ECOLOGY A. Ecology Ecology comes from the Greek words ______
... ___________________ – No organism is isolated. An organism’s _____________ ____________ ______ the __________________ with other organisms ____________ _______________________________________________ _______________________________________________ ...
... ___________________ – No organism is isolated. An organism’s _____________ ____________ ______ the __________________ with other organisms ____________ _______________________________________________ _______________________________________________ ...
Woodland Hills - Science 8 - Lesson 15 Guided Notes Answer Key
... -Cutting down forests to build homes and roads destroys natural habitats. -Polluting water and air reduces the number of wild organisms that can use it. -Bringing in species from other parts of the world can change a native ecosystem. -Populations of native species can decline or disappear. Every e ...
... -Cutting down forests to build homes and roads destroys natural habitats. -Polluting water and air reduces the number of wild organisms that can use it. -Bringing in species from other parts of the world can change a native ecosystem. -Populations of native species can decline or disappear. Every e ...
The Built Environment and Human Health
... The scope and scale of global environmental change, which encompasses not only climate change but other challenges like the decline in biodiversity and the attrition of ecosystem services, poses dire threats to human health. The magnitude of the problem is reflected by the increasing size of humanit ...
... The scope and scale of global environmental change, which encompasses not only climate change but other challenges like the decline in biodiversity and the attrition of ecosystem services, poses dire threats to human health. The magnitude of the problem is reflected by the increasing size of humanit ...
PopulationsPP
... • The continuous flow of phosphorus from land to water to organisms and back to land, • P is important in the production of DNA and RNA. • phosphorus is NOT found in the atmosphere. Found in rocks and minerals. ...
... • The continuous flow of phosphorus from land to water to organisms and back to land, • P is important in the production of DNA and RNA. • phosphorus is NOT found in the atmosphere. Found in rocks and minerals. ...
C. Threats to Natural Habitats and Wildlife
... Deforestation is one of the causes of increasing the atmospheric carbon dioxide on earth. This is simply by handicapping the carbon cycle (described in Topic “The importance of air” of Theme “The Air We Breathe”). (The effects of increasing atmospheric carbon dioxide are found in Topic “Global warmi ...
... Deforestation is one of the causes of increasing the atmospheric carbon dioxide on earth. This is simply by handicapping the carbon cycle (described in Topic “The importance of air” of Theme “The Air We Breathe”). (The effects of increasing atmospheric carbon dioxide are found in Topic “Global warmi ...
Ecosystems: Everything is Connected
... • Every population is part of a community. • The most obvious difference between communities is the types of species they have. ...
... • Every population is part of a community. • The most obvious difference between communities is the types of species they have. ...
AP Environmental
... (C) the organism a parasite feeds on is its prey (D) a parasite generally harms, but does not kill the organism it feeds on (E) a parasite feeds on another organism over an extended period of time 23. A relationship in which two organisms both benefit is (A) not found in nature (B) known as mutualis ...
... (C) the organism a parasite feeds on is its prey (D) a parasite generally harms, but does not kill the organism it feeds on (E) a parasite feeds on another organism over an extended period of time 23. A relationship in which two organisms both benefit is (A) not found in nature (B) known as mutualis ...
APES review #2
... • Respiration (All living things) oxygen + sugars ATP +water + carbon dioxide ...
... • Respiration (All living things) oxygen + sugars ATP +water + carbon dioxide ...
Includes interspecific interactions
... 1. Interspecific Competition (-/-) can lead to the competitive exclusion principle or one species will out compete another and can lead to character displacement Fundimental Niche – Niche a species could have Realized Niche – Portion of the Fundimental Niche a species lives in ...
... 1. Interspecific Competition (-/-) can lead to the competitive exclusion principle or one species will out compete another and can lead to character displacement Fundimental Niche – Niche a species could have Realized Niche – Portion of the Fundimental Niche a species lives in ...
glossary - National Tree Day
... ranging from decades to millions of years. These shifts can be caused by changing processes on earth, external forces such as meteor impacts and variations in sunlight intensity, and more recently human activity. Currently, climate change refers to the rapid changes, including global temperature ris ...
... ranging from decades to millions of years. These shifts can be caused by changing processes on earth, external forces such as meteor impacts and variations in sunlight intensity, and more recently human activity. Currently, climate change refers to the rapid changes, including global temperature ris ...
What is Ecology? - MsHollandScience
... The Role of Climate • Climate-average conditions over long periods – Patterns of temperature and precipitation over many years ...
... The Role of Climate • Climate-average conditions over long periods – Patterns of temperature and precipitation over many years ...
Ecosystems
... Marine ecosystems are found in the salty waters of the oceans. Kelp forests, seagrass communities, and coral reefs are found near land. The open ocean, far from land, has plankton and large predators, such as dolphins, whales, and sharks. ...
... Marine ecosystems are found in the salty waters of the oceans. Kelp forests, seagrass communities, and coral reefs are found near land. The open ocean, far from land, has plankton and large predators, such as dolphins, whales, and sharks. ...
Ecology Review Sheet
... Plants are small – roots cannot penetrate the permafrost. Some plants are covered with hair – help keep them warm. 36. What variations and adaptations would you expect to see in animals in the desert? Many animals migrate during the dry season to search for water. Animals borrow for protection from ...
... Plants are small – roots cannot penetrate the permafrost. Some plants are covered with hair – help keep them warm. 36. What variations and adaptations would you expect to see in animals in the desert? Many animals migrate during the dry season to search for water. Animals borrow for protection from ...
Review Ecology 2016 Key
... Plants are small – roots cannot penetrate the permafrost. Some plants are covered with hair – help keep them warm. 36. What variations and adaptations would you expect to see in animals in the desert? Many animals migrate during the dry season to search for water. Animals borrow for protection from ...
