Microbial endemism: does phosphorus limitation enhance speciation?
... paradoxical, as microorganisms reproduce by binary fission and therefore are ‘natural cloners’. Thus, every new microbial lineage would seem to be a new ‘species’. However, because of the widespread occurrence of horizontal gene transfer (HGT), this is not the case2. Although HGT provides an importa ...
... paradoxical, as microorganisms reproduce by binary fission and therefore are ‘natural cloners’. Thus, every new microbial lineage would seem to be a new ‘species’. However, because of the widespread occurrence of horizontal gene transfer (HGT), this is not the case2. Although HGT provides an importa ...
Segregating Variation in the Transcriptome: Cis Regulation and
... genetically variable genes: ‘‘development,’’ ‘‘regulation,’’ ‘‘metabolism,’’ and ‘‘cell communication’’ for biological process and ‘‘catalytic (enzymatic) activity,’’ ‘‘signal transduction,’’ ‘‘regulation of transcription,’’ and ‘‘structural molecule’’ for molecular function (Rifkin et al. 2003). We ...
... genetically variable genes: ‘‘development,’’ ‘‘regulation,’’ ‘‘metabolism,’’ and ‘‘cell communication’’ for biological process and ‘‘catalytic (enzymatic) activity,’’ ‘‘signal transduction,’’ ‘‘regulation of transcription,’’ and ‘‘structural molecule’’ for molecular function (Rifkin et al. 2003). We ...
Epigenetic inheritance speeds up evolution of artificial organisms
... current target by switching between different stable states of its regulation network. To this aim, evolution should optimize the “epigenetic landscape” encoded by the regulation network and create pathways between the different local minima associated to the target phenotypes. All the details of th ...
... current target by switching between different stable states of its regulation network. To this aim, evolution should optimize the “epigenetic landscape” encoded by the regulation network and create pathways between the different local minima associated to the target phenotypes. All the details of th ...
1.18 Cellular Respiration
... Bread may be leavened (assisted to rise) by mixing live yeast cells with starches (in flour) and water. The yeast cells ferment the glucose (from the starch in flour) and release carbon dioxide and ethanol. Small bubbles of carbon dioxide gas cause the bread to rise, and the ethanol evaporates away ...
... Bread may be leavened (assisted to rise) by mixing live yeast cells with starches (in flour) and water. The yeast cells ferment the glucose (from the starch in flour) and release carbon dioxide and ethanol. Small bubbles of carbon dioxide gas cause the bread to rise, and the ethanol evaporates away ...
WHRHS BIOLOGY K PROFICIENCIES
... 46. Explain how Watson and Crick derived the DNA model. Discuss the importance of polymers to life. 47. Describe DNA replication. 48. Describe the 3 types of RNA and state function of each. 49. Compare and contrast DNA and RNA. 50. Explain how the order of nucleotides in DNA codes for different amin ...
... 46. Explain how Watson and Crick derived the DNA model. Discuss the importance of polymers to life. 47. Describe DNA replication. 48. Describe the 3 types of RNA and state function of each. 49. Compare and contrast DNA and RNA. 50. Explain how the order of nucleotides in DNA codes for different amin ...
UNIT I
... Structurally a sugar consists of a carbon backbone of three or more carbon atoms with either an aldehyde or carbonyl group on one carbon and hydroxyl groups on each of the other carbons. The most common monosaccharide is glucose, C6H12O6. Glucose is the form of sugar generally transported in the hum ...
... Structurally a sugar consists of a carbon backbone of three or more carbon atoms with either an aldehyde or carbonyl group on one carbon and hydroxyl groups on each of the other carbons. The most common monosaccharide is glucose, C6H12O6. Glucose is the form of sugar generally transported in the hum ...
Cell Division – Revision Pack (B3)
... organs; stem cells are an example of an ‘undifferentiated’ cell. Stem cells can be obtained from embryos and could be potentially used to treat many medical conditions including Parkinson’s disease and paralysis. Many people have a problem with the use of stem cells because they think that it’s wron ...
... organs; stem cells are an example of an ‘undifferentiated’ cell. Stem cells can be obtained from embryos and could be potentially used to treat many medical conditions including Parkinson’s disease and paralysis. Many people have a problem with the use of stem cells because they think that it’s wron ...
$doc.title
... be influenced by so many genes that it seems likely that the marker loci themselves would have individual or epistatic effects on fitness, thereby confounding the analysis and its interpretation. Thus, the classical approach to mapping bacterial genes is well suited to the ‘plus or minus’ phenotypes ...
... be influenced by so many genes that it seems likely that the marker loci themselves would have individual or epistatic effects on fitness, thereby confounding the analysis and its interpretation. Thus, the classical approach to mapping bacterial genes is well suited to the ‘plus or minus’ phenotypes ...
Life Science
... ● Identify populations within a community that are in competition with one another for resources ( DOK 2) ● Identify the factors that affect the number and types of organisms an ecosystem can support are food availability, abiotic factors such as quantity of light and water, temperature and temperat ...
