Section 3 Theoretical Perspectives
... The Origins of Sociology (pages 14–22) Sociology is a young science. It started with the writings of European scholars like Auguste Comte, Harriet Spencer, Karl Marx, Emile Durkheim, and Max Weber. Jane Addams and W.E.B. Du Bois helped to focus America’s attention on social issues. After World War I ...
... The Origins of Sociology (pages 14–22) Sociology is a young science. It started with the writings of European scholars like Auguste Comte, Harriet Spencer, Karl Marx, Emile Durkheim, and Max Weber. Jane Addams and W.E.B. Du Bois helped to focus America’s attention on social issues. After World War I ...
Section 3 Theoretical Perspectives
... The Origins of Sociology (pages 14–22) Sociology is a young science. It started with the writings of European scholars like Auguste Comte, Harriet Spencer, Karl Marx, Emile Durkheim, and Max Weber. Jane Addams and W.E.B. Du Bois helped to focus America’s attention on social issues. After World War I ...
... The Origins of Sociology (pages 14–22) Sociology is a young science. It started with the writings of European scholars like Auguste Comte, Harriet Spencer, Karl Marx, Emile Durkheim, and Max Weber. Jane Addams and W.E.B. Du Bois helped to focus America’s attention on social issues. After World War I ...
What is Knowledge Today power point
... institutions, at least not institutions housed in brick and mortar. Instead, many social scientists today look to studies of media technologies, to studies of the differences between print (book) culture and digital culture, and to the fields of rhetoric and semiotics for an understanding of the way ...
... institutions, at least not institutions housed in brick and mortar. Instead, many social scientists today look to studies of media technologies, to studies of the differences between print (book) culture and digital culture, and to the fields of rhetoric and semiotics for an understanding of the way ...
Sociology AM 30
... Paper I is designed to test the candidates’ knowledge and understanding of the nature and contribution of sociology as a discipline. Candidates will answer three questions out of 5. Each question carries equal marks. Paper II will be divided into Part I and Part II. Part I is designed to test the ca ...
... Paper I is designed to test the candidates’ knowledge and understanding of the nature and contribution of sociology as a discipline. Candidates will answer three questions out of 5. Each question carries equal marks. Paper II will be divided into Part I and Part II. Part I is designed to test the ca ...
Social Interaction in Everyday Life
... To become more aware of the world we help create, Harold Garfinkel (1967) devised ethnomethodology, the study of the way people make sense of their surroundings Erving Goffman was another sociologist who analysed social interaction, explaining that people live their lives much like actors performing ...
... To become more aware of the world we help create, Harold Garfinkel (1967) devised ethnomethodology, the study of the way people make sense of their surroundings Erving Goffman was another sociologist who analysed social interaction, explaining that people live their lives much like actors performing ...
Sociology (SOCI) Social Sciences (SSCI)
... Sophomores and Social Sciences faculty explore: What questions do social scientists ask? What evidence and methods do they use? How does theory shape social science research? Prepares majors for upper-division coursework, prospective majors to explore the social sciences, and all students to be soci ...
... Sophomores and Social Sciences faculty explore: What questions do social scientists ask? What evidence and methods do they use? How does theory shape social science research? Prepares majors for upper-division coursework, prospective majors to explore the social sciences, and all students to be soci ...
Challenge and Change in Society
... • These are called ‘Roles’ • Roles range and change as we live our life • Roles are based on our ‘status’ in a group • Roles require ‘hierarchies’ • Roles can sometimes conflict – “Role Conflict” ...
... • These are called ‘Roles’ • Roles range and change as we live our life • Roles are based on our ‘status’ in a group • Roles require ‘hierarchies’ • Roles can sometimes conflict – “Role Conflict” ...
SOCIOLOGY Ninth Edition
... A society is a relatively integrated whole. A society tends to seek relative stability. Most aspects of a society contribute to the society’s well-being and survival. Society rests on the consensus of its members (consensus of values). Emphasizes the contributions/impacts of the functions of the soc ...
... A society is a relatively integrated whole. A society tends to seek relative stability. Most aspects of a society contribute to the society’s well-being and survival. Society rests on the consensus of its members (consensus of values). Emphasizes the contributions/impacts of the functions of the soc ...
Sociological Theories
... A required course in the sociology major & minor. Also recommended for students with interest in social philosophy and in the history in nineteenth and twentieth century social thought. The course is also recommended for students in American Studies as it treats, among other topics, Alexis de Tocque ...
... A required course in the sociology major & minor. Also recommended for students with interest in social philosophy and in the history in nineteenth and twentieth century social thought. The course is also recommended for students in American Studies as it treats, among other topics, Alexis de Tocque ...
Chapter 15 Vocabulary
... Urban ecology – the sociological approach to the study of cities. Concentric Zone model – a sociological model that describes a city as spreading from outward from the center, creating rings or zones around it. Sector Model – a sociological model that describes a city a spreading out in wedges rathe ...
... Urban ecology – the sociological approach to the study of cities. Concentric Zone model – a sociological model that describes a city as spreading from outward from the center, creating rings or zones around it. Sector Model – a sociological model that describes a city a spreading out in wedges rathe ...
SOCI 1100 Introduction to Sociology
... Barton County Community College assesses student learning at several levels: institutional, program, degree and classroom. The goal of these assessment activities is to improve student learning. As a student in this course, you will participate in various assessment activities. Results of these acti ...
... Barton County Community College assesses student learning at several levels: institutional, program, degree and classroom. The goal of these assessment activities is to improve student learning. As a student in this course, you will participate in various assessment activities. Results of these acti ...
SOC202 CONTEMPORARY SOCIOLOGICAL THEORY
... You are required to give one tutorial presentation (30% of your total mark), write one term paper (30% of your total mark), and sit an end of term examination (40% of your total mark). All work must be in English. Tutorial presentations should be clear, invite discussion and be between 25 and 30 mi ...
