Chenoweth Sociology Chapter 1 Vocabulary and Questions
... Vocabulary and Questions Directions: Please define and explain the terms, key people and questions below with complete thoughts. 1. Sociology: 2. Society: 3. Applied Sociology: 4. Social interaction: 5. Social integration: 6. Sociological perspective: 7. Functional analysis: 8. Theory: 9. Conflict T ...
... Vocabulary and Questions Directions: Please define and explain the terms, key people and questions below with complete thoughts. 1. Sociology: 2. Society: 3. Applied Sociology: 4. Social interaction: 5. Social integration: 6. Sociological perspective: 7. Functional analysis: 8. Theory: 9. Conflict T ...
Unit 1 - Cobb Learning
... script that suggests appropriate line, gesture and behavior Social structure – the larger structure of the play in which the roles are played ...
... script that suggests appropriate line, gesture and behavior Social structure – the larger structure of the play in which the roles are played ...
Lesson 45 Social Movements
... i. Government legalization of Unions in early 1900’s c. Bureaucratization: When the movement gains a formal structure in the Government. i. Growth of Labor Unions ...
... i. Government legalization of Unions in early 1900’s c. Bureaucratization: When the movement gains a formal structure in the Government. i. Growth of Labor Unions ...
Document
... to be shy, reserved, or introverted. They might begin by doing or saying one thing online and a member of the community will call them a troll. They then adopt the persona of troll and will browse online communities and instigate arguments. The internet gives them a sense of anonymity to become some ...
... to be shy, reserved, or introverted. They might begin by doing or saying one thing online and a member of the community will call them a troll. They then adopt the persona of troll and will browse online communities and instigate arguments. The internet gives them a sense of anonymity to become some ...
Society - anuppstu
... control system. On the other hand, government is the regulating system of society. 4. Both have distributing system. Bloodcirculating system in the biological organism and communication system is the counterpart for the society. ...
... control system. On the other hand, government is the regulating system of society. 4. Both have distributing system. Bloodcirculating system in the biological organism and communication system is the counterpart for the society. ...
theoretical perspectives
... society how these parts are functional (have beneficial consequences) or dysfunctional (have negative consequences) ...
... society how these parts are functional (have beneficial consequences) or dysfunctional (have negative consequences) ...
Sociology in Our Times The Essentials 3/e
... Directs attention to women’s experience and the importance of gender as an element of social structure. Assumes that gender is socially created and that change is essential for people to achieve their human potential without limits based on gender. ...
... Directs attention to women’s experience and the importance of gender as an element of social structure. Assumes that gender is socially created and that change is essential for people to achieve their human potential without limits based on gender. ...
Introduction to Sociology Chapter 1, Section 1
... Connect the larger world with personal life= sociological imagination. ...
... Connect the larger world with personal life= sociological imagination. ...
Introduction to Sociology
... Connect the larger world with personal life= sociological imagination. ...
... Connect the larger world with personal life= sociological imagination. ...
What is Knowledge Today power point
... in specific economic classes, social organizations or institutions, at least not institutions housed in brick and mortar. Instead, many social scientists today look to studies of media technologies, to studies of the differences between print (book) culture and digital culture, and to the fields of ...
... in specific economic classes, social organizations or institutions, at least not institutions housed in brick and mortar. Instead, many social scientists today look to studies of media technologies, to studies of the differences between print (book) culture and digital culture, and to the fields of ...
Welcome Lecture
... dynamics of society, and their intricate connections to patterns of human behavior and individual life changes. ...
... dynamics of society, and their intricate connections to patterns of human behavior and individual life changes. ...
SYA 4110 – Development of Sociological Thought Tuesday October
... The number and variety of structural changes within a society increase as institutions become larger, more embracing, and more interconnected. Change has sped up (FASTER!) in the modern era, and the changes have become far more consequential for all—for those who are in control of these enlarged org ...
... The number and variety of structural changes within a society increase as institutions become larger, more embracing, and more interconnected. Change has sped up (FASTER!) in the modern era, and the changes have become far more consequential for all—for those who are in control of these enlarged org ...
