Ecological Interactions and Succession
... When a population reaches a state where it can no longer grow, the population has reached its carrying capacity. Ex: Wolves and Moose Even without predators there is a limit to the number of Moose that can live in an area due to the amount of food and space. ...
... When a population reaches a state where it can no longer grow, the population has reached its carrying capacity. Ex: Wolves and Moose Even without predators there is a limit to the number of Moose that can live in an area due to the amount of food and space. ...
Year 9 – Ecology Student Program 2015
... Populations and Adaptations Explain how the following factors can limit population growth: competition, disease, destruction of habitats, introduced species, immigration and emigration, births/deaths. Understand that the survival and/or reproduction of an organism are dependent on its characteri ...
... Populations and Adaptations Explain how the following factors can limit population growth: competition, disease, destruction of habitats, introduced species, immigration and emigration, births/deaths. Understand that the survival and/or reproduction of an organism are dependent on its characteri ...
Forest Mortality and Australian Terrestrial Carbon Stores
... There is strong evidence for a global convergence in the vulnerability of forests to future climate extremes. Mitchell et al. (in review Global Change Biology) demonstrate a common climatic threshold beyond which all forests are at increased risk of mortality from extreme heat and drought. The proba ...
... There is strong evidence for a global convergence in the vulnerability of forests to future climate extremes. Mitchell et al. (in review Global Change Biology) demonstrate a common climatic threshold beyond which all forests are at increased risk of mortality from extreme heat and drought. The proba ...
2014-Ecology in the Methow
... of conifer and broadleaf trees and their leaves/needles, the strategies of evergreen verses deciduous leaves, and the strategies of annual, perennial and woody plants are all varied responses to how moisture is delivered and how long it is available. 4. Where do the nutrients critical to life (carbo ...
... of conifer and broadleaf trees and their leaves/needles, the strategies of evergreen verses deciduous leaves, and the strategies of annual, perennial and woody plants are all varied responses to how moisture is delivered and how long it is available. 4. Where do the nutrients critical to life (carbo ...
Maintaining Homeostasis
... Sheet 07— Temperature Homeostasis Name: __________________________________ The human body has a natural ability to maintain a balanced internal environment when exposed to changes in its external environment. This maintenance of balance is called homeostasis. This activity aims to identify how the ...
... Sheet 07— Temperature Homeostasis Name: __________________________________ The human body has a natural ability to maintain a balanced internal environment when exposed to changes in its external environment. This maintenance of balance is called homeostasis. This activity aims to identify how the ...
UNIT 1: PRINCIPLES OF BIOLOGY AND ECOLOGY
... B. Limiting factors may be biotic or abiotic but regardless they will restrict the existence, numbers, reproduction or distribution of organisms. C. Factors that limit one population in a community may have an indirect effect on another. D. Biotic and abiotic factors can fluctuate; organisms that ca ...
... B. Limiting factors may be biotic or abiotic but regardless they will restrict the existence, numbers, reproduction or distribution of organisms. C. Factors that limit one population in a community may have an indirect effect on another. D. Biotic and abiotic factors can fluctuate; organisms that ca ...
Ecosystems and Climate
... Interactions among ecosystems Interaction of organisms with their temporal and spatial environment ...
... Interactions among ecosystems Interaction of organisms with their temporal and spatial environment ...
File
... Biotic factors-living things Ex: trees, animals, bacteria Abiotic factors-non-living things Ex: sun, soil, air, water Examples of ecosystems made up of biotic and abiotic factors: ...
... Biotic factors-living things Ex: trees, animals, bacteria Abiotic factors-non-living things Ex: sun, soil, air, water Examples of ecosystems made up of biotic and abiotic factors: ...
Nitrogen cycle review - North Penn School District
... A limiting factor is something that, when limited, determines the carrying capacity of an ecosystem for a particular species. The carrying capacity is the largest population that an environment can support at any given time. If an important resource is limited, such as food, the carrying capacity wi ...
... A limiting factor is something that, when limited, determines the carrying capacity of an ecosystem for a particular species. The carrying capacity is the largest population that an environment can support at any given time. If an important resource is limited, such as food, the carrying capacity wi ...
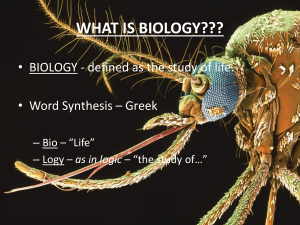
The Study of Life
... • BIOLOGY – the scientific study of all forms of life, or all types of organisms • ORGANISM – any individual living thing – All share certain characteristics, but not all ...
... • BIOLOGY – the scientific study of all forms of life, or all types of organisms • ORGANISM – any individual living thing – All share certain characteristics, but not all ...
Silence of the Frogs
... Acid rain and pesticides can therefore go through their skin easily. This affects their ability to reproduce ...
... Acid rain and pesticides can therefore go through their skin easily. This affects their ability to reproduce ...
hydrosphere test 2016
... saltwater with other Earth systems? a. the ocean interacts with the geosphere to cause plate tectonics b. the ocean redistributes thermal energy to the geosphere c. the ocean interacts with the biosphere to influence climate and weather d. the ocean interacts with the atmosphere to influence climate ...
... saltwater with other Earth systems? a. the ocean interacts with the geosphere to cause plate tectonics b. the ocean redistributes thermal energy to the geosphere c. the ocean interacts with the biosphere to influence climate and weather d. the ocean interacts with the atmosphere to influence climate ...
