The genetic basis of inherited anomalies of the teeth: Part 1: Clinical
... The genetic control of dental development represents a complex series of events, which can very schematically be divided in two pathways: specification of type, size and position of each dental organ, and specific processes for the formation of enamel and dentin. Several genes linked with early toot ...
... The genetic control of dental development represents a complex series of events, which can very schematically be divided in two pathways: specification of type, size and position of each dental organ, and specific processes for the formation of enamel and dentin. Several genes linked with early toot ...
Gene conversion rapidly generates major histocompatibility complex
... adaptive genetic diversity in isolated populations is therefore central to evolution, and given the role of such diversity in the persistence of populations, is key from a long-term conservation perspective. Vertebrate major histocompatibility complex (MHC) genes are arguably the best studied exampl ...
... adaptive genetic diversity in isolated populations is therefore central to evolution, and given the role of such diversity in the persistence of populations, is key from a long-term conservation perspective. Vertebrate major histocompatibility complex (MHC) genes are arguably the best studied exampl ...
Human cytochromes P450 in health and disease
... of CYP enzymes in the eicosanoid pathway is likely to be redundant with lipoxygenases and other peroxidases [40]. There are now more than 150 identified eicosanoids [40], which participate in virtually every imaginable critical life process (table 3). In all likelihood due to redundancy, allelic var ...
... of CYP enzymes in the eicosanoid pathway is likely to be redundant with lipoxygenases and other peroxidases [40]. There are now more than 150 identified eicosanoids [40], which participate in virtually every imaginable critical life process (table 3). In all likelihood due to redundancy, allelic var ...
Machine Evolution - 서울대 Biointelligence lab
... point is selected at random and parts of the two parent chromosomes are swapped to create two offspring with a probability which is called crossover rate. ...
... point is selected at random and parts of the two parent chromosomes are swapped to create two offspring with a probability which is called crossover rate. ...
Machine Evolution - 서울대 Biointelligence lab
... point is selected at random and parts of the two parent chromosomes are swapped to create two offspring with a probability which is called crossover rate. ...
... point is selected at random and parts of the two parent chromosomes are swapped to create two offspring with a probability which is called crossover rate. ...
Complete Laboratory PDF
... another on a chromosome, the greater the chance that they will be inherited together as a unit (linked). Conversely, locations farther apart on the chromosome are more likely to be separated by chromosome recombination during meiosis. Thus, the frequency of recombination with previously mapped genes ...
... another on a chromosome, the greater the chance that they will be inherited together as a unit (linked). Conversely, locations farther apart on the chromosome are more likely to be separated by chromosome recombination during meiosis. Thus, the frequency of recombination with previously mapped genes ...
20 Years after finding the Duchenne Gene
... and also three other diseases with the same mode of heredity. So with Uta Francke, it could be shown that all three genes were missing, there was a very large deletion in the X chromosome that could be seen. Other patients turned up with smaller deletions also close to the place where the Duchenne g ...
... and also three other diseases with the same mode of heredity. So with Uta Francke, it could be shown that all three genes were missing, there was a very large deletion in the X chromosome that could be seen. Other patients turned up with smaller deletions also close to the place where the Duchenne g ...
The Plastidic Phosphoglucomutase from
... intermediates fructose-1,6-bisphosphate and ribulose-1,5-bisphosphate exerted an inhibitory effect on PGM activity, supporting its proposed involvement in controlling photosynthetic carbon flow. A point mutation was identified in the AtPGMp gene of the Arabidopsis pgm-1 mutant. The mutation in the m ...
... intermediates fructose-1,6-bisphosphate and ribulose-1,5-bisphosphate exerted an inhibitory effect on PGM activity, supporting its proposed involvement in controlling photosynthetic carbon flow. A point mutation was identified in the AtPGMp gene of the Arabidopsis pgm-1 mutant. The mutation in the m ...
Criterion for a Correct Response - Delaware Department of Education
... © Delaware Department of Education ...
... © Delaware Department of Education ...
The molecular basis of human retinal and vitreoretinal
... of retinal degenerations (Leber congenital amaurosis, LCA) to less severe or rather mild retinal dysfunctions (night blindness, achromatopsia). For most of them, no treatment can be offered. In the past 20-25 years, the knowledge about the molecular basis of retinal diseases has tremendously progres ...
... of retinal degenerations (Leber congenital amaurosis, LCA) to less severe or rather mild retinal dysfunctions (night blindness, achromatopsia). For most of them, no treatment can be offered. In the past 20-25 years, the knowledge about the molecular basis of retinal diseases has tremendously progres ...
PDF - 2.3 MB
... Phage T4 expresses an enzyme tysozyme, which enabtes phage to lyse infected ceils. Mutations in the lysozyme gene can prevent T4 from forming a plaques on a lawn of E. coil. You have isolated two T4 mutants that can not make plaques on wild type (Su-), but that can make plaques on an E. co//strain c ...
