Molecular Geometry Why?
... is based on the premise that electrons around a central atom repel each other. Electron domains are areas of high electron density such as bonds (single, double or triple) and lone-pairs of electrons. In simple terms VSEPR means that all electron bonding domains and electron nonbonding domains aroun ...
... is based on the premise that electrons around a central atom repel each other. Electron domains are areas of high electron density such as bonds (single, double or triple) and lone-pairs of electrons. In simple terms VSEPR means that all electron bonding domains and electron nonbonding domains aroun ...
The atomic packing factor
... University of Babylon , College of Engineering , Eng. Materials, Maithem H - Rasheed ...
... University of Babylon , College of Engineering , Eng. Materials, Maithem H - Rasheed ...
Abstract - BMB Reports
... attractive target for the development of antibiotics against protozoa, bacteria, and fungi and also widely used to produce various high-value stereoisomers in the chemical and pharmaceutical industry. In this study, crystal structures of class II Escherichia coli FBA (EcFBA) were determined from fou ...
... attractive target for the development of antibiotics against protozoa, bacteria, and fungi and also widely used to produce various high-value stereoisomers in the chemical and pharmaceutical industry. In this study, crystal structures of class II Escherichia coli FBA (EcFBA) were determined from fou ...
Summary The properties of chiral molecules can be different in living
... monopolization of large (S)-2 crystals and vice versa. The large crystals can then be separated by applying a simple washing step in which the small crystals of the undesired handedness are washed away, yielding an enantiopure solid phase of large crystals. The findings so far also touch on the fund ...
... monopolization of large (S)-2 crystals and vice versa. The large crystals can then be separated by applying a simple washing step in which the small crystals of the undesired handedness are washed away, yielding an enantiopure solid phase of large crystals. The findings so far also touch on the fund ...
Effect of Hippuric Acid on the Growth, Structural and Optical
... Abstract: Non-linear optical potassium dihydrogen phosphate (KDP) and ammonium dihydrogen phosphate (ADP) single crystals with 1 mol% of hippuric acid dopant were grown from aqueous solution by employing slow evaporation technique. With appropriate dopants, the KDP and ADP crystals exhibit several d ...
... Abstract: Non-linear optical potassium dihydrogen phosphate (KDP) and ammonium dihydrogen phosphate (ADP) single crystals with 1 mol% of hippuric acid dopant were grown from aqueous solution by employing slow evaporation technique. With appropriate dopants, the KDP and ADP crystals exhibit several d ...
IOSR Journal of Applied Physics (IOSR-JAP)
... Βeta Alanine Thiourea Oxalate single crystals were grown succesfully using slow evaporation solution growth method. BATO crystallized in monoclinic structure and the unitcell parameters were found out from single cell X-ray diffraction analysis. Powder X-ray diffraction pattern revealed the good cry ...
... Βeta Alanine Thiourea Oxalate single crystals were grown succesfully using slow evaporation solution growth method. BATO crystallized in monoclinic structure and the unitcell parameters were found out from single cell X-ray diffraction analysis. Powder X-ray diffraction pattern revealed the good cry ...
Free electron theory of metals
... • Crystal looks like positive ion cores of charge +e embedded in a sea of conduction electrons • Conduction electrons can interact with each other and ion cores but these interactions are weak because: ...
... • Crystal looks like positive ion cores of charge +e embedded in a sea of conduction electrons • Conduction electrons can interact with each other and ion cores but these interactions are weak because: ...
EBSD: Current state, prospects and comparison with XRD
... bands in the diffraction pattern is so reduced to the simpler task of searching for isolated peaks. The “butterfly peak” is localized by a peak search with constraints or by evaluating some coefficients of a 1D FFT of this Radon domain [18]. The Hough transform [19] was established for the detection ...
... bands in the diffraction pattern is so reduced to the simpler task of searching for isolated peaks. The “butterfly peak” is localized by a peak search with constraints or by evaluating some coefficients of a 1D FFT of this Radon domain [18]. The Hough transform [19] was established for the detection ...
the development of a diver deployed x
... energy. The energy of the x-ray must be greater than the binding energy of the inner shell electron. Compton scattering dominates at higher x-ray energies. In this mechanism, x-rays interact with an outer shell electron which is ejected from the atom. The incident x-ray is scattered in a different d ...
... energy. The energy of the x-ray must be greater than the binding energy of the inner shell electron. Compton scattering dominates at higher x-ray energies. In this mechanism, x-rays interact with an outer shell electron which is ejected from the atom. The incident x-ray is scattered in a different d ...
Structure of Bacillus halmapalus α-amylase crystallized with and
... Interestingly, the structure of a maltohexaose-producing G6amylase from the alkalophilic Bacillus sp. 707 (which shares 85% sequence identity with BHA) has also been solved (Kanai et al., 2004) after crystallization from 2-methylpentane-2,4-diol and phosphate at pH 8.5. The active binding sites are ...
