Proposal for 431 531 - Oregon State University
... In 1986, I was able to do a reasonable job of presenting the principles of plant genetics to an undergraduate audience with little or no background in the subject. I was able to offer sufficient additional material to justify offering the course for graduate credit, particularly for students new to ...
... In 1986, I was able to do a reasonable job of presenting the principles of plant genetics to an undergraduate audience with little or no background in the subject. I was able to offer sufficient additional material to justify offering the course for graduate credit, particularly for students new to ...
Chapter 19 - Microbiology and Molecular Genetics at Oklahoma
... – Useful for differentiating very similar organisms – Hybridization values 70% or higher suggest strains belong to the same species – Values of at least 25% suggest same genus ...
... – Useful for differentiating very similar organisms – Hybridization values 70% or higher suggest strains belong to the same species – Values of at least 25% suggest same genus ...
Ch. 5: Presentation Slides
... • DNA consists of two polynucleotide chains which run 5’ to 3’ in opposite directions = antiparallel • DNA chains are held together by hydrogen bonds between bases • DNA bases pair by Chargaff’s rules: - Adenine (A) pairs with Thymine (T) by 2 H-bounds - Guanine (G) pairs with Cytosine (C) by 3 boun ...
... • DNA consists of two polynucleotide chains which run 5’ to 3’ in opposite directions = antiparallel • DNA chains are held together by hydrogen bonds between bases • DNA bases pair by Chargaff’s rules: - Adenine (A) pairs with Thymine (T) by 2 H-bounds - Guanine (G) pairs with Cytosine (C) by 3 boun ...
Showing the 3D shape of our chromosomes
... gene silencing, DNA replication and DNA repair. In fact, just about any genome function has a spatial component that has been implicated in its control. Dr Fraser added: “These unique images not only show us the structure of the chromosome, but also the path of the DNA in it, allowing us to map spec ...
... gene silencing, DNA replication and DNA repair. In fact, just about any genome function has a spatial component that has been implicated in its control. Dr Fraser added: “These unique images not only show us the structure of the chromosome, but also the path of the DNA in it, allowing us to map spec ...
15 points each
... B. when a stop codon is coded for instead of Methionine C. when the mRNA sequence begins with the mutation D. when the point mutation still codes for the same ...
... B. when a stop codon is coded for instead of Methionine C. when the mRNA sequence begins with the mutation D. when the point mutation still codes for the same ...
1) - life.illinois.edu
... between attDOT and attB by staggered cleavages seven base apart on each att site. The sites of cleavage in attDOT are shown between the D and D’ sites in the sequence. In vitro experiments indicated that the IntDOT integrase, which catalyzes the reaction, binds to two classes of sites in attDOT. One ...
... between attDOT and attB by staggered cleavages seven base apart on each att site. The sites of cleavage in attDOT are shown between the D and D’ sites in the sequence. In vitro experiments indicated that the IntDOT integrase, which catalyzes the reaction, binds to two classes of sites in attDOT. One ...
BCH-201:Nucleotides and Nucleic acids
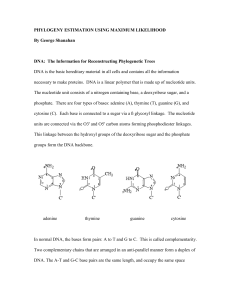
... Nucleic acids are defined as biopolymers that are involved in the preservation/storage and transmission of genetic information from one generation to another.The nucleotides that make up the nucleic acids are linked by phosphodiester bonds between 3’ and 5’ positions of the sugars. The linkage is ca ...
... Nucleic acids are defined as biopolymers that are involved in the preservation/storage and transmission of genetic information from one generation to another.The nucleotides that make up the nucleic acids are linked by phosphodiester bonds between 3’ and 5’ positions of the sugars. The linkage is ca ...
lecture1
... Nucleic acids are defined as biopolymers that are involved in the preservation/storage and transmission of genetic information from one generation to another.The nucleotides that make up the nucleic acids are linked by phosphodiester bonds between 3’ and 5’ positions of the sugars. The linkage is ca ...