... You are required to give one tutorial presentation (30% of your total mark), write one term paper (30% of your total mark), and sit an end of term examination (40% of your total mark). All work must be in English. Tutorial presentations should be clear, invite discussion and be between 25 and 30 mi ...
What is Sociological Theory?
... people are contained—structures such as state, class, trade unions, and sweatshops. Sociologist’s role is to provide the info on which a reformist state can be established and make policy. Probably didn’t see herself as a member of a subordinate class (and why would she? She was rich) though wor ...
... people are contained—structures such as state, class, trade unions, and sweatshops. Sociologist’s role is to provide the info on which a reformist state can be established and make policy. Probably didn’t see herself as a member of a subordinate class (and why would she? She was rich) though wor ...
Durkheim`s Ideas
... Volume=Most people involved Intensity=Felt deeply about it Rigidity=Clearly defined Content=Religious & economic ...
... Volume=Most people involved Intensity=Felt deeply about it Rigidity=Clearly defined Content=Religious & economic ...
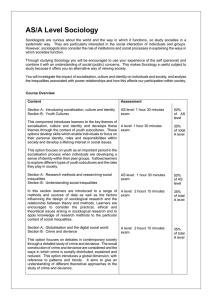
A Level Sociology
... systematic way. They are particularly interested in the social interaction of individuals and groups. However, sociologists also consider the role of institutions and social processes in explaining the ways in which societies function. Through studying Sociology you will be encouraged to use your ex ...
... systematic way. They are particularly interested in the social interaction of individuals and groups. However, sociologists also consider the role of institutions and social processes in explaining the ways in which societies function. Through studying Sociology you will be encouraged to use your ex ...
Making sense of reification - Liceo da Vinci
... a) Sociology of Knowledge studies how humans produce (social origin of Knowledge), distribute and use (social distribution of Knowledge) collective and individual knowledge (like science, religion, common sense, tradition, political ideology) for the purpose of sharing, dominating, creating and orga ...
... a) Sociology of Knowledge studies how humans produce (social origin of Knowledge), distribute and use (social distribution of Knowledge) collective and individual knowledge (like science, religion, common sense, tradition, political ideology) for the purpose of sharing, dominating, creating and orga ...
THE SOCIOLOGICAL SPIRIT (Second edition) Earl Babbie Chapter
... None of the paradigms is better than the other; each simply offers a different perspective that might be more or less useful for a given purpose. That’s the nature of paradigms. (21) There are three major paradigms commonly used in modern sociology. . . . The interactionist paradigm in sociology foc ...
... None of the paradigms is better than the other; each simply offers a different perspective that might be more or less useful for a given purpose. That’s the nature of paradigms. (21) There are three major paradigms commonly used in modern sociology. . . . The interactionist paradigm in sociology foc ...
Unit 1: All in the Family
... Structural Functionalism: • Society functions like a body; each part works independently to benefit the whole. • Is the sociological theory that attempts to explain how a society is organized to perform its required functions effectively • Is the oldest sociological theory, and also used by anthrop ...
... Structural Functionalism: • Society functions like a body; each part works independently to benefit the whole. • Is the sociological theory that attempts to explain how a society is organized to perform its required functions effectively • Is the oldest sociological theory, and also used by anthrop ...
Week 2
... develop within a harmony and with peaceful functions of all organs in it. Division, power, inequality and struggle should be studied. • This theory was developed as critical answer to functionalism. According to this theory, sociology has to look at how factors such as colour of skin, ethnic origin, ...
... develop within a harmony and with peaceful functions of all organs in it. Division, power, inequality and struggle should be studied. • This theory was developed as critical answer to functionalism. According to this theory, sociology has to look at how factors such as colour of skin, ethnic origin, ...
SOCI-101: Introduction to Sociology
... To interpret the extent of social inequality that exist in the United States. (Evaluation) To categorize the various social classes in America. (Synthesis) To distinguish relative from absolute deprivation. (Comprehension) To show the role of social class in terms of health values and family lifesty ...
... To interpret the extent of social inequality that exist in the United States. (Evaluation) To categorize the various social classes in America. (Synthesis) To distinguish relative from absolute deprivation. (Comprehension) To show the role of social class in terms of health values and family lifesty ...
Invisible colleges - University of Pennsylvania
... general model that would capture the essentials of the social aspectsof scientific change. The model was, in a sense, highly speculative. Our data at the time were very limited, It was an attempt to guess what the most general characteristics of the sociological processes of scientific growth might ...
... general model that would capture the essentials of the social aspectsof scientific change. The model was, in a sense, highly speculative. Our data at the time were very limited, It was an attempt to guess what the most general characteristics of the sociological processes of scientific growth might ...
sociol.perspective_
... terms of spatiality and sociality…in “position as a full-fledged member” …inside the group and outside, and as an insider has to a degree gained the trust and confidence of the group ? Does commitment come into play in the role of the stranger? Why or why not? Can you think of any examples from peop ...
... terms of spatiality and sociality…in “position as a full-fledged member” …inside the group and outside, and as an insider has to a degree gained the trust and confidence of the group ? Does commitment come into play in the role of the stranger? Why or why not? Can you think of any examples from peop ...
Chapter_1-1_PowerPoint-E
... • A viewing of the behavior of groups in a systematic way. • Allows you to see beyond your own day-today life by viewing the world through other’s eyes. • Can look beyond commonly held beliefs to the hidden meanings behind human actions. ...
... • A viewing of the behavior of groups in a systematic way. • Allows you to see beyond your own day-today life by viewing the world through other’s eyes. • Can look beyond commonly held beliefs to the hidden meanings behind human actions. ...