Science - edl.io
... Directions: Go to the Science Spot at http://sciencespot.net/ and click the Kid Zone graphic. Click “Biology” and then choose “Ecology and Environment”. Temperatures (highs/lows) Tundra ...
... Directions: Go to the Science Spot at http://sciencespot.net/ and click the Kid Zone graphic. Click “Biology” and then choose “Ecology and Environment”. Temperatures (highs/lows) Tundra ...
Sample 5.3.B.2 Complete
... 1. Understand that an ecosystem is a community of organisms that interact with one another and with their physical environment by a one-way flow of energy and a cycling of materials. 2. Describe how changes in one ecosystem, (for example, due to a natural disaster or extinction of a species) can hav ...
... 1. Understand that an ecosystem is a community of organisms that interact with one another and with their physical environment by a one-way flow of energy and a cycling of materials. 2. Describe how changes in one ecosystem, (for example, due to a natural disaster or extinction of a species) can hav ...
Chapter 4 here
... • Climate is caused by a combination of factors including the heat trapped in the atmosphere, the latitude, the transport of heat by winds and ocean currents, and the amount of precipitation in a region. The shape and elevation of the land also contributes to the local climate and global climate pat ...
... • Climate is caused by a combination of factors including the heat trapped in the atmosphere, the latitude, the transport of heat by winds and ocean currents, and the amount of precipitation in a region. The shape and elevation of the land also contributes to the local climate and global climate pat ...
No Slide Title
... The Carbon Cycle • Carbon - stored in the bodies of organisms as fat, oils, carbohydrates, etc. ; Released into the soil or air when the organisms dies. • Carbon molecules form deposits of coal, oil, or natural gas, which are known as fossil fuels. • Fossil fuels store carbon left over from bodies ...
... The Carbon Cycle • Carbon - stored in the bodies of organisms as fat, oils, carbohydrates, etc. ; Released into the soil or air when the organisms dies. • Carbon molecules form deposits of coal, oil, or natural gas, which are known as fossil fuels. • Fossil fuels store carbon left over from bodies ...
Biology Syllabus for Tallwood High School
... Unit II-3weeks-Ecology Students will: -explain the interaction among biotic and abiotic fators which contribute to homeostasis in populations, communities, and ecosystems -understand global processes such as energy flow, succession patterns, and nutrient cycling in ecosystems, competition, predatio ...
... Unit II-3weeks-Ecology Students will: -explain the interaction among biotic and abiotic fators which contribute to homeostasis in populations, communities, and ecosystems -understand global processes such as energy flow, succession patterns, and nutrient cycling in ecosystems, competition, predatio ...
Chapter 3 Notes
... Ecologists who study individuals are primarily concerned with how the environment affects the behavioural and physical characteristics of an organism Ecologists who study populations study why the size and composition of a population changes with time, and what factors drive those changes ...
... Ecologists who study individuals are primarily concerned with how the environment affects the behavioural and physical characteristics of an organism Ecologists who study populations study why the size and composition of a population changes with time, and what factors drive those changes ...
1) the study of how organisms interact with their environment. It
... 1)_____________________is the study of how organisms interact with their environment. It begins with a group of organisms of the same 2)_______________ which are capable of interbreeding and producing fertile offspring. When the living populations of organisms interact with their nonliving or physic ...
... 1)_____________________is the study of how organisms interact with their environment. It begins with a group of organisms of the same 2)_______________ which are capable of interbreeding and producing fertile offspring. When the living populations of organisms interact with their nonliving or physic ...
Ecosystems and Population Change
... when there is more precipitation, there will be more ground water and the water table will rise. In little rainfall, the water table is lower. Plants adapt to this by sending roots down into the soil to the groundwater layer or down to the water table to bring up water and minerals. ...
... when there is more precipitation, there will be more ground water and the water table will rise. In little rainfall, the water table is lower. Plants adapt to this by sending roots down into the soil to the groundwater layer or down to the water table to bring up water and minerals. ...
bioch2b - Otterville R
... We share the earth with all of the other creatures; removing any organism from an environment can have many diverse consequences - not always predictable ones. Ecology is the study of the interactions of organisms with the living and nonliving parts of their environment. An interacting group of org ...
... We share the earth with all of the other creatures; removing any organism from an environment can have many diverse consequences - not always predictable ones. Ecology is the study of the interactions of organisms with the living and nonliving parts of their environment. An interacting group of org ...
Chapter 52: An Introduction to Ecology and the Biosphere
... Earth’s curved shape causes latitudinal variation in the intensity of sunlight. Because sunlight strikes the tropics (those regions that lie between 23.5° north latitude and 23.5° south latitude) most directly, more heat and light per unit of surface area are delivered there. At higher latitudes, su ...
... Earth’s curved shape causes latitudinal variation in the intensity of sunlight. Because sunlight strikes the tropics (those regions that lie between 23.5° north latitude and 23.5° south latitude) most directly, more heat and light per unit of surface area are delivered there. At higher latitudes, su ...
Envir Science - Ecosystem OEQs
... What would happen if predation was non-existent? Energy transfers through an ecosystem throughout different channels. Describe how energy transfers though an ecosystem, beginning with producers. Give an example of each level of a food chain and describe what would happen if producers were remo ...
... What would happen if predation was non-existent? Energy transfers through an ecosystem throughout different channels. Describe how energy transfers though an ecosystem, beginning with producers. Give an example of each level of a food chain and describe what would happen if producers were remo ...