SOCIOLOGY STUDY GUIDE UNIT 1
... 3. Why are some relations easier to study than others? 4. What goals does Sociology share with the sciences? 5. Does Sociology give the solutions to problems directly? 6. What are social facts 7. List some social facts that could contribute to riots? 8. Describe the “Scientific Method”. 9. What did ...
... 3. Why are some relations easier to study than others? 4. What goals does Sociology share with the sciences? 5. Does Sociology give the solutions to problems directly? 6. What are social facts 7. List some social facts that could contribute to riots? 8. Describe the “Scientific Method”. 9. What did ...
Chapter 2 - HCC Learning Web
... Positivism-a need to make moral sense of society in a time of declining religious authority; social reform Herbert Spencer-Social Darwinism-survival of the fittest, liked status quo, did not believe sociology should be used for social reform. Harriet Martineau-translated Comte into English One of th ...
... Positivism-a need to make moral sense of society in a time of declining religious authority; social reform Herbert Spencer-Social Darwinism-survival of the fittest, liked status quo, did not believe sociology should be used for social reform. Harriet Martineau-translated Comte into English One of th ...
SOCIOLOGY
... SOCIOLOGY General Information: Sociology is the study of social life, social change, and the social cause and consequences of human behavior. Sociologists research the structure of groups, organizations, and societies; and people interaction within them. Though graduate work is required in order to ...
... SOCIOLOGY General Information: Sociology is the study of social life, social change, and the social cause and consequences of human behavior. Sociologists research the structure of groups, organizations, and societies; and people interaction within them. Though graduate work is required in order to ...
Sociological Imagination
... Resource-rich country Consumption-oriented culture (capitalism) Ability to access resources from foreign sources ...
... Resource-rich country Consumption-oriented culture (capitalism) Ability to access resources from foreign sources ...
Click here if you lost your Chapter 1 study guide
... imagination, a term introduced by C. Wright Mills, make a difference in your life? 11. How did Robert Merton divide functions? ...
... imagination, a term introduced by C. Wright Mills, make a difference in your life? 11. How did Robert Merton divide functions? ...
Chapter 1, Why Sociology?
... which its members interact and the degree to which they share beliefs, values and morals; suicide rates are lowest at intermediate levels of social solidarity and highest at low and high levels of social solidarity. ...
... which its members interact and the degree to which they share beliefs, values and morals; suicide rates are lowest at intermediate levels of social solidarity and highest at low and high levels of social solidarity. ...
Evolution of Management and Organizational Theory
... – Regardless what the researchers did, productivity went up – High morale was noticed – Informal organization important ...
... – Regardless what the researchers did, productivity went up – High morale was noticed – Informal organization important ...
What is Sociology anyways?
... How those relationships influence people’s behavior How societies develop and change ...
... How those relationships influence people’s behavior How societies develop and change ...
Unit 5 Study Guide - Eagan High School
... Unit 5 Study Guide Unit Objectives: 1. Students will understand the dimensions of social stratification and how the different contributing factors impact professions and individual’s places in society. 2. Students will understand the different ways in which rank is determined for creating social cla ...
... Unit 5 Study Guide Unit Objectives: 1. Students will understand the dimensions of social stratification and how the different contributing factors impact professions and individual’s places in society. 2. Students will understand the different ways in which rank is determined for creating social cla ...
PowerPoint
... determined who traded in the Spice Islands. • Because Japan is an island that is mostly mountainous, people live in densely populated areas along the coast. ...
... determined who traded in the Spice Islands. • Because Japan is an island that is mostly mountainous, people live in densely populated areas along the coast. ...
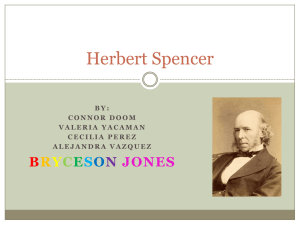
Herbert Spencer
... Out of nine siblings he was the only one to survive to adulthood He trained in civil engineering for railways but turned to journalism political writing in his early 20s His first book was titled Social Statics: The Conditions Essential to Human Happiness in which he predicted that humanity would ev ...
... Out of nine siblings he was the only one to survive to adulthood He trained in civil engineering for railways but turned to journalism political writing in his early 20s His first book was titled Social Statics: The Conditions Essential to Human Happiness in which he predicted that humanity would ev ...