CHEMISTRY IM 06 SYLLABUS
... themselves how chemists work. It may not be possible for students following this course to participate actively in laboratory work: to make up for this, tutors should be very generous with experimental demonstrations. The syllabus is organised in two sections, namely Chemical Principles and Descript ...
... themselves how chemists work. It may not be possible for students following this course to participate actively in laboratory work: to make up for this, tutors should be very generous with experimental demonstrations. The syllabus is organised in two sections, namely Chemical Principles and Descript ...
CHEMISTRY IM 06 SYLLABUS
... themselves how chemists work. It may not be possible for students following this course to participate actively in laboratory work: to make up for this, tutors should be very generous with experimental demonstrations. The syllabus is organised in two sections, namely Chemical Principles and Descript ...
... themselves how chemists work. It may not be possible for students following this course to participate actively in laboratory work: to make up for this, tutors should be very generous with experimental demonstrations. The syllabus is organised in two sections, namely Chemical Principles and Descript ...
Chapter 10_Handouts_6
... definite proportions. In a mixture, the components are not present in a specific ratio by mass. ...
... definite proportions. In a mixture, the components are not present in a specific ratio by mass. ...
Chapter 10 Handouts_1
... 10-7. The Periodic Table The Russian chemist Dmitri Mendeleev formulated the periodic law about 1869 which states that when elements are listed in order of atomic number, elements with similar chemical and physical properties appear at regular intervals. The periodic table is a listing of the eleme ...
... 10-7. The Periodic Table The Russian chemist Dmitri Mendeleev formulated the periodic law about 1869 which states that when elements are listed in order of atomic number, elements with similar chemical and physical properties appear at regular intervals. The periodic table is a listing of the eleme ...
File
... 1) How many different substances are described on the “left side” of the equation? 2) How many different substances described on the “right side” of the equation? 3) What does this tell me? I can look at an equation to see if a change is chemical or physical. In this case, since a new substance is f ...
... 1) How many different substances are described on the “left side” of the equation? 2) How many different substances described on the “right side” of the equation? 3) What does this tell me? I can look at an equation to see if a change is chemical or physical. In this case, since a new substance is f ...
Chapter 10 Handouts - Bakersfield College
... 10-7. The Periodic Table The Russian chemist Dmitri Mendeleev formulated the periodic law about 1869 which states that when elements are listed in order of atomic number, elements with similar chemical and physical properties appear at regular intervals. The periodic table is a listing of the elemen ...
... 10-7. The Periodic Table The Russian chemist Dmitri Mendeleev formulated the periodic law about 1869 which states that when elements are listed in order of atomic number, elements with similar chemical and physical properties appear at regular intervals. The periodic table is a listing of the elemen ...
3.032 Mechanical Behavior of Materials Fall 2007
... Courtesy of Sidney Yip. Used with permission. ...
... Courtesy of Sidney Yip. Used with permission. ...
atom a very small particle that makes up most kinds of matters and
... up most kinds of matters and consists of smaller parts called protons, neutrons and electrons. the basic building block of matter - the smallest particle of an element that still has all the properties of that element a number equal to the sum of the number of protons and neutron in an atom’s nucleu ...
... up most kinds of matters and consists of smaller parts called protons, neutrons and electrons. the basic building block of matter - the smallest particle of an element that still has all the properties of that element a number equal to the sum of the number of protons and neutron in an atom’s nucleu ...
Molecules, Compounds, and Chemical Equations (Chapter 3)
... % C and x determined from amount of CO2 produced % H and y determined from amount of H2O produced % O (if present) and z must be determined by difference ...
... % C and x determined from amount of CO2 produced % H and y determined from amount of H2O produced % O (if present) and z must be determined by difference ...
Grade 10 NSC Chemistry Curriculum
... sharing of electrons in the formation of a covalent bond, single, double and triple bonds electron diagrams of simple covalent molecules, names and formulae of covalent compounds. • Ionic bonding: transfer of electrons in the formation of ionic bonding, cations and anions, electron diagrams of simpl ...
... sharing of electrons in the formation of a covalent bond, single, double and triple bonds electron diagrams of simple covalent molecules, names and formulae of covalent compounds. • Ionic bonding: transfer of electrons in the formation of ionic bonding, cations and anions, electron diagrams of simpl ...
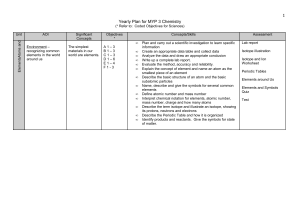
Yearly Plan for MYP 1 Science
... everyday lives. In a chemical change, elements are rearranged to form new compounds. We represent chemical changes with chemical equations. Amounts of chemicals used and produced in chemical changes can be calculated by using moles. ...
... everyday lives. In a chemical change, elements are rearranged to form new compounds. We represent chemical changes with chemical equations. Amounts of chemicals used and produced in chemical changes can be calculated by using moles. ...
Review 3rd Qtr KEY
... Given calculations with the calculator answer, write the answers with the appropriate # of significant figures. ...
