Environments Through Time - NagleEarthandEnvironmental
... through the sediment to reach the sunlight (photosynthesis) thus forming a new layer of bacteria on top. Stromatolites grow very, very slowly (1mm per year) 4 billion years ago these organisms were so common and populated that they changed the atmosphere of the world by adding oxygen as a by pro ...
... through the sediment to reach the sunlight (photosynthesis) thus forming a new layer of bacteria on top. Stromatolites grow very, very slowly (1mm per year) 4 billion years ago these organisms were so common and populated that they changed the atmosphere of the world by adding oxygen as a by pro ...
New B1 B2 B3 Revision
... Dead organisms are broken down by microorganisms (decomposition) to release carbon and this becomes part of a new organism. ...
... Dead organisms are broken down by microorganisms (decomposition) to release carbon and this becomes part of a new organism. ...
Document
... • We will spend the next several lectures looking at connections between environments. ...
... • We will spend the next several lectures looking at connections between environments. ...
Homeostasis - centralmountainbiology
... • The levels of dissolved oxygen and carbon dioxide in the blood must be regulated to allow respiration to take place. • Ex. Fish perform gas exchange through gills Water flows over the capillaries in the gills, which contain a higher concentration of carbon dioxide and a lower concentration of oxyg ...
... • The levels of dissolved oxygen and carbon dioxide in the blood must be regulated to allow respiration to take place. • Ex. Fish perform gas exchange through gills Water flows over the capillaries in the gills, which contain a higher concentration of carbon dioxide and a lower concentration of oxyg ...
Chapter 3 Ecosystems Notes 1
... occur regardless of how large or small the population. They are mostly abiotic; weather changes, natural pollution, natural disasters. 3. Abiotic and Biotic factors- affect population size and balance abiotic- water, shelter, oxygen, food, temperature, amount of sunlight, and precipitation. biotic- ...
... occur regardless of how large or small the population. They are mostly abiotic; weather changes, natural pollution, natural disasters. 3. Abiotic and Biotic factors- affect population size and balance abiotic- water, shelter, oxygen, food, temperature, amount of sunlight, and precipitation. biotic- ...
Ch15 Student Presentation
... -may be rare, endangered , keystone, or culturally significant species -two types: a. indicator species- a species associated with an endangered biological community or set of unique ecosystem processes Ex. spotted owl in the U.S. Northwest is an indicator of old growth forest Ex. red-cockaded woodp ...
... -may be rare, endangered , keystone, or culturally significant species -two types: a. indicator species- a species associated with an endangered biological community or set of unique ecosystem processes Ex. spotted owl in the U.S. Northwest is an indicator of old growth forest Ex. red-cockaded woodp ...
Unit XII Teacher Notes - Ecology
... they consume for life processes in order to maintain homeostasis (cell respiration, movement, reproduction); and some is released or lost to the environment as heat. Therefore, at each trophic level, the energy stored by the organism is about one-tenth of that stored by the organisms in the level be ...
... they consume for life processes in order to maintain homeostasis (cell respiration, movement, reproduction); and some is released or lost to the environment as heat. Therefore, at each trophic level, the energy stored by the organism is about one-tenth of that stored by the organisms in the level be ...
biodiversity in lake macquarie
... different plants, animals and microorganisms, the genes they contain, and the ecosystems they form. It is usually considered at three levels: genetic diversity, species diversity and ecosystem diversity. ...
... different plants, animals and microorganisms, the genes they contain, and the ecosystems they form. It is usually considered at three levels: genetic diversity, species diversity and ecosystem diversity. ...
Biodiversity:
... Biodiversity is the variety and differences among living organisms from all sources, including terrestrial, marine, and other aquatic ecosystems and the ecological complexes of which they are a part. It is virtually synonymous with “Life on earth”. Biologists most often define "biological dive ...