... Interestingly, the structure of a maltohexaose-producing G6amylase from the alkalophilic Bacillus sp. 707 (which shares 85% sequence identity with BHA) has also been solved (Kanai et al., 2004) after crystallization from 2-methylpentane-2,4-diol and phosphate at pH 8.5. The active binding sites are ...
What is a Mineral?
... A mineral is a natural, usually inorganic solid that has a characteristic chemical composition, an orderly internal structure, and a characteristic set of physical properties. ...
... A mineral is a natural, usually inorganic solid that has a characteristic chemical composition, an orderly internal structure, and a characteristic set of physical properties. ...
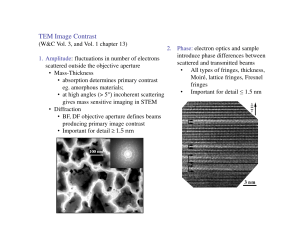
TEM Image Contrast
... Density and thickness determine contrast. • At high detector angles STEM mode: Z-contrast imaging annular dark field detector (ADF) or high angle ADF detects electrons scattered through larger angles than for diffraction. Absorption varies with degree of diffraction • away from strong Bragg diffract ...
... Density and thickness determine contrast. • At high detector angles STEM mode: Z-contrast imaging annular dark field detector (ADF) or high angle ADF detects electrons scattered through larger angles than for diffraction. Absorption varies with degree of diffraction • away from strong Bragg diffract ...
MINERALS
... • Naturally occurring • Inorganic (never alive) • Definite chemical composition • Crystal structure because of the internal arrangement of atoms A mineral is the building block of rocks ...
... • Naturally occurring • Inorganic (never alive) • Definite chemical composition • Crystal structure because of the internal arrangement of atoms A mineral is the building block of rocks ...
Symmetry - West Virginia University
... 5-fold, 7-fold and other symmetries are not possible in crystals, because you can’t fill space with 5-sided objects ...
... 5-fold, 7-fold and other symmetries are not possible in crystals, because you can’t fill space with 5-sided objects ...
Chapter505.ppt
... • Atoms of different minerals are clustered into geometric forms such as cubes, bricks, hexagons, etc. and so the shape a crystal has is essentially a reflection of the orderly three-dimensional stacking of these tiny geometric forms. ...
... • Atoms of different minerals are clustered into geometric forms such as cubes, bricks, hexagons, etc. and so the shape a crystal has is essentially a reflection of the orderly three-dimensional stacking of these tiny geometric forms. ...
Atoms, Molecules and Minerals
... – Evaporite Minerals (seawater evaporation) • Gypsum - CaSO4-2H2O ...
... – Evaporite Minerals (seawater evaporation) • Gypsum - CaSO4-2H2O ...
Heat load estimates for XFEL beamline optics
... take longer to remove the heat from the centre of the beam footprint compared to areas on the edge that still have very high thermal diffusivity. The temperature profile will be therefore different from equation (1) and will qualitatively change its shape during the pulse train. To model this non-tr ...
... take longer to remove the heat from the centre of the beam footprint compared to areas on the edge that still have very high thermal diffusivity. The temperature profile will be therefore different from equation (1) and will qualitatively change its shape during the pulse train. To model this non-tr ...
Differentiation of Igneous Rocks: Crystal Fractionation and Layered
... He thought all igneous rocks came from a basaltic parent; mainly by crystal fractionation His idea was too extreme, but very important as a starting point This is the origin of Bowen’s Reaction Series - see handout from before ...
... He thought all igneous rocks came from a basaltic parent; mainly by crystal fractionation His idea was too extreme, but very important as a starting point This is the origin of Bowen’s Reaction Series - see handout from before ...
Transmission Electron Microscopy of Mineralogy
... Mineralogy, Springer-Verlag, This book changed the aspect of mineralogy. ...
... Mineralogy, Springer-Verlag, This book changed the aspect of mineralogy. ...
0378.PDF
... of lattice planes doesn't fit after slippage, or transformations to crystals and approximants. It turns out that the types of defects in the quasicrystal are indeed different from those of the monatomic crystal, but similar to those in the binary crystal. The relation between the shock wave velocity ...
... of lattice planes doesn't fit after slippage, or transformations to crystals and approximants. It turns out that the types of defects in the quasicrystal are indeed different from those of the monatomic crystal, but similar to those in the binary crystal. The relation between the shock wave velocity ...
Synthesis, Growth and characterization of L-Histidine
... FT-IR 8400s by the KBr pellet technique in the range 4000-400cm-1. The optical transmission spectrum of the crystal was carried out using a Lambda 35 model perkin Elmer double beam UV-Vis-NIR spectrophotometer. The Thermo Gravimetric Analysis (TGA) and Differential Thermal Analysis (DTA) were carrie ...
... FT-IR 8400s by the KBr pellet technique in the range 4000-400cm-1. The optical transmission spectrum of the crystal was carried out using a Lambda 35 model perkin Elmer double beam UV-Vis-NIR spectrophotometer. The Thermo Gravimetric Analysis (TGA) and Differential Thermal Analysis (DTA) were carrie ...