... ● Identify populations within a community that are in competition with one another for resources ( DOK 2) ● Identify the factors that affect the number and types of organisms an ecosystem can support are food availability, abiotic factors such as quantity of light and water, temperature and temperat ...
Chapter 5 pages/jg - Sinauer Associates
... animals, and fungi. Invertebrate biology texts have traditionally treated the “protozoa,” and for many biology students this coverage will be their only detailed exposure to this important group of organisms. In this chapter we include those groups traditionally lumped under the name “protozoa” (i.e ...
... animals, and fungi. Invertebrate biology texts have traditionally treated the “protozoa,” and for many biology students this coverage will be their only detailed exposure to this important group of organisms. In this chapter we include those groups traditionally lumped under the name “protozoa” (i.e ...
Akashi+3_Genetica_98
... Codon usage is biased toward a subset of synonymous codons for each amino acid. In multi-cellular animals, tRNA abundances and gene expression levels can be tissue- and developmental-stage specific and are thus difficult to quantify. However, major codons correspond to abundant tRNAs for the three a ...
... Codon usage is biased toward a subset of synonymous codons for each amino acid. In multi-cellular animals, tRNA abundances and gene expression levels can be tissue- and developmental-stage specific and are thus difficult to quantify. However, major codons correspond to abundant tRNAs for the three a ...
Nonpolar region of phospholipid.
... 16) Microfilaments are thin strands of the contractile protein myosin. Answer: FALSE 17) Interstitial fluid represents one type of extracellular material. Answer: TRUE ...
... 16) Microfilaments are thin strands of the contractile protein myosin. Answer: FALSE 17) Interstitial fluid represents one type of extracellular material. Answer: TRUE ...
Biology I Course Syllabus
... d. Explain and describe how plant structures (vascular and nonvascular) and cellular functions are related to the survival of plants (e.g., movement of materials, plant reproduction). (DOK 1) Competency 6: Demonstrate an understanding of principles that explain the diversity of life and biological e ...
... d. Explain and describe how plant structures (vascular and nonvascular) and cellular functions are related to the survival of plants (e.g., movement of materials, plant reproduction). (DOK 1) Competency 6: Demonstrate an understanding of principles that explain the diversity of life and biological e ...
Biology for AIEEE - CET 2009-10
... In tobacco plant, combinations of alleles in eggs and pollen have been found to influence the reproductive compatibility of the plants. Homozygous combinations such as S1S1 do not develop because S1 pollen is not effective on S1 stigmas. S1 pollen, is however effective in S2S3 stigma. What progeny m ...
... In tobacco plant, combinations of alleles in eggs and pollen have been found to influence the reproductive compatibility of the plants. Homozygous combinations such as S1S1 do not develop because S1 pollen is not effective on S1 stigmas. S1 pollen, is however effective in S2S3 stigma. What progeny m ...
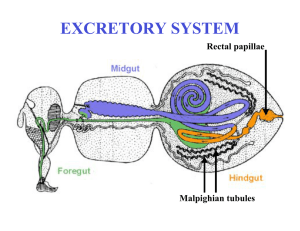
Excretory system - Faculty Support Site
... pigment, thus they appear yellow. Amino acids are derived from proteins in foods. They are used by cells for synthesis of new body protein or other nitrogen-containing molecules. The amino acids not used for synthesis are oxidized to generate energy or are converted to fats or carbohydrates that can ...
... pigment, thus they appear yellow. Amino acids are derived from proteins in foods. They are used by cells for synthesis of new body protein or other nitrogen-containing molecules. The amino acids not used for synthesis are oxidized to generate energy or are converted to fats or carbohydrates that can ...
glossary - McGraw Hill Higher Education
... endosperm of cereal grains that produces enzymes required for endosperm breakdown. algae A general name for unicellular, colonial or multicellular eukaryotic photosynthetic organisms of simple structure of marine and freshwater habitats. algal bloom A population explosion of ‘algal’ cells in water b ...
... endosperm of cereal grains that produces enzymes required for endosperm breakdown. algae A general name for unicellular, colonial or multicellular eukaryotic photosynthetic organisms of simple structure of marine and freshwater habitats. algal bloom A population explosion of ‘algal’ cells in water b ...
Adaptation in Natural Microbial Populations
... Plate Count Anomaly. Sequencing of the phylogenetic marker gene 16S rRNA gives broad insights into community composition and has become the most common approach for characterizing microbial diversity (Ward et al. 1990). However, it is also possible to sequence genes known to be involved in specific ...
... Plate Count Anomaly. Sequencing of the phylogenetic marker gene 16S rRNA gives broad insights into community composition and has become the most common approach for characterizing microbial diversity (Ward et al. 1990). However, it is also possible to sequence genes known to be involved in specific ...
Obj 2 & 3
... which obtain their energy by photosynthesis of light from the Sun, are eaten by small shrimp, which are then eaten by whales. However, the amount of energy that the phytoplankton have obtained from the Sun is far greater than the amount of energy available to the whales. Which of the following provi ...