... Biodiversity is the variety and differences among living organisms from all sources, including terrestrial, marine, and other aquatic ecosystems and the ecological complexes of which they are a part. It is virtually synonymous with “Life on earth”. Biologists most often define "biological dive ...
How do Changes in Ocean Temperature affect Marine Ecosystems?
... of the temperature-dependence of larval duration remains untested. Knowing the larval dispersal distance, which is believed to be influenced by the duration of the larval period, is a critical component for managing commercially important or invasive species. Recently, American researchers have stud ...
... of the temperature-dependence of larval duration remains untested. Knowing the larval dispersal distance, which is believed to be influenced by the duration of the larval period, is a critical component for managing commercially important or invasive species. Recently, American researchers have stud ...
Ecology Levels of Organization PowerPoint
... - Observing how a drought affects the number of blossoms on a Saguaro cactus? - Determining the effects of warming ocean temperatures on krill populations in the Antarctic? - Observing the behavior of Arctic wolves as they hunt migrating caribou in the Arctic? ...
... - Observing how a drought affects the number of blossoms on a Saguaro cactus? - Determining the effects of warming ocean temperatures on krill populations in the Antarctic? - Observing the behavior of Arctic wolves as they hunt migrating caribou in the Arctic? ...
Ecosystem
... population density reaches a specific level. (too many for ecosystem to support) Competition, predation, parasitism, and ...
... population density reaches a specific level. (too many for ecosystem to support) Competition, predation, parasitism, and ...
Human Body Systems Unit Plan
... Human Body Systems Unit Plan BIG IDEA Multicellular organisms have organ systems that enable them to survive and interact within their environment. • Elaboration ...
... Human Body Systems Unit Plan BIG IDEA Multicellular organisms have organ systems that enable them to survive and interact within their environment. • Elaboration ...
Air Pollution & Air Quality Monitoring
... atmosphere must be taken as dry air at sea level. • Neither completely cover other factors that we might also call pollution such as the release of energy, radiation, odour or noise. ...
... atmosphere must be taken as dry air at sea level. • Neither completely cover other factors that we might also call pollution such as the release of energy, radiation, odour or noise. ...
Abiotic Factors
... • Now, I want you to pick up a handful of soil in each place. What differences would you find? • Woodland soil is rich in organic matter and holds water well. The desert’s sandy soil has little organic matter and does not hold water. ...
... • Now, I want you to pick up a handful of soil in each place. What differences would you find? • Woodland soil is rich in organic matter and holds water well. The desert’s sandy soil has little organic matter and does not hold water. ...
Ecosystems
... • Brightly colored plants called lichens grow on rocks. • Plants have to adapt to cold temperature and little sunlight • Can have many brightly colored plants, mosses and lichens • Some plants have developed large leaves to absorb as much sun as possible. • Any animals that live her have thick fur a ...
... • Brightly colored plants called lichens grow on rocks. • Plants have to adapt to cold temperature and little sunlight • Can have many brightly colored plants, mosses and lichens • Some plants have developed large leaves to absorb as much sun as possible. • Any animals that live her have thick fur a ...
Ch 3 Notes
... abiotic factors: – Biotic Factors – living organisms (dead or alive) – Abiotic Factors – nonliving parts (physical components such as temperature, air, water, wind, humidity, sun, soil, rain, nutrients) ...
... abiotic factors: – Biotic Factors – living organisms (dead or alive) – Abiotic Factors – nonliving parts (physical components such as temperature, air, water, wind, humidity, sun, soil, rain, nutrients) ...
Science Notebook Chapter 2 - Answer Key
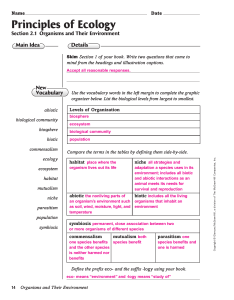
... Use the vocabulary words in the left margin to complete the graphic organizer below. List the biological levels from largest to smallest. Levels of Organization biosphere ecosystem ...
