Intro To ECOLOGY
... captures, kills, and consumes another (prey) • Natural Selection and adaptation play a big role in this relationship • Predators adapt to become better at capturing prey; prey adapt to become better at avoiding predators ...
... captures, kills, and consumes another (prey) • Natural Selection and adaptation play a big role in this relationship • Predators adapt to become better at capturing prey; prey adapt to become better at avoiding predators ...
Vocabulary Review
... abiotic: describes the nonliving part of the environment, including water, rocks, light, and temperature biotic: the living organisms in an ecosystem ecosystem: the community of organisms that live in a particular area, along with their nonliving surroundings organism: Any living thing population: a ...
... abiotic: describes the nonliving part of the environment, including water, rocks, light, and temperature biotic: the living organisms in an ecosystem ecosystem: the community of organisms that live in a particular area, along with their nonliving surroundings organism: Any living thing population: a ...
Study Questions
... What are the 3 general categories of fire intensity? What strategies have been used by ecologists to study succession, given that it may take 100’s or 1000's of years? What biotic interactions influence succession? Which are thought to be most important early in primary succession? Why would life hi ...
... What are the 3 general categories of fire intensity? What strategies have been used by ecologists to study succession, given that it may take 100’s or 1000's of years? What biotic interactions influence succession? Which are thought to be most important early in primary succession? Why would life hi ...
Ecosystems and Adaptations
... All living and non-living organisms live in an environment. The physical environment includes all non-living things, such as soil, weather, landforms, air, and water ! A single organism in an environment is called an individual. ...
... All living and non-living organisms live in an environment. The physical environment includes all non-living things, such as soil, weather, landforms, air, and water ! A single organism in an environment is called an individual. ...
BioBullies Glossary - Natural Biodiversity
... Anthropocentric (An-throw-po-cen-trick): A human-centered view of the world where the environment is only seen as a resource for human use. Best Management Practices (BMPs): Specially developed management plans which prescribe more sustainable ways of managing, processing or controlling a resource, ...
... Anthropocentric (An-throw-po-cen-trick): A human-centered view of the world where the environment is only seen as a resource for human use. Best Management Practices (BMPs): Specially developed management plans which prescribe more sustainable ways of managing, processing or controlling a resource, ...
Importance of Biodiversity
... and microorganisms, the genes they contain, and the ecosystems they form. This living wealth is the product of hundreds of millions of years of evolutionary history. ...
... and microorganisms, the genes they contain, and the ecosystems they form. This living wealth is the product of hundreds of millions of years of evolutionary history. ...
ecology terms matching exercise
... Complex process of how water, carbon, nitrogen, oxygen, and other nutrients necessary for life are recycled through ecosystems from organic matter to inorganic matter and back The role or position a species occupies in its ecosystem; how it contributes to its function, how it captures energy, where ...
... Complex process of how water, carbon, nitrogen, oxygen, and other nutrients necessary for life are recycled through ecosystems from organic matter to inorganic matter and back The role or position a species occupies in its ecosystem; how it contributes to its function, how it captures energy, where ...
2015 8th grade Science Study Guide Extended Version
... Ecosystem—interactive systems that include both biological (biotic) and physical (abiotic) components of the environment Population—group of organisms belonging to the same species that live in a particular area Predation—interaction between species in which one species (predator) eats the other (pr ...
... Ecosystem—interactive systems that include both biological (biotic) and physical (abiotic) components of the environment Population—group of organisms belonging to the same species that live in a particular area Predation—interaction between species in which one species (predator) eats the other (pr ...
Charles Darwin and Natural Selection
... Organisms produce more offspring than can survive because of: ...
... Organisms produce more offspring than can survive because of: ...
Desert Connections Wild Workshop
... the components usually influence one another. SC03-S2C2-02: Explain why a system may not work if a component is defective or missing. SC03-S4C3-01: Identify the living and nonliving components of an ecosystem. SC03-S4C3-03: Explain the interrelationships among plants and animals in different e ...
... the components usually influence one another. SC03-S2C2-02: Explain why a system may not work if a component is defective or missing. SC03-S4C3-01: Identify the living and nonliving components of an ecosystem. SC03-S4C3-03: Explain the interrelationships among plants and animals in different e ...
Humans and the Environment - Warren Hills Regional School District
... of forests and lakes. Sulfur dioxide from coalburning factories and nitrogen oxides from car exhaust combine with water vapor in the air to form acidic droplets. ...
... of forests and lakes. Sulfur dioxide from coalburning factories and nitrogen oxides from car exhaust combine with water vapor in the air to form acidic droplets. ...
Cell Division and Mitosis
... 1. In the hydrologic cycle, oxygen and hydrogen move as water molecules. 2. In the atmospheric cycles, elements can move in the gaseous phase; examples include carbon (mainly CO2) and nitrogen. ...
... 1. In the hydrologic cycle, oxygen and hydrogen move as water molecules. 2. In the atmospheric cycles, elements can move in the gaseous phase; examples include carbon (mainly CO2) and nitrogen. ...
Ch.2-1 PPT - Nicholas County Schools
... geographic location at the same time 3. Biological Community: a group of interacting populations that occupy the same geographic area at the same time ...
... geographic location at the same time 3. Biological Community: a group of interacting populations that occupy the same geographic area at the same time ...
SCREENING TEST type centers in box with 9 point
... D loss of water for sea lions 23. Approximately how much of Earth’s land area has soil that is well suited to farming? A one half B almost all C three quarters D one third ...
... D loss of water for sea lions 23. Approximately how much of Earth’s land area has soil that is well suited to farming? A one half B almost all C three quarters D one third ...