File
... Unlike the one-way flow of energy (food pyramid), matter is recycled within and between ecosystems. Biogeochemical cycle-process in which elements, chemical compounds, and other forms of matter are passed from one organism to another and from one part of the biosphere to another. ...
... Unlike the one-way flow of energy (food pyramid), matter is recycled within and between ecosystems. Biogeochemical cycle-process in which elements, chemical compounds, and other forms of matter are passed from one organism to another and from one part of the biosphere to another. ...
Midterm Review PPT WKST
... these traits, farmers direct the evolution of crop plants to produce larger, ...
... these traits, farmers direct the evolution of crop plants to produce larger, ...
Date Honors Biology Chapter 4 Outline 4.1 Climate Weather and C
... Climate refers to average conditions over long periods of time A regions climate is defined by year-after-year patterns of temperature and precipitation Environmental conditions can vary over small distances, creating microclimates Factors that Effect Climate Global climate is shaped by many factors ...
... Climate refers to average conditions over long periods of time A regions climate is defined by year-after-year patterns of temperature and precipitation Environmental conditions can vary over small distances, creating microclimates Factors that Effect Climate Global climate is shaped by many factors ...
Conserving Resources
... • Groundwater can become polluted as it seeps through particles of rock and soil or collects in underground ...
... • Groundwater can become polluted as it seeps through particles of rock and soil or collects in underground ...
Benchmark 3 study guide with answers
... 27. Some frogs are brightly colored to warn predators not to eat them. What warning could their bright colors be? It’s bright colors warns predators that it could be poisonous. 28. Many animals that live in hot climates are nocturnal. Why is this? They are nocturnal because it is easier to keep thei ...
... 27. Some frogs are brightly colored to warn predators not to eat them. What warning could their bright colors be? It’s bright colors warns predators that it could be poisonous. 28. Many animals that live in hot climates are nocturnal. Why is this? They are nocturnal because it is easier to keep thei ...
ch04_sec1 revised
... species that live in the same habitat and interact with each other. • Every population is part of a community. • The most obvious difference between communities is the types of species they have. • Land communities are often dominated by a few species of plants. These plants then determine what othe ...
... species that live in the same habitat and interact with each other. • Every population is part of a community. • The most obvious difference between communities is the types of species they have. • Land communities are often dominated by a few species of plants. These plants then determine what othe ...
4.1 Notes
... species that live in the same habitat and interact with each other. • Every population is part of a community. • The most obvious difference between communities is the types of species they have. • Land communities are often dominated by a few species of plants. These plants then determine what othe ...
... species that live in the same habitat and interact with each other. • Every population is part of a community. • The most obvious difference between communities is the types of species they have. • Land communities are often dominated by a few species of plants. These plants then determine what othe ...
The Organization of Life Section 1 Defining an Ecosystem Ecosystems
... species that live in the same habitat and interact with each other. • Every population is part of a community. • The most obvious difference between communities is the types of species they have. • Land communities are often dominated by a few species of plants. These plants then determine what othe ...
... species that live in the same habitat and interact with each other. • Every population is part of a community. • The most obvious difference between communities is the types of species they have. • Land communities are often dominated by a few species of plants. These plants then determine what othe ...
What you Need to Know for the Ecology Test
... Know about Ecological Succession!! Watch the crash course ecological succession video ...
... Know about Ecological Succession!! Watch the crash course ecological succession video ...
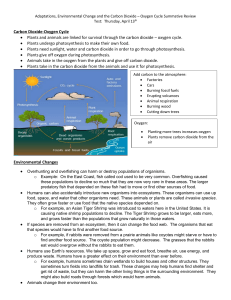
Carbon Dioxide-Oxygen Cycle • Plants and animals are linked for
... o For example, humans sometimes drain wetlands to build houses and other structures. They sometimes turn fields into landfills for trash. These changes may help humans find shelter and get rid of waste, but they can harm the other living things in the surrounding environment. They might also build r ...
... o For example, humans sometimes drain wetlands to build houses and other structures. They sometimes turn fields into landfills for trash. These changes may help humans find shelter and get rid of waste, but they can harm the other living things in the surrounding environment. They might also build r ...
Natural environment

The natural environment encompasses all living and non-living things occurring naturally on Earth or some region thereof. It is an environment that encompasses the interaction of all living species. Climate, weather, and natural resources that affect human survival and economic activity.The concept of the natural environment can be distinguished by components: Complete ecological units that function as natural systems without massive civilized human intervention, including all vegetation, microorganisms, soil, rocks, atmosphere, and natural phenomena that occur within their boundaries Universal natural resources and physical phenomena that lack clear-cut boundaries, such as air, water, and climate, as well as energy, radiation, electric charge, and magnetism, not originating from civilized human activityIn contrast to the natural environment is the built environment. In such areas where man has fundamentally transformed landscapes such as urban settings and agricultural land conversion, the natural environment is greatly modified and diminished, with a much more simplified human environment largely replacing it. Even events which seem less extreme such as hydroelectric dam construction, or photovoltaic system construction in the desert, the natural environment is substantially altered.It is difficult to find absolutely natural environments, and it is common that the naturalness varies in a continuum, from ideally 100% natural in one extreme to 0% natural in the other. More precisely, we can consider the different aspects or components of an environment, and see that their degree of naturalness is not uniform. If, for instance, we take an agricultural field, and consider the mineralogic composition and the structure of its soil, we will find that whereas the first is quite similar to that of an undisturbed forest soil, the structure is quite different.Natural environment is often used as a synonym for habitat. For instance, when we say that the natural environment of giraffes is the savanna.