... Phage T4 expresses an enzyme tysozyme, which enabtes phage to lyse infected ceils. Mutations in the lysozyme gene can prevent T4 from forming a plaques on a lawn of E. coil. You have isolated two T4 mutants that can not make plaques on wild type (Su-), but that can make plaques on an E. co//strain c ...
Environmental Microbiology
... repair, the recombination between non-identical genes, or reassortment of gene segments if the genome is not present in one molecule (Borst, 2003). Programmed and unprogrammed phase variation are subject to regulation. Especially in a host–pathogen situation the regulation of phase variation is impo ...
... repair, the recombination between non-identical genes, or reassortment of gene segments if the genome is not present in one molecule (Borst, 2003). Programmed and unprogrammed phase variation are subject to regulation. Especially in a host–pathogen situation the regulation of phase variation is impo ...
A NEW TAIL-SHORT MUTATION IN THE MOUSE
... The inbred line which gave rise to the Ts mutants traced back to the C-strain (Bagg albinos), in certain matings in the F M generation, "tail-short" mice T J appeared— (nt means "normal tail" in this chart). numbers of normal and mutant offspring; while matings of mutant by mutant should gire about ...
... The inbred line which gave rise to the Ts mutants traced back to the C-strain (Bagg albinos), in certain matings in the F M generation, "tail-short" mice T J appeared— (nt means "normal tail" in this chart). numbers of normal and mutant offspring; while matings of mutant by mutant should gire about ...
Running title Variation in Barley Brassinosteroid
... Today, more than 50 different brassinosteroids have been identified in plants (Bajguz and Tretyn, 2003). Most are intermediates of the complex biosynthetic pathway (Shimada et al., 2001). Approximately nine genes code for the enzymes that participate in the biosynthetic pathway from episterol to bra ...
... Today, more than 50 different brassinosteroids have been identified in plants (Bajguz and Tretyn, 2003). Most are intermediates of the complex biosynthetic pathway (Shimada et al., 2001). Approximately nine genes code for the enzymes that participate in the biosynthetic pathway from episterol to bra ...
The genetic causes of convergent evolution
... that results from similar molecular mechanisms acting in divergent taxa can occur through three historical paths, illustrated here in a phylogenetic framework. a | Parallel evolution refers to mutations that arise and spread in independent lineages. In this case, the ancestral state (A) independentl ...
... that results from similar molecular mechanisms acting in divergent taxa can occur through three historical paths, illustrated here in a phylogenetic framework. a | Parallel evolution refers to mutations that arise and spread in independent lineages. In this case, the ancestral state (A) independentl ...
Genetic Inversion: Relationships Among Species
... row is the target sequence. The second row is the sequence you need to transform into the target sequence. Click on two tiles that mark the beginning and end of the subsequence you want to invert. X’s appear on the two tiles, if you make a mistake, clicking again on a tile removes its X. Once you ha ...
... row is the target sequence. The second row is the sequence you need to transform into the target sequence. Click on two tiles that mark the beginning and end of the subsequence you want to invert. X’s appear on the two tiles, if you make a mistake, clicking again on a tile removes its X. Once you ha ...
Genetic Codes with No Dedicated Stop Codon: Context
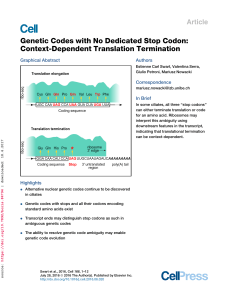
... the abolishment of recognition of certain stop codons by mutations in the stop-recognizing translation termination factor eukaryotic release factor 1 (eRF1) allowing codon reassignment have therefore been proposed (Lozupone et al., 2001). While the genetic code is classically taught as being unambig ...
... the abolishment of recognition of certain stop codons by mutations in the stop-recognizing translation termination factor eukaryotic release factor 1 (eRF1) allowing codon reassignment have therefore been proposed (Lozupone et al., 2001). While the genetic code is classically taught as being unambig ...
The Genetics of CFTR: Genotype – Phenotype Relationship
... 2.1 Maturation, protein domains and mutational classes The CFTR gene codes for a symmetric transmembrane protein of 1480 aminoacids that belongs to the family of ATP-binding cassette transporters (ABC transporters). The CFTR protein undergoes a complex transport and maturation process within the cel ...
... 2.1 Maturation, protein domains and mutational classes The CFTR gene codes for a symmetric transmembrane protein of 1480 aminoacids that belongs to the family of ATP-binding cassette transporters (ABC transporters). The CFTR protein undergoes a complex transport and maturation process within the cel ...
Technical standards and guidelines for spinal muscular atrophy testing
... that the neuronal population is more sensitive to decreases in the SMN protein level. Possibly, the altered splicing of a unique set of premessenger RNAs results in deficient proteins, which are necessary for motor neuron growth and survival. In addition to its role in spliceosomal ribonucleoprotein ...