... Nucleic acids are defined as biopolymers that are involved in the preservation/storage and transmission of genetic information from one generation to another.The nucleotides that make up the nucleic acids are linked by phosphodiester bonds between 3’ and 5’ positions of the sugars. The linkage is ca ...
Can Nurture Influence Nature? - Prof. Sir David Baulcombe
... • evolution requires variation in heritable traits • heritable variation can be achieved other than by genetic mutation – epimutation • epimutations differ from genetic mutations in that they may be unstable and in that they can be induced and targeted • RNA can initiate variation that is inherited ...
... • evolution requires variation in heritable traits • heritable variation can be achieved other than by genetic mutation – epimutation • epimutations differ from genetic mutations in that they may be unstable and in that they can be induced and targeted • RNA can initiate variation that is inherited ...
Gene rearrangements occur via various mechanisms
... without the donating chromosome being changed. Gene conversion occurs at high frequency at the actual site of the recombination event during meiosis. It is a process by which a DNA sequence is copied from one DNA helix (which remains unchanged) to another DNA helix, whose sequence is altered. Gene c ...
... without the donating chromosome being changed. Gene conversion occurs at high frequency at the actual site of the recombination event during meiosis. It is a process by which a DNA sequence is copied from one DNA helix (which remains unchanged) to another DNA helix, whose sequence is altered. Gene c ...
A kinetic proofreading mechanism for disentanglement of
... DNA segments through one another in a random way1. These type II topoisomerases (of less than 10 nm in diameter) thus use ATP hydrolysis to sense and remove entanglements spread along flexible DNA strands of up to 3,000 nm long. Here we propose a mechanism for this, based on the higher rate of colli ...
... DNA segments through one another in a random way1. These type II topoisomerases (of less than 10 nm in diameter) thus use ATP hydrolysis to sense and remove entanglements spread along flexible DNA strands of up to 3,000 nm long. Here we propose a mechanism for this, based on the higher rate of colli ...
modification of gene expression
... sequence of DNA bases. • SINGLE NUCLEOTIDE POLYMORPHISMS (SNPs) - Single nucleotide change at a specific location in DNA • These small differences in DNA result in small differences in the proteins made by cells, and contribute to each person’s unique ...
... sequence of DNA bases. • SINGLE NUCLEOTIDE POLYMORPHISMS (SNPs) - Single nucleotide change at a specific location in DNA • These small differences in DNA result in small differences in the proteins made by cells, and contribute to each person’s unique ...
Biotoxins
... host by well established physiological means. §III-F-4. Those that consist entirely of DNA from an eukaryotic host including its chloroplasts, mitochondria, or plasmids (but excluding viruses) when propagated only in that host (or a closely related strain of the same species). §III-F-5. Those that c ...
... host by well established physiological means. §III-F-4. Those that consist entirely of DNA from an eukaryotic host including its chloroplasts, mitochondria, or plasmids (but excluding viruses) when propagated only in that host (or a closely related strain of the same species). §III-F-5. Those that c ...
gal
... – …bacteria also have plasmids (T Plasmids) that they transfer to other organisms, – …upon infection, the T plasmid enters the host cell, becomes incorporated in the host genome, and the T plasmid genes become expressed, – …Agrobacterium tumefaceins transfers genes that force plants to make strange ...
... – …bacteria also have plasmids (T Plasmids) that they transfer to other organisms, – …upon infection, the T plasmid enters the host cell, becomes incorporated in the host genome, and the T plasmid genes become expressed, – …Agrobacterium tumefaceins transfers genes that force plants to make strange ...
Preview from Notesale.co.uk Page 12 of 32
... Forensic Science Exam Notes Kastle-Meyer (KM) Test (presumptive or screening) A simple colour indicating test to determine if substance IS blood or NOT ...
... Forensic Science Exam Notes Kastle-Meyer (KM) Test (presumptive or screening) A simple colour indicating test to determine if substance IS blood or NOT ...