... Plants are small – roots cannot penetrate the permafrost. Some plants are covered with hair – help keep them warm. 36. What variations and adaptations would you expect to see in animals in the desert? Many animals migrate during the dry season to search for water. Animals borrow for protection from ...
My Ecology Notes
... Ecology is a branch of biology concerned with the study of the interactions of living organisms with each other and with their environment. An ecosystem is a community of organisms that interact with their environment. Biosphere is a region of the earth where life can exist.(atmosphere, hygros ...
... Ecology is a branch of biology concerned with the study of the interactions of living organisms with each other and with their environment. An ecosystem is a community of organisms that interact with their environment. Biosphere is a region of the earth where life can exist.(atmosphere, hygros ...
Ecology Review Sheet
... Plants are small – roots cannot penetrate the permafrost. Some plants are covered with hair – help keep them warm. 36. What variations and adaptations would you expect to see in animals in the desert? Many animals migrate during the dry season to search for water. Animals borrow for protection from ...
... Plants are small – roots cannot penetrate the permafrost. Some plants are covered with hair – help keep them warm. 36. What variations and adaptations would you expect to see in animals in the desert? Many animals migrate during the dry season to search for water. Animals borrow for protection from ...
Organisms and Their Environment
... • An ecosystem includes all of the organisms as well as the climate, soil, water, rocks and other nonliving things in a given area. ...
... • An ecosystem includes all of the organisms as well as the climate, soil, water, rocks and other nonliving things in a given area. ...
Unit 5
... abundance of organisms are products of both long-term evolutionary changes and ongoing interactions with the environment. 3. Explain the importance of temperature, water, light, soil, and wind to living organisms. a. Temperature is an important factor in the distribution of organisms because of its ...
... abundance of organisms are products of both long-term evolutionary changes and ongoing interactions with the environment. 3. Explain the importance of temperature, water, light, soil, and wind to living organisms. a. Temperature is an important factor in the distribution of organisms because of its ...
Environmental science PSAE QUESTIONS 2009
... d. Ocean currents redistribute warm and cold masses of water. 35. A true statement concerning the physical properties of air is that a. warm air sinks toward Earth’s surface. b. warm air can hold more water vapor than an equal amount of cold air. c. as air warms, the water vapor it holds condenses. ...
... d. Ocean currents redistribute warm and cold masses of water. 35. A true statement concerning the physical properties of air is that a. warm air sinks toward Earth’s surface. b. warm air can hold more water vapor than an equal amount of cold air. c. as air warms, the water vapor it holds condenses. ...
Characteristics of Populations
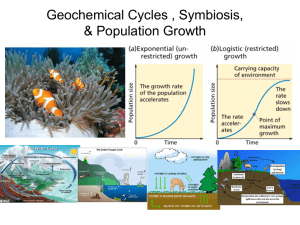
... • Logistic growth •As resources become less available, the population growth rate slows or stops ...
... • Logistic growth •As resources become less available, the population growth rate slows or stops ...
Ecology Review
... atmosphere and blocks harmful rays of the sun. The release of CFC’s from aerosol cans and other sources of air pollution interact with the atmosphere and deplete the ozone layer. If the ozone layer is destroyed, harmful rays from the sun would cause catastrophic mutations and would threaten all ...
... atmosphere and blocks harmful rays of the sun. The release of CFC’s from aerosol cans and other sources of air pollution interact with the atmosphere and deplete the ozone layer. If the ozone layer is destroyed, harmful rays from the sun would cause catastrophic mutations and would threaten all ...
Ecology Earth Cycles Pyramids (1)
... atmosphere and blocks harmful rays of the sun. The release of CFC’s from aerosol cans and other sources of air pollution interact with the atmosphere and deplete the ozone layer. If the ozone layer is destroyed, harmful rays from the sun would cause catastrophic mutations and would threaten all ...
... atmosphere and blocks harmful rays of the sun. The release of CFC’s from aerosol cans and other sources of air pollution interact with the atmosphere and deplete the ozone layer. If the ozone layer is destroyed, harmful rays from the sun would cause catastrophic mutations and would threaten all ...
Natural environment

The natural environment encompasses all living and non-living things occurring naturally on Earth or some region thereof. It is an environment that encompasses the interaction of all living species. Climate, weather, and natural resources that affect human survival and economic activity.The concept of the natural environment can be distinguished by components: Complete ecological units that function as natural systems without massive civilized human intervention, including all vegetation, microorganisms, soil, rocks, atmosphere, and natural phenomena that occur within their boundaries Universal natural resources and physical phenomena that lack clear-cut boundaries, such as air, water, and climate, as well as energy, radiation, electric charge, and magnetism, not originating from civilized human activityIn contrast to the natural environment is the built environment. In such areas where man has fundamentally transformed landscapes such as urban settings and agricultural land conversion, the natural environment is greatly modified and diminished, with a much more simplified human environment largely replacing it. Even events which seem less extreme such as hydroelectric dam construction, or photovoltaic system construction in the desert, the natural environment is substantially altered.It is difficult to find absolutely natural environments, and it is common that the naturalness varies in a continuum, from ideally 100% natural in one extreme to 0% natural in the other. More precisely, we can consider the different aspects or components of an environment, and see that their degree of naturalness is not uniform. If, for instance, we take an agricultural field, and consider the mineralogic composition and the structure of its soil, we will find that whereas the first is quite similar to that of an undisturbed forest soil, the structure is quite different.Natural environment is often used as a synonym for habitat. For instance, when we say that the natural environment of giraffes is the savanna.