staining methods. If a clinical diagnosis of PXE is suspected, an initial molecular analysis of exons 18, 24, 28 and 29 of the ABCC6 gene is performed and the presence of the frequent 23-29 multi-exon deletion is verified. This set of exons contains 80% of the mutat ...
江 苏 大 学 试 题 (A)卷
... from the mother. B) The molecules used to carry out photosynthesis are encoded in nuclear DNA and mitochondrial DNA. C) cpDNA is found in the chloroplasts. D) Molecular evidence suggests that DNA sequences may have been transferred between mtDNA and nuclear DNA. E) Variegated four o'clock leaves hav ...
... from the mother. B) The molecules used to carry out photosynthesis are encoded in nuclear DNA and mitochondrial DNA. C) cpDNA is found in the chloroplasts. D) Molecular evidence suggests that DNA sequences may have been transferred between mtDNA and nuclear DNA. E) Variegated four o'clock leaves hav ...
2006
... Next, you introduce a copy of the supD amber suppressor (inserts Serine) and find that the strain is still a proline auxotroph. A). (1 point). What is the likely explanation for this result? [Replacement of tyrosine with serine does not restore activity of the protein (or the suppressor is not effic ...
... Next, you introduce a copy of the supD amber suppressor (inserts Serine) and find that the strain is still a proline auxotroph. A). (1 point). What is the likely explanation for this result? [Replacement of tyrosine with serine does not restore activity of the protein (or the suppressor is not effic ...
Genetic Diseases and Diagnosis: Word Scramble Read each clue
... TRULDNSAUO The technique that allows one to see a fetus by using a camera on an endoscope. ETOCYFSOP The term used for something in the environment capable of causing a gene mutation. AGENMUT ...
... TRULDNSAUO The technique that allows one to see a fetus by using a camera on an endoscope. ETOCYFSOP The term used for something in the environment capable of causing a gene mutation. AGENMUT ...
bio-of-cells-lent-restriction-enzymes-information-for-exam
... Restriction enzyme mapping - determining the order of fragments produced by cutting a DNA molecule with a restriction enzyme. RFLP - restriction fragment length polymorphism, a difference in the size of a genomic DNA fragment produced by digestion with a particular enzyme. A useful DNA marker. RFLPs ...
... Restriction enzyme mapping - determining the order of fragments produced by cutting a DNA molecule with a restriction enzyme. RFLP - restriction fragment length polymorphism, a difference in the size of a genomic DNA fragment produced by digestion with a particular enzyme. A useful DNA marker. RFLPs ...
Normal pairing
... A powerful carcinogen originally isolated from peanuts infected with fungus. Alfatoxin attaches to guanine at the N-7 position. This leads to the breakage of the bond between the base and the sugar, thereby liberating the base and resulting in an apurinic site. Agents that cause depurination at gua ...
... A powerful carcinogen originally isolated from peanuts infected with fungus. Alfatoxin attaches to guanine at the N-7 position. This leads to the breakage of the bond between the base and the sugar, thereby liberating the base and resulting in an apurinic site. Agents that cause depurination at gua ...
Protein Synthesis Section 3 Transcription and Translation
... leaves the nucleus to the cytoplasm 2) mRNA attaches to the ribosome 3) The codon on the mRNA is read by the anticodon on the tRNA 4) tRNA brings the amino acid as it reads mRNA 5) The amino acids are joined together to form a polypeptide (protein) 6) When a stop codon is reached (UAA, UAG, UGA) pro ...
... leaves the nucleus to the cytoplasm 2) mRNA attaches to the ribosome 3) The codon on the mRNA is read by the anticodon on the tRNA 4) tRNA brings the amino acid as it reads mRNA 5) The amino acids are joined together to form a polypeptide (protein) 6) When a stop codon is reached (UAA, UAG, UGA) pro ...
heterozygous nephew cystic fibrosis symptoms than her codon in
... Correspondence to Professor Cassiman. Received for publication 22 May 1990. Accepted for publication 18 June 1990. ...
... Correspondence to Professor Cassiman. Received for publication 22 May 1990. Accepted for publication 18 June 1990. ...
Index case of acute myeloid leukemia in a family
... minimum allele frequency of 0.1 and a maximum P value of .9. Bcftools (v1.3) was used to soft-filter nonsomatic mutations and somatic mutations were filtered using strategies implemented in bcbio-nextgen (https://github.com/ chapmanb/bcbio-nextgen) for VarDict: ((allele frequency 3 read depth , 6) & ...
... minimum allele frequency of 0.1 and a maximum P value of .9. Bcftools (v1.3) was used to soft-filter nonsomatic mutations and somatic mutations were filtered using strategies implemented in bcbio-nextgen (https://github.com/ chapmanb/bcbio-nextgen) for VarDict: ((allele frequency 3 read depth , 6) & ...
Ch. 12 Review- pg. 315 1-23 Answers The process by which one
... Name two major types of mutations. Why do they have in common? Who are they different? Give an example for each. Gene and chromosomal; both change the DNA sequence that affects genetic information. Gene mutations involve a change in one or several nucleotides in a single gene, whereas chromosomal mu ...
... Name two major types of mutations. Why do they have in common? Who are they different? Give an example for each. Gene and chromosomal; both change the DNA sequence that affects genetic information. Gene mutations involve a change in one or several nucleotides in a single gene, whereas chromosomal mu ...
Frameshift mutation

A frameshift mutation (also called a framing error or a reading frame shift) is a genetic mutation caused by indels (insertions or deletions) of a number of nucleotides in a DNA sequence that is not divisible by three. Due to the triplet nature of gene expression by codons, the insertion or deletion can change the reading frame (the grouping of the codons), resulting in a completely different translation from the original. The earlier in the sequence the deletion or insertion occurs, the more altered the protein. A frameshift mutation is not the same as a single-nucleotide polymorphism in which a nucleotide is replaced, rather than inserted or deleted. A frameshift mutation will in general cause the reading of the codons after the mutation to code for different amino acids. The frameshift mutation will also alter the first stop codon (""UAA"", ""UGA"" or ""UAG"") encountered in the sequence. The polypeptide being created could be abnormally short or abnormally long, and will most likely not be functional.Frameshift mutations are apparent in severe genetic diseases such as Tay-Sachs disease and Cystic Fibrosis; they increase susceptibility to certain cancers and classes of familial hypercholesterolaemia; in 1997, a frameshift mutation was linked to resistance to infection by the HIV retrovirus. Frameshift mutations have been proposed as a source of biological novelty, as with the alleged creation of nylonase, however, this interpretation is controversial. A study by Negoro et al (2006) found that a frameshift mutation was unlikely to have been the cause and that rather a two amino acid substitution in the catalytic cleft of an ancestral esterase amplified Ald-hydrolytic activity.