(LHS), A Novel Organic NLO Material
... (NLO) materials has been given much importance due to their significant impact in various fields like waveguides, frequency conversion devices, optical switching, parametric oscillators etc. [1-3]. Organic nonlinear optical materials have been of particular interest since they have large optical sus ...
... (NLO) materials has been given much importance due to their significant impact in various fields like waveguides, frequency conversion devices, optical switching, parametric oscillators etc. [1-3]. Organic nonlinear optical materials have been of particular interest since they have large optical sus ...
Lecture 25 – The Solid State: types of crystals, lattice energies and
... It should be realized that the value of any ionic radius only serves as a useful but approximate size of the ion.. The fact that the ionic radius of Na+ is 0.98Å does not mean that the electron cloud of the ion never extends beyond this value. It is significant because when it is added together with ...
... It should be realized that the value of any ionic radius only serves as a useful but approximate size of the ion.. The fact that the ionic radius of Na+ is 0.98Å does not mean that the electron cloud of the ion never extends beyond this value. It is significant because when it is added together with ...
Isomeric forms of Cu(quinoline-2-carboxylate) O Spectroscopic and magnetic properties H
... assigned to the dxz, dyz → dx2 – y2 and dz2 → dx2 – y2 transitions on the basis of the information reported by Hathaway et al. [15]. A strong bonding of the ν(OH) stretching region, observed at 3294 cm–1, is in good agreement with polymeric intermolecular O–H...O association [16], confirmed by the X ...
... assigned to the dxz, dyz → dx2 – y2 and dz2 → dx2 – y2 transitions on the basis of the information reported by Hathaway et al. [15]. A strong bonding of the ν(OH) stretching region, observed at 3294 cm–1, is in good agreement with polymeric intermolecular O–H...O association [16], confirmed by the X ...
Session #20: Homework Solutions
... (3) edge dislocations → explain slip; visible as etch pits and in X–ray topography (4) grain boundaries → visible in reflected light; evidence by X–ray diffraction (5) micro–precipitates → visible in X–ray transmission, IR transmission Problem #5 Attempt to account for the fact that polycrystalline ...
... (3) edge dislocations → explain slip; visible as etch pits and in X–ray topography (4) grain boundaries → visible in reflected light; evidence by X–ray diffraction (5) micro–precipitates → visible in X–ray transmission, IR transmission Problem #5 Attempt to account for the fact that polycrystalline ...
X-ray crystallography

X-ray crystallography is a tool used for identifying the atomic and molecular structure of a crystal, in which the crystalline atoms cause a beam of incident X-rays to diffract into many specific directions. By measuring the angles and intensities of these diffracted beams, a crystallographer can produce a three-dimensional picture of the density of electrons within the crystal. From this electron density, the mean positions of the atoms in the crystal can be determined, as well as their chemical bonds, their disorder and various other information.Since many materials can form crystals—such as salts, metals, minerals, semiconductors, as well as various inorganic, organic and biological molecules—X-ray crystallography has been fundamental in the development of many scientific fields. In its first decades of use, this method determined the size of atoms, the lengths and types of chemical bonds, and the atomic-scale differences among various materials, especially minerals and alloys. The method also revealed the structure and function of many biological molecules, including vitamins, drugs, proteins and nucleic acids such as DNA. X-ray crystallography is still the chief method for characterizing the atomic structure of new materials and in discerning materials that appear similar by other experiments. X-ray crystal structures can also account for unusual electronic or elastic properties of a material, shed light on chemical interactions and processes, or serve as the basis for designing pharmaceuticals against diseases.In a single-crystal X-ray diffraction measurement, a crystal is mounted on a goniometer. The goniometer is used to position the crystal at selected orientations. The crystal is bombarded with a finely focused monochromatic beam of X-rays, producing a diffraction pattern of regularly spaced spots known as reflections. The two-dimensional images taken at different rotations are converted into a three-dimensional model of the density of electrons within the crystal using the mathematical method of Fourier transforms, combined with chemical data known for the sample. Poor resolution (fuzziness) or even errors may result if the crystals are too small, or not uniform enough in their internal makeup.X-ray crystallography is related to several other methods for determining atomic structures. Similar diffraction patterns can be produced by scattering electrons or neutrons, which are likewise interpreted by Fourier transformation. If single crystals of sufficient size cannot be obtained, various other X-ray methods can be applied to obtain less detailed information; such methods include fiber diffraction, powder diffraction and (if the sample is not crystallized) small-angle X-ray scattering (SAXS).If the material under investigation is only available in the form of nanocrystalline powders or suffers from poor crystallinity, the methods of electron crystallography can be applied for determining the atomic structure.For all above mentioned X-ray diffraction methods, the scattering is elastic; the scattered X-rays have the same wavelength as the incoming X-ray. By contrast, inelastic X-ray scattering methods are useful in studying excitations of the sample, rather than the distribution of its atoms.