WTHS Biology - Centennial School District
... This packet contains helpful information for you to prepare for the upcoming Biology Keystone Test on May 15th and 16th . As you will see, this packet is broken down into several major themes that the Keystone Test will cover. You will be assigned to do parts of this packet over the next several day ...
... This packet contains helpful information for you to prepare for the upcoming Biology Keystone Test on May 15th and 16th . As you will see, this packet is broken down into several major themes that the Keystone Test will cover. You will be assigned to do parts of this packet over the next several day ...
Science and the Environment Section 2
... • Developed countries have higher incomes, slower population growth, diverse industrial economies, and stronger social support. • Developing countries have lower average incomes, simple agriculture-based communities, and rapid population growth. ...
... • Developed countries have higher incomes, slower population growth, diverse industrial economies, and stronger social support. • Developing countries have lower average incomes, simple agriculture-based communities, and rapid population growth. ...
lesson 3-interactions within biotic and abiotic factors
... • How do these abiotic factors affect the biotic parts of an ecosystem? ...
... • How do these abiotic factors affect the biotic parts of an ecosystem? ...
Energy flow notes
... o Only about 10% of the energy stored in an organism is transferred to the next trophic level o The more levels that exist between producers and top-level consumers in an ecosystem, the less energy that remains from the original amount Biomass pyramid represents the total amount of living tissue ava ...
... o Only about 10% of the energy stored in an organism is transferred to the next trophic level o The more levels that exist between producers and top-level consumers in an ecosystem, the less energy that remains from the original amount Biomass pyramid represents the total amount of living tissue ava ...
C - Midland ISD
... 1. The picture below shows a type of plant called kudzu. Kudzu is a fastgrowing Asian vine that was introduced into the United States. Kudzu quickly uses available resources and can completely cover the plants in an area. What effect does the rapid growth of kudzu most likely have on an ecosystem? F ...
... 1. The picture below shows a type of plant called kudzu. Kudzu is a fastgrowing Asian vine that was introduced into the United States. Kudzu quickly uses available resources and can completely cover the plants in an area. What effect does the rapid growth of kudzu most likely have on an ecosystem? F ...
APES Vocabulary Review
... Baby Boom- The jump in birthrates in the years after World War Two. “Baby boomers” are the generation born between 1945 and about 1960. In this period, more than 65 million children were born. They grew up in a generally prosperous period in American life, but also experienced as teenagers the uncer ...
... Baby Boom- The jump in birthrates in the years after World War Two. “Baby boomers” are the generation born between 1945 and about 1960. In this period, more than 65 million children were born. They grew up in a generally prosperous period in American life, but also experienced as teenagers the uncer ...
Ecology
... • The ice and steam in Iceland’s landscape (background slide) is an example of a specific environment. ...
... • The ice and steam in Iceland’s landscape (background slide) is an example of a specific environment. ...
Bio 11A
... 2. What factors directly affect population size and growth? 3. How do you define population growth? 4. What does "zero population growth" mean? 5. Describe exponential growth (curve shape, limiting factors) and give an example. 6. What is the equation that describes exponential growth? 7. Explain "d ...
... 2. What factors directly affect population size and growth? 3. How do you define population growth? 4. What does "zero population growth" mean? 5. Describe exponential growth (curve shape, limiting factors) and give an example. 6. What is the equation that describes exponential growth? 7. Explain "d ...
Chapter 5: How Ecosystems Work
... Increased levels of carbon dioxide may contribute to __________________________________________. ...
... Increased levels of carbon dioxide may contribute to __________________________________________. ...
Chapter 23
... a. animals are multicellular organisms b. bodies of animals are composed of groups of cells organized into tissues, organs, and organ systems c. cells have a nucleus but lack cell walls d. heterotrophic e. able to move from place to place or move one part of their body with respect to other parts 23 ...
... a. animals are multicellular organisms b. bodies of animals are composed of groups of cells organized into tissues, organs, and organ systems c. cells have a nucleus but lack cell walls d. heterotrophic e. able to move from place to place or move one part of their body with respect to other parts 23 ...
Natural environment

The natural environment encompasses all living and non-living things occurring naturally on Earth or some region thereof. It is an environment that encompasses the interaction of all living species. Climate, weather, and natural resources that affect human survival and economic activity.The concept of the natural environment can be distinguished by components: Complete ecological units that function as natural systems without massive civilized human intervention, including all vegetation, microorganisms, soil, rocks, atmosphere, and natural phenomena that occur within their boundaries Universal natural resources and physical phenomena that lack clear-cut boundaries, such as air, water, and climate, as well as energy, radiation, electric charge, and magnetism, not originating from civilized human activityIn contrast to the natural environment is the built environment. In such areas where man has fundamentally transformed landscapes such as urban settings and agricultural land conversion, the natural environment is greatly modified and diminished, with a much more simplified human environment largely replacing it. Even events which seem less extreme such as hydroelectric dam construction, or photovoltaic system construction in the desert, the natural environment is substantially altered.It is difficult to find absolutely natural environments, and it is common that the naturalness varies in a continuum, from ideally 100% natural in one extreme to 0% natural in the other. More precisely, we can consider the different aspects or components of an environment, and see that their degree of naturalness is not uniform. If, for instance, we take an agricultural field, and consider the mineralogic composition and the structure of its soil, we will find that whereas the first is quite similar to that of an undisturbed forest soil, the structure is quite different.Natural environment is often used as a synonym for habitat. For instance, when we say that the natural environment of giraffes is the savanna.