DNA extraction from cheek cells protocol I mailed to you
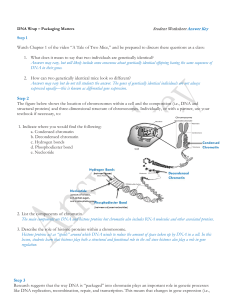
... Each chromosome in the nucleus of a cell contains a very long molecule of DNA. If you stretched out the DNA found in one of your cells, it would be 2-3 meters long. To fit all of this DNA inside a tiny cell nucleus, the DNA is wrapped tightly around proteins. The enzyme in meat tenderizer is a prote ...
... Each chromosome in the nucleus of a cell contains a very long molecule of DNA. If you stretched out the DNA found in one of your cells, it would be 2-3 meters long. To fit all of this DNA inside a tiny cell nucleus, the DNA is wrapped tightly around proteins. The enzyme in meat tenderizer is a prote ...
Homework #2
... c) If trisomies and monsomies entailing chromosome 13 and 22 are letha, what proportion of the surviving offspring will be carriers of the translocation? ...
... c) If trisomies and monsomies entailing chromosome 13 and 22 are letha, what proportion of the surviving offspring will be carriers of the translocation? ...
Bill Nye Genes Video WKSHT
... 8. Why is the white blood cell dark on the computer screen? 9. What does the nucleus of the cell contain? 10. What can you do with DNA after you take it out of an organism? a. b. 11. What 2 organisms were combined to create the message to Bill in the petri dish? 12. What do genes do? 13. Mom tells R ...
... 8. Why is the white blood cell dark on the computer screen? 9. What does the nucleus of the cell contain? 10. What can you do with DNA after you take it out of an organism? a. b. 11. What 2 organisms were combined to create the message to Bill in the petri dish? 12. What do genes do? 13. Mom tells R ...
Bill Nye Genes Video WKSHT
... 8. Why is the white blood cell dark on the computer screen? Because it has chromosomes in it. 9. What can you do with DNA after you take it out of an organism? a. Cut it into smaller pieces b. Place into another organism 10. What 2 organisms were combined to create the message to Bill in the petri d ...
... 8. Why is the white blood cell dark on the computer screen? Because it has chromosomes in it. 9. What can you do with DNA after you take it out of an organism? a. Cut it into smaller pieces b. Place into another organism 10. What 2 organisms were combined to create the message to Bill in the petri d ...
Name Date “Bill Nye: Genes” Video Worksheet 1. Where do your
... 8. Why is the white blood cell dark on the computer screen? Because it has chromosomes in it. 9. What can you do with DNA after you take it out of an organism? a. Cut it into smaller pieces b. Place into another organism 10. What 2 organisms were combined to create the message to Bill in the petri d ...
... 8. Why is the white blood cell dark on the computer screen? Because it has chromosomes in it. 9. What can you do with DNA after you take it out of an organism? a. Cut it into smaller pieces b. Place into another organism 10. What 2 organisms were combined to create the message to Bill in the petri d ...
Biotechnology
... genes & organisms, then you need a set of tools to work with this unit is a survey of those tools… ...
... genes & organisms, then you need a set of tools to work with this unit is a survey of those tools… ...
Bill Nye: Genes
... 8. Why is the white blood cell dark on the computer screen? Because it has chromosomes in it. 9. What can you do with DNA after you take it out of an organism? a. Cut it into smaller pieces b. Place into another organism 10. What 2 organisms were combined to create the message to Bill in the petri d ...
... 8. Why is the white blood cell dark on the computer screen? Because it has chromosomes in it. 9. What can you do with DNA after you take it out of an organism? a. Cut it into smaller pieces b. Place into another organism 10. What 2 organisms were combined to create the message to Bill in the petri d ...
The Molecular - MolGen | RuG
... heterogeneity and specificity of function, essential requirements for the hereditary material. Moreover, little was known about nucleic acids, whose physical and chemical properties ...
... heterogeneity and specificity of function, essential requirements for the hereditary material. Moreover, little was known about nucleic acids, whose physical and chemical properties ...