... Given calculations with the calculator answer, write the answers with the appropriate # of significant figures. ...
SOL Essential Knowledge
... a positive charge (cation). 6. Gain of electrons by a neutral atom results in the formation of an ion with negative charge (anion). F. State and identify the location of the following on the periodic table: alkali metals, alkaline earth metals, transition metals, halogens, chalcogens, noble gases, a ...
... a positive charge (cation). 6. Gain of electrons by a neutral atom results in the formation of an ion with negative charge (anion). F. State and identify the location of the following on the periodic table: alkali metals, alkaline earth metals, transition metals, halogens, chalcogens, noble gases, a ...
3 - Greene County ESC
... Students demonstrate an understanding of the composition of physical systems and the concepts and principles that describe and predict physical interactions and events in the natural world. This includes demonstrating an understanding of the structure and properties of matter, the properties of mate ...
... Students demonstrate an understanding of the composition of physical systems and the concepts and principles that describe and predict physical interactions and events in the natural world. This includes demonstrating an understanding of the structure and properties of matter, the properties of mate ...
Lecture 3 Chemistry
... To understand the way living things function, it is necessary to understand basic chemical processes ...
... To understand the way living things function, it is necessary to understand basic chemical processes ...
Final Exam Class Review - Mrs. Kittrell`s Science Classes
... – Pure substances are substances with a fixed ...
... – Pure substances are substances with a fixed ...
water, h2o
... concerted transfer over multiple oxygen centers. The excess mobility of the proton arises simply from the increased step size of the random walk, i.e., diffusion, as the proton charge is moved across the diameter of a single water molecule (≈2.5 Å) in about 1 ps, the Debye (rotational) relaxation ti ...
... concerted transfer over multiple oxygen centers. The excess mobility of the proton arises simply from the increased step size of the random walk, i.e., diffusion, as the proton charge is moved across the diameter of a single water molecule (≈2.5 Å) in about 1 ps, the Debye (rotational) relaxation ti ...
Seminars and Public Lecture by Professor Mamoun M. Bader
... 9.00 am 12 January 2010 (Tuesday) Seminar Hall, Institute Ibnu Sina, UTM This talk will be mainly focus on how computational methods can be used in identifying target molecules worth pursuing synthetically for electronic applications. Electronic and geometric structures are computed for series of st ...
... 9.00 am 12 January 2010 (Tuesday) Seminar Hall, Institute Ibnu Sina, UTM This talk will be mainly focus on how computational methods can be used in identifying target molecules worth pursuing synthetically for electronic applications. Electronic and geometric structures are computed for series of st ...
Earth System - Mineral Identification
... 4. What word describes the material involved in a streak test? a. Fractured b. Powdered c. Scratched d. Liquid 5. What tool would you need discover whether a mineral has fracture? a. A hammer b. A file c. A grinder d. A harder mineral ...
... 4. What word describes the material involved in a streak test? a. Fractured b. Powdered c. Scratched d. Liquid 5. What tool would you need discover whether a mineral has fracture? a. A hammer b. A file c. A grinder d. A harder mineral ...
Lecture 5 (2.1-2.3)
... – Boyle (17th century) – “… simple bodies not made of any other bodies …” – Lavoisier (18th century) – natural laws – Dalton’s atomic theory (19th century) – Atomic structure (20th century) ...
... – Boyle (17th century) – “… simple bodies not made of any other bodies …” – Lavoisier (18th century) – natural laws – Dalton’s atomic theory (19th century) – Atomic structure (20th century) ...
Microbial Metabolism
... Nitrogen (NH3, NO3-, organic N-compounds) Phosphorus (PO43-) Sulfur (H2S, SO42-, organic compounds) Potassium (K+) Magnesium (Mg2+, salts) Sodium (Na+) Calcium (Ca2+, salts) Iron (Fe3+, Fe2+, or salts) ...
... Nitrogen (NH3, NO3-, organic N-compounds) Phosphorus (PO43-) Sulfur (H2S, SO42-, organic compounds) Potassium (K+) Magnesium (Mg2+, salts) Sodium (Na+) Calcium (Ca2+, salts) Iron (Fe3+, Fe2+, or salts) ...
pretest - Allen County Schools
... 8. The temperature at which a substance changes from a solid to a liquid is its… a. boiling point c. sublimation point b. melting point d. evaporation point 9. The temperature at which a liquid changes into a liquid to a solid is its… a. boiling point c. sublimation point b. melting point d. freezin ...
... 8. The temperature at which a substance changes from a solid to a liquid is its… a. boiling point c. sublimation point b. melting point d. evaporation point 9. The temperature at which a liquid changes into a liquid to a solid is its… a. boiling point c. sublimation point b. melting point d. freezin ...
Chapt3
... % C and x determined from amount of CO2 produced % H and y determined from amount of H2O produced % O (if present) and z must be determined by difference ...
... % C and x determined from amount of CO2 produced % H and y determined from amount of H2O produced % O (if present) and z must be determined by difference ...