... Use the vocabulary words in the left margin to complete the graphic organizer below. List the biological levels from largest to smallest. Levels of Organization biosphere ecosystem ...
1. What is the study of interactions between
... 36. If there is 100 grams of energy at the primary level, approximately, how much is going to be available at the ...
... 36. If there is 100 grams of energy at the primary level, approximately, how much is going to be available at the ...
AquaticBiome
... warmest since it is shallow and can absorb more of the Sun’s heat sustains a fairly diverse community, which can include several species of algae (like diatoms), rooted and floating aquatic plants, grazing snails, clams, insects, crustaceans, fishes, and amphibians the egg and larvae stages of some ...
... warmest since it is shallow and can absorb more of the Sun’s heat sustains a fairly diverse community, which can include several species of algae (like diatoms), rooted and floating aquatic plants, grazing snails, clams, insects, crustaceans, fishes, and amphibians the egg and larvae stages of some ...
organism
... the most abundant elements on Earth. • Compounds containing Carbon are called organic compounds. • All cells contain Carbon. It is one the most essential building blocks of life. • Carbon can exist in 3 states of matter: solid, liquid, and gas. ...
... the most abundant elements on Earth. • Compounds containing Carbon are called organic compounds. • All cells contain Carbon. It is one the most essential building blocks of life. • Carbon can exist in 3 states of matter: solid, liquid, and gas. ...
TEKS Presentation Organisms and the Enviornment
... Ecosystem – includes the living & nonliving parts of an environment. Nonliving- water, soil, light, air Living- plants, animals & other living organisms (makes up the community) ...
... Ecosystem – includes the living & nonliving parts of an environment. Nonliving- water, soil, light, air Living- plants, animals & other living organisms (makes up the community) ...
The living planet
... might be in a plain, with many other rocks, small grass , and grazing animals – this, too, is an ecosystem. This plain might be in the tundra, which is also an ecosystem. The surface of the Earth, all the matter which composes it, the air and all living organisms can be considered one huge ecosystem ...
... might be in a plain, with many other rocks, small grass , and grazing animals – this, too, is an ecosystem. This plain might be in the tundra, which is also an ecosystem. The surface of the Earth, all the matter which composes it, the air and all living organisms can be considered one huge ecosystem ...
What is a species?
... a diagram that looks a bit like a family tree, showing who the nearest relatives were and who shared a common ancestor, and when. ...
... a diagram that looks a bit like a family tree, showing who the nearest relatives were and who shared a common ancestor, and when. ...
Natural environment

The natural environment encompasses all living and non-living things occurring naturally on Earth or some region thereof. It is an environment that encompasses the interaction of all living species. Climate, weather, and natural resources that affect human survival and economic activity.The concept of the natural environment can be distinguished by components: Complete ecological units that function as natural systems without massive civilized human intervention, including all vegetation, microorganisms, soil, rocks, atmosphere, and natural phenomena that occur within their boundaries Universal natural resources and physical phenomena that lack clear-cut boundaries, such as air, water, and climate, as well as energy, radiation, electric charge, and magnetism, not originating from civilized human activityIn contrast to the natural environment is the built environment. In such areas where man has fundamentally transformed landscapes such as urban settings and agricultural land conversion, the natural environment is greatly modified and diminished, with a much more simplified human environment largely replacing it. Even events which seem less extreme such as hydroelectric dam construction, or photovoltaic system construction in the desert, the natural environment is substantially altered.It is difficult to find absolutely natural environments, and it is common that the naturalness varies in a continuum, from ideally 100% natural in one extreme to 0% natural in the other. More precisely, we can consider the different aspects or components of an environment, and see that their degree of naturalness is not uniform. If, for instance, we take an agricultural field, and consider the mineralogic composition and the structure of its soil, we will find that whereas the first is quite similar to that of an undisturbed forest soil, the structure is quite different.Natural environment is often used as a synonym for habitat. For instance, when we say that the natural environment of giraffes is the savanna.