Final Review Answer Key - Mercer Island School District
... cannot reproduce on their own, and they do not metabolize on their own (build molecules etc.) Viruses reproduce by attaching to a host cell (each type of virus may be specific for certain types of host cells that it can attach to). The virus’ genetic material (DNA or RNA)is injected into the host ce ...
... cannot reproduce on their own, and they do not metabolize on their own (build molecules etc.) Viruses reproduce by attaching to a host cell (each type of virus may be specific for certain types of host cells that it can attach to). The virus’ genetic material (DNA or RNA)is injected into the host ce ...
Genetics
... 28. In order to make proteins, DNA is first transcribed as ______________ 29. Give one structural difference between DNA and RNA. 30. Name the nitrogenous bases whose first letters are A and C. 31. DNA contains the instructions needed to make protein. These instructions are called the ______________ ...
... 28. In order to make proteins, DNA is first transcribed as ______________ 29. Give one structural difference between DNA and RNA. 30. Name the nitrogenous bases whose first letters are A and C. 31. DNA contains the instructions needed to make protein. These instructions are called the ______________ ...
BIOLOGY 12 MUTATIONS FRAMESHIFT MUTATIONS
... nucleotide bases so that they look like other nucleotide bases. ...
... nucleotide bases so that they look like other nucleotide bases. ...
A. Overview - eweb.furman.edu
... Genomics A. Overview: B. Sequencing: - Basically, you sequence the longest fragments of DNA that you can, by the methods we have described already. - Then, you enter the sequence in a computer, and you group together “contiguous sequences” (contigs) based on regions of overlap. Eventually, you cove ...
... Genomics A. Overview: B. Sequencing: - Basically, you sequence the longest fragments of DNA that you can, by the methods we have described already. - Then, you enter the sequence in a computer, and you group together “contiguous sequences” (contigs) based on regions of overlap. Eventually, you cove ...
Uptake of foreign DNA
... inhibits cell growth. Only cells that can inactivate the ampicillin around them will grow. • Ampicillin resistance fluorescent protein gene ...
... inhibits cell growth. Only cells that can inactivate the ampicillin around them will grow. • Ampicillin resistance fluorescent protein gene ...
Human Genetics Lec 4
... Most genetic information of a cell is organized, stored, and retrieved in small intracellular structures called chromosomes. Although the chromosomes are visible only in dividing cells, they retain their integrity between cell divisions. The chromosomes are arranged in pairs; one member of the pair ...
... Most genetic information of a cell is organized, stored, and retrieved in small intracellular structures called chromosomes. Although the chromosomes are visible only in dividing cells, they retain their integrity between cell divisions. The chromosomes are arranged in pairs; one member of the pair ...
File - NCEA Level 3 Biology
... microscopic pellets (gold or tungsten) and fired into a cell with a gun. • This is useful for introducing DNA into plant cells that are not susceptible to infection. ...
... microscopic pellets (gold or tungsten) and fired into a cell with a gun. • This is useful for introducing DNA into plant cells that are not susceptible to infection. ...
Chapter 10: Molecular Biology of the Gene
... exact three dimensional structure of DNA as a double helix held together by H bonds. Won 1962 Nobel Prize. DNA is an antiparallel double helix: 5’ end of one strand is paired to 3’ end of other strand. A & T and G & C are paired up by hydrogen bonds Two strands are complementary to each other. ...
... exact three dimensional structure of DNA as a double helix held together by H bonds. Won 1962 Nobel Prize. DNA is an antiparallel double helix: 5’ end of one strand is paired to 3’ end of other strand. A & T and G & C are paired up by hydrogen bonds Two strands are complementary to each other. ...
DNA
... exact three dimensional structure of DNA as a double helix held together by H bonds. Won 1962 Nobel Prize. DNA is an antiparallel double helix: 5’ end of one strand is paired to 3’ end of other strand. A & T and G & C are paired up by hydrogen bonds Two strands are complementary to each other. ...
... exact three dimensional structure of DNA as a double helix held together by H bonds. Won 1962 Nobel Prize. DNA is an antiparallel double helix: 5’ end of one strand is paired to 3’ end of other strand. A & T and G & C are paired up by hydrogen bonds Two strands are complementary to each other. ...