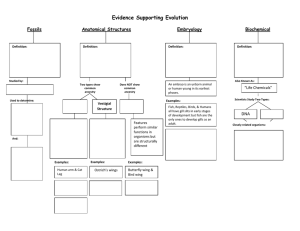
Evidence Supporting Evolution
... structures in early stages of development but humans do not develop tails in mature forms like fish, reptiles, & birds do ...
... structures in early stages of development but humans do not develop tails in mature forms like fish, reptiles, & birds do ...
The Links Between the Biota and Climate
... other features of climate that have a bearing on living systems. Wind seems to be important as a means of transport for some insects such as moths, dragonflies, and locusts. The location of the major prevailing winds often determines the distribution of migratory birds, which may use the winds quite ...
... other features of climate that have a bearing on living systems. Wind seems to be important as a means of transport for some insects such as moths, dragonflies, and locusts. The location of the major prevailing winds often determines the distribution of migratory birds, which may use the winds quite ...
LIFS 3160 Ecology - Division of Life Science
... Brief description: This course is designed to equip students with basic understanding in ecology, which includes the diversity of life in major ecosystems (weeks 1 – 3), the definition and intrinsic characteristics of population as a basic biological unit in an ecosystem (weeks 4 6), intra- and inte ...
... Brief description: This course is designed to equip students with basic understanding in ecology, which includes the diversity of life in major ecosystems (weeks 1 – 3), the definition and intrinsic characteristics of population as a basic biological unit in an ecosystem (weeks 4 6), intra- and inte ...
Climate and life zones
... Local modifications of climate Global life zone classification Major assertion: With a few simple physical principles, we can explain much of global vegetation patterns ...
... Local modifications of climate Global life zone classification Major assertion: With a few simple physical principles, we can explain much of global vegetation patterns ...
Addressing Natural Resource Management in Bangladesh
... resources, especially water and land, is contributing to the deteriorating state of natural environment in Bangladesh. This is due to physical and behavioural changes combined with poor governance. The Green Revolution and the Farakka barrage have triggered environmental disasters for the country’s ...
... resources, especially water and land, is contributing to the deteriorating state of natural environment in Bangladesh. This is due to physical and behavioural changes combined with poor governance. The Green Revolution and the Farakka barrage have triggered environmental disasters for the country’s ...
Madro-Tertiary Geoflora of the Pacific Northwest
... Subsequent uplift of the Cascades increased the rainshadow effect in the interior PNW especially in the last ~20 million years. Rainshadow effects of the Olympic Mountains and Vancouver Island have created enough aridity for some of the drought-adapted Madro Tertiary Geoflora to extend well into Wes ...
... Subsequent uplift of the Cascades increased the rainshadow effect in the interior PNW especially in the last ~20 million years. Rainshadow effects of the Olympic Mountains and Vancouver Island have created enough aridity for some of the drought-adapted Madro Tertiary Geoflora to extend well into Wes ...
ECOSYSTEMS - twpunionschools.org
... Habitat: the place within an ecosystem that provides food, water, shelter, and other biotic and abiotic factors that an organism needs to survive and reproduce Population: All the organisms of the same species that live in the same area at the same ...
... Habitat: the place within an ecosystem that provides food, water, shelter, and other biotic and abiotic factors that an organism needs to survive and reproduce Population: All the organisms of the same species that live in the same area at the same ...
File
... biotic factors, which include plants, fish, invertebrates, and single-celled organisms. • The non-living components, or abiotic factors, include the physical and chemical components in the environment—temperature, wind, water, sunlight, and oxygen. ...
... biotic factors, which include plants, fish, invertebrates, and single-celled organisms. • The non-living components, or abiotic factors, include the physical and chemical components in the environment—temperature, wind, water, sunlight, and oxygen. ...
Chapter 3 Outline
... existence, numbers, reproduction, or distribution of organisms A. Availability of food & water B. Predation C. Temperature – timberline D. Sunlight E. Climate F. Space ...
... existence, numbers, reproduction, or distribution of organisms A. Availability of food & water B. Predation C. Temperature – timberline D. Sunlight E. Climate F. Space ...
Natural environment

The natural environment encompasses all living and non-living things occurring naturally on Earth or some region thereof. It is an environment that encompasses the interaction of all living species. Climate, weather, and natural resources that affect human survival and economic activity.The concept of the natural environment can be distinguished by components: Complete ecological units that function as natural systems without massive civilized human intervention, including all vegetation, microorganisms, soil, rocks, atmosphere, and natural phenomena that occur within their boundaries Universal natural resources and physical phenomena that lack clear-cut boundaries, such as air, water, and climate, as well as energy, radiation, electric charge, and magnetism, not originating from civilized human activityIn contrast to the natural environment is the built environment. In such areas where man has fundamentally transformed landscapes such as urban settings and agricultural land conversion, the natural environment is greatly modified and diminished, with a much more simplified human environment largely replacing it. Even events which seem less extreme such as hydroelectric dam construction, or photovoltaic system construction in the desert, the natural environment is substantially altered.It is difficult to find absolutely natural environments, and it is common that the naturalness varies in a continuum, from ideally 100% natural in one extreme to 0% natural in the other. More precisely, we can consider the different aspects or components of an environment, and see that their degree of naturalness is not uniform. If, for instance, we take an agricultural field, and consider the mineralogic composition and the structure of its soil, we will find that whereas the first is quite similar to that of an undisturbed forest soil, the structure is quite different.Natural environment is often used as a synonym for habitat. For instance, when we say that the natural environment of giraffes is the savanna.