... that the neuronal population is more sensitive to decreases in the SMN protein level. Possibly, the altered splicing of a unique set of premessenger RNAs results in deficient proteins, which are necessary for motor neuron growth and survival. In addition to its role in spliceosomal ribonucleoprotein ...
105 - Heritable Diseases of Connective Tissue
... are close to total height in an average-proportioned individual. A short-limbed individual has an arm span considerably shorter than the height. As in any disorder that has a genetic basis, it is crucial to obtain an accurate family history. This should include any history of previously affected chi ...
... are close to total height in an average-proportioned individual. A short-limbed individual has an arm span considerably shorter than the height. As in any disorder that has a genetic basis, it is crucial to obtain an accurate family history. This should include any history of previously affected chi ...
Consulta: subjectFacets:"Phenotype" Registros recuperados: 25
... Autores: Polizzi,Angela; Tesse,Riccardina; Santostasi,Teresa; Diana,Anna; Manca,Antonio; Logrillo,Vito Paolo; Cazzato,Maria Domenica; Pantaleo,Maria Giuseppa; Armenio,Lucio. Cystic fibrosis (CF) is caused by CFTR (cystic fibrosis transmembrane conductance regulator) gene mutations. We ascertained fi ...
... Autores: Polizzi,Angela; Tesse,Riccardina; Santostasi,Teresa; Diana,Anna; Manca,Antonio; Logrillo,Vito Paolo; Cazzato,Maria Domenica; Pantaleo,Maria Giuseppa; Armenio,Lucio. Cystic fibrosis (CF) is caused by CFTR (cystic fibrosis transmembrane conductance regulator) gene mutations. We ascertained fi ...
Lecture 7: Gene Finding by Computational Analysis Gene
... • Eukaryotic genes contain introns & exons – Introns are seq that are ultimately spliced out of mRNA – Introns normally satisfy GT-AG rule, viz. begin w/ GT & end w/ AG – Each gene can have many introns & each intron can have thousands bases ...
... • Eukaryotic genes contain introns & exons – Introns are seq that are ultimately spliced out of mRNA – Introns normally satisfy GT-AG rule, viz. begin w/ GT & end w/ AG – Each gene can have many introns & each intron can have thousands bases ...
DIFFERENTIAL GENE RESPONSE TO MUTAGENS IN
... mutants were detected by the Muller-5 technique, though a small number occurred in attached-X experiments and were also included. In Muller-5 tests, cultures yielding only M-5 males (scslB(ZnS)wascg/Y)and completely lacking in the potentially wild type male class, were scored as sex-linked recessive ...
... mutants were detected by the Muller-5 technique, though a small number occurred in attached-X experiments and were also included. In Muller-5 tests, cultures yielding only M-5 males (scslB(ZnS)wascg/Y)and completely lacking in the potentially wild type male class, were scored as sex-linked recessive ...
Japanese morning glory dusky mutants displaying reddish
... (Hagiwara, 1931; Imai, 1931). Recessive magenta and purple mutants bloom magenta and purple flowers, respectively, and double mutants carrying both magenta and purple alleles display red flowers (Figure 1d). The Magenta gene was shown to encode flavonoid 3¢-hydorxylase, which hydroxylates the 3¢ pos ...
... (Hagiwara, 1931; Imai, 1931). Recessive magenta and purple mutants bloom magenta and purple flowers, respectively, and double mutants carrying both magenta and purple alleles display red flowers (Figure 1d). The Magenta gene was shown to encode flavonoid 3¢-hydorxylase, which hydroxylates the 3¢ pos ...
Frameshift mutation

A frameshift mutation (also called a framing error or a reading frame shift) is a genetic mutation caused by indels (insertions or deletions) of a number of nucleotides in a DNA sequence that is not divisible by three. Due to the triplet nature of gene expression by codons, the insertion or deletion can change the reading frame (the grouping of the codons), resulting in a completely different translation from the original. The earlier in the sequence the deletion or insertion occurs, the more altered the protein. A frameshift mutation is not the same as a single-nucleotide polymorphism in which a nucleotide is replaced, rather than inserted or deleted. A frameshift mutation will in general cause the reading of the codons after the mutation to code for different amino acids. The frameshift mutation will also alter the first stop codon (""UAA"", ""UGA"" or ""UAG"") encountered in the sequence. The polypeptide being created could be abnormally short or abnormally long, and will most likely not be functional.Frameshift mutations are apparent in severe genetic diseases such as Tay-Sachs disease and Cystic Fibrosis; they increase susceptibility to certain cancers and classes of familial hypercholesterolaemia; in 1997, a frameshift mutation was linked to resistance to infection by the HIV retrovirus. Frameshift mutations have been proposed as a source of biological novelty, as with the alleged creation of nylonase, however, this interpretation is controversial. A study by Negoro et al (2006) found that a frameshift mutation was unlikely to have been the cause and that rather a two amino acid substitution in the catalytic cleft of an ancestral esterase amplified Ald-hydrolytic activity.