Ch - TeacherWeb
... forms a peptide bond with the amino acid on the second tRNA and detaches from the first tRNA. Step 6: The first tRNA is kicked out as the ribosome moves down the mRNA molecule. Step 7: A new tRNA molecules binds to match with the next codon sequence. Step 8: Steps 5-7 are repeated until a stop ...
... forms a peptide bond with the amino acid on the second tRNA and detaches from the first tRNA. Step 6: The first tRNA is kicked out as the ribosome moves down the mRNA molecule. Step 7: A new tRNA molecules binds to match with the next codon sequence. Step 8: Steps 5-7 are repeated until a stop ...
File
... Making mRNA (done by RNA polymerase) RNA is only single stranded so it is always copied off the 3’ to 5’ DNA strand so that it can easily grow in the 5’ to 3’ direction. Binding site where transcription begins is called the TATA box ...
... Making mRNA (done by RNA polymerase) RNA is only single stranded so it is always copied off the 3’ to 5’ DNA strand so that it can easily grow in the 5’ to 3’ direction. Binding site where transcription begins is called the TATA box ...
document
... Answers may vary, but will likely include some consensus about genetically identical offspring having the same sequences of DNA in their genes. 2. How can two genetically identical mice look so different? Answers may vary but do not tell students the answer. The genes of genetically identical indivi ...
... Answers may vary, but will likely include some consensus about genetically identical offspring having the same sequences of DNA in their genes. 2. How can two genetically identical mice look so different? Answers may vary but do not tell students the answer. The genes of genetically identical indivi ...
Exam3-1406_Fall2007ch9-10-11.doc
... D) A = U and G = C in any molecule of RNA. E) DNA and RNA are made up of the same four nitrogenous bases. 10) The X-ray diffraction pattern for DNA suggested to Wilkins and Franklin all of the following features about DNA EXCEPT A) a DNA molecule is helical. B) a DNA molecule has a diameter of 2 nan ...
... D) A = U and G = C in any molecule of RNA. E) DNA and RNA are made up of the same four nitrogenous bases. 10) The X-ray diffraction pattern for DNA suggested to Wilkins and Franklin all of the following features about DNA EXCEPT A) a DNA molecule is helical. B) a DNA molecule has a diameter of 2 nan ...
Biology Honors Final Review
... 7. What is the function of mRNA, tRNA and rRNA? 8. Why does DNA make mRNA? What is this process called? Where does it happen? 9. Describe the steps of making mRNA from DNA. 10. Compare and contrast RNA and DNA. 11. What are the building blocks of proteins? How many different types are there? 12. How ...
... 7. What is the function of mRNA, tRNA and rRNA? 8. Why does DNA make mRNA? What is this process called? Where does it happen? 9. Describe the steps of making mRNA from DNA. 10. Compare and contrast RNA and DNA. 11. What are the building blocks of proteins? How many different types are there? 12. How ...
Protein Synthesis Pre Test
... a. carry a message that, when translated, forms proteins. b. form a portion of ribosomes, a cell's protein factories. c. string together complementary RNA and DNA strands. d. bring amino acids from the cytoplasm to the ribosomes. McDougal Biology Florida 2012 ____ 4. A primary difference between tra ...
... a. carry a message that, when translated, forms proteins. b. form a portion of ribosomes, a cell's protein factories. c. string together complementary RNA and DNA strands. d. bring amino acids from the cytoplasm to the ribosomes. McDougal Biology Florida 2012 ____ 4. A primary difference between tra ...
Nucleic acid double helix

In molecular biology, the term double helix refers to the structure formed by double-stranded molecules of nucleic acids such as DNA. The double helical structure of a nucleic acid complex arises as a consequence of its secondary structure, and is a fundamental component in determining its tertiary structure. The term entered popular culture with the publication in 1968 of The Double Helix: A Personal Account of the Discovery of the Structure of DNA, by James Watson.The DNA double helix polymer of nucleic acids, held together by nucleotides which base pair together. In B-DNA, the most common double helical structure, the double helix is right-handed with about 10–10.5 base pairs per turn. This translates into about 20-21 nucleotides per turn. The double helix structure of DNA contains a major groove and minor groove. In B-DNA the major groove is wider than the minor groove. Given the difference in widths of the major groove and minor groove, many proteins which bind to B-DNA do so through the wider major groove.