1. (a) When a cell divides, the genetic material can divide by mitosis
... which are located on different chromosomes. The dominant allele of one gene, G, controls the production of enzyme G which converts a precursor to linamarin. The dominant allele of the other gene, E, controls the production of enzyme E which converts linamarin to hydrogen cyanide. This is summarised ...
... which are located on different chromosomes. The dominant allele of one gene, G, controls the production of enzyme G which converts a precursor to linamarin. The dominant allele of the other gene, E, controls the production of enzyme E which converts linamarin to hydrogen cyanide. This is summarised ...
PATENT PROTECTION FOR GENE SEQUENCES WHAT IS
... proteins copy onto the mRNA strand, which allows for the production of the proteins after a translation process. • *RNA is similar to DNA, but uracil substitutes for adenine and ribose substitutes for deoxyribose. ...
... proteins copy onto the mRNA strand, which allows for the production of the proteins after a translation process. • *RNA is similar to DNA, but uracil substitutes for adenine and ribose substitutes for deoxyribose. ...
60Ch14DNAhistory2008..
... developed double helix model of DNA other leading scientists working on question: ...
... developed double helix model of DNA other leading scientists working on question: ...
Unoshan_project
... The results of fiber and single crystal x-ray crystallographic studies have shown that DNA can have several conformations. The most common one is called B-DNA. B-DNA ...
... The results of fiber and single crystal x-ray crystallographic studies have shown that DNA can have several conformations. The most common one is called B-DNA. B-DNA ...
Molecular structure of nucleic acids. A Structure for Deoxyribose
... has novel features which are of considerable biological interest. A structure for nucleic acid has already been proposed by Pauling and Corey [1]. Their model consists of three intertwined chains, with the phosphates near the fibre axis, and the bases on the outside. We wish to put forward a radical ...
... has novel features which are of considerable biological interest. A structure for nucleic acid has already been proposed by Pauling and Corey [1]. Their model consists of three intertwined chains, with the phosphates near the fibre axis, and the bases on the outside. We wish to put forward a radical ...
History of DNA DNA History 14-15
... developed double helix model of DNA other leading scientists working on question: ...
... developed double helix model of DNA other leading scientists working on question: ...
DNA ppt notes 2015
... Significance James Watson, Francis Crick, and Maurice Wilkins jointly received the Nobel Prize in 1962 for their determination of the structure of DNA. What is interesting about this fact is that Rosalind Franklin had as much to do with the discovery as the other three gentlemen with her work with X ...
... Significance James Watson, Francis Crick, and Maurice Wilkins jointly received the Nobel Prize in 1962 for their determination of the structure of DNA. What is interesting about this fact is that Rosalind Franklin had as much to do with the discovery as the other three gentlemen with her work with X ...
Cells and DNA Table of Contents
... genes are the same in all people, but a small number of genes (less than 1 percent of the total) are slightly different between people. Alleles are forms of the same gene with small differences in their sequence of DNA bases. These small differences contribute to each person’s unique physical featur ...
... genes are the same in all people, but a small number of genes (less than 1 percent of the total) are slightly different between people. Alleles are forms of the same gene with small differences in their sequence of DNA bases. These small differences contribute to each person’s unique physical featur ...
Nucleic acid double helix

In molecular biology, the term double helix refers to the structure formed by double-stranded molecules of nucleic acids such as DNA. The double helical structure of a nucleic acid complex arises as a consequence of its secondary structure, and is a fundamental component in determining its tertiary structure. The term entered popular culture with the publication in 1968 of The Double Helix: A Personal Account of the Discovery of the Structure of DNA, by James Watson.The DNA double helix polymer of nucleic acids, held together by nucleotides which base pair together. In B-DNA, the most common double helical structure, the double helix is right-handed with about 10–10.5 base pairs per turn. This translates into about 20-21 nucleotides per turn. The double helix structure of DNA contains a major groove and minor groove. In B-DNA the major groove is wider than the minor groove. Given the difference in widths of the major groove and minor groove, many proteins which bind to B-DNA do so through the wider major groove.