... which obtain their energy by photosynthesis of light from the Sun, are eaten by small shrimp, which are then eaten by whales. However, the amount of energy that the phytoplankton have obtained from the Sun is far greater than the amount of energy available to the whales. Which of the following provi ...
Parasitology Glossary
... animate vector is involved, the vector itself seeks out the host and brings to it the parasite, as in African trypanosomiasis. (2) When an active, aggressive parasite is involved, the parasite itself seeks out the host and enters it, as in schistosomiasis. ...
... animate vector is involved, the vector itself seeks out the host and brings to it the parasite, as in African trypanosomiasis. (2) When an active, aggressive parasite is involved, the parasite itself seeks out the host and enters it, as in schistosomiasis. ...
01_Lecture_Presentation_PC
... DNA Structure and Function • Each chromosome has one long DNA molecule with hundreds or thousands of genes • Genes encode information for building proteins • DNA is inherited by offspring from their parents • DNA controls the development and maintenance of organisms ...
... DNA Structure and Function • Each chromosome has one long DNA molecule with hundreds or thousands of genes • Genes encode information for building proteins • DNA is inherited by offspring from their parents • DNA controls the development and maintenance of organisms ...
[edit] Introduction
... 4. Growth and Development 5. Reproduction o hereditary mechanisms to make more of self; DNA based. 6. Regulation, including homeostasis. 7. Evolution. ...
... 4. Growth and Development 5. Reproduction o hereditary mechanisms to make more of self; DNA based. 6. Regulation, including homeostasis. 7. Evolution. ...
EvoDevo and niche construction: building bridges
... often fed by external environmental cues, with each stage of development highly contingent on the state of the organism at the previous stage, and each cell’s activity dependent on the state of neighboring cells (Gilbert et al., ’96; Amundson, 2005; Kirschner and Gerhart, 2005). Second, even if it w ...
... often fed by external environmental cues, with each stage of development highly contingent on the state of the organism at the previous stage, and each cell’s activity dependent on the state of neighboring cells (Gilbert et al., ’96; Amundson, 2005; Kirschner and Gerhart, 2005). Second, even if it w ...
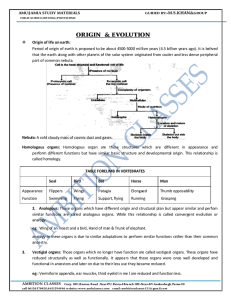
Now! - ambition classes
... 2. Analogous: Those organs which have different origin and structural plan but appear similar and perfom similar functions are called analogous organs. While this relationship is called convergent evolution or analogy. eg : Wing of an insect and a bird, Hand of man & Trunk of elephant. analogy in th ...
... 2. Analogous: Those organs which have different origin and structural plan but appear similar and perfom similar functions are called analogous organs. While this relationship is called convergent evolution or analogy. eg : Wing of an insect and a bird, Hand of man & Trunk of elephant. analogy in th ...
SBL100 for 2nd Semester 2014-1515 Slot C -
... symbiotic relationship inside another cell. The two organisms are known jointly as Cyanophora paradoxa. The ʺcyano‐ bacteriumʺ is in the process of dividing JGomes, SBS IITD ...
... symbiotic relationship inside another cell. The two organisms are known jointly as Cyanophora paradoxa. The ʺcyano‐ bacteriumʺ is in the process of dividing JGomes, SBS IITD ...
Biology lecture # 1 Levels of Life (From Atom to Biosphere)
... Molecules make organelles. Organelles are sub-cellular structures, assemble together to make cells – the units of life, e.g., mitochondria, lysosomes, Golgi bodies, nucleus. For example, mitochondria of a cell (Singular: mitochondrion) is called “powerhouse” of the cell. This organelle is present in ...
... Molecules make organelles. Organelles are sub-cellular structures, assemble together to make cells – the units of life, e.g., mitochondria, lysosomes, Golgi bodies, nucleus. For example, mitochondria of a cell (Singular: mitochondrion) is called “powerhouse” of the cell. This organelle is present in ...
Symbiogenesis

Symbiogenesis, or endosymbiotic theory, is an evolutionary theory that explains the origin of eukaryotic cells from prokaryotes. It states that several key organelles of eukaryotes originated as a symbiosis between separate single-celled organisms. According to this theory, mitochondria, plastids (for example chloroplasts), and possibly other organelles representing formerly free-living bacteria were taken inside another cell as an endosymbiont around 1.5 billion years ago. Molecular and biochemical evidence suggest that mitochondria developed from proteobacteria (in particular, Rickettsiales, the SAR11 clade, or close relatives) and chloroplasts from cyanobacteria (in particular, nitrogen-fixing filamentous cyanobacteria).
















![[edit] Introduction](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/009143166_1-ca023f871830add4513896e27ac21415-300x300.png)