quantum mechanics
... 6th Semester. Lectures: 34 hours, Seminars: 34 hours 7th Semester. Lectures: 32 hours, Seminars: 30 hours ...
... 6th Semester. Lectures: 34 hours, Seminars: 34 hours 7th Semester. Lectures: 32 hours, Seminars: 30 hours ...
icnfp_2015_v5
... Simplicity of this formula should not camouflage a highly nontrivial physical fact, that the force depends on the only parameter of the body - its mass (and not, for example, on its chemical composition, entropy etc). The situation gets more complex if the test body is immersed into gas or fluid. Th ...
... Simplicity of this formula should not camouflage a highly nontrivial physical fact, that the force depends on the only parameter of the body - its mass (and not, for example, on its chemical composition, entropy etc). The situation gets more complex if the test body is immersed into gas or fluid. Th ...
powerpoint - University of Illinois Urbana
... (a) uniform energy separation, (b) zeropoint energy, (c) larger probability at turning points. We introduce the concept of orthogonal polynomials. Here, we encounter the first set: Hermite polynomials. ...
... (a) uniform energy separation, (b) zeropoint energy, (c) larger probability at turning points. We introduce the concept of orthogonal polynomials. Here, we encounter the first set: Hermite polynomials. ...
this document - ITP Lecture Archive
... • Give a pedagogical presentation demonstrating solid understanding of the material. • Be present at least 80% of the time. • Hand in a written report of your talk (around 10 pages, in English, as PDF file). Each presentation should last around 60 minutes, but not more. It is followed by a general d ...
... • Give a pedagogical presentation demonstrating solid understanding of the material. • Be present at least 80% of the time. • Hand in a written report of your talk (around 10 pages, in English, as PDF file). Each presentation should last around 60 minutes, but not more. It is followed by a general d ...
Some beautiful equations of mathematical physics
... Despite this broad physical scope the basic particle physics of the Dirac equation is straightforward. It is a first-order equation so one must specify the four components of ψ(x, 0) as initial data. There are four quantum degrees of freedom, namely for each momentum p, a particle and antiparticle, ...
... Despite this broad physical scope the basic particle physics of the Dirac equation is straightforward. It is a first-order equation so one must specify the four components of ψ(x, 0) as initial data. There are four quantum degrees of freedom, namely for each momentum p, a particle and antiparticle, ...
Slide - University of Maryland
... But we worked in P-smooth gauges. What is the description there? Well, how does a point on the manifold “change” under a gauge transformation… ...
... But we worked in P-smooth gauges. What is the description there? Well, how does a point on the manifold “change” under a gauge transformation… ...
20070822140014201
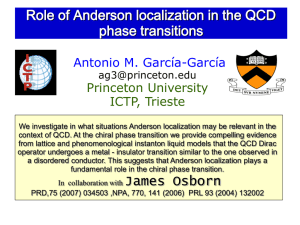
... 2. QCD but only consider certain classical solutions (t'Hooft): Instantons (chiral), Monopoles and vortices (confinement). Instanton do not dissapear at the transiton (Shuryak,Schafer). We propose that quantum interference and tunneling, namely, Anderson localization plays an important role. Nuclear ...
... 2. QCD but only consider certain classical solutions (t'Hooft): Instantons (chiral), Monopoles and vortices (confinement). Instanton do not dissapear at the transiton (Shuryak,Schafer). We propose that quantum interference and tunneling, namely, Anderson localization plays an important role. Nuclear ...
another Exam2
... n = 2 states due to this electric field. (Give your answers in terms of e , E0 , a0 , etc.) (b) (10) Calculate the 4 energy eigenstates as superpositions of the original unperturbed states 200 , 210 , 211 , and 21, !1 . (I.e., if the new states are labeled 1 , 2 , 3 , 4 , you might obtain solutions ...
... n = 2 states due to this electric field. (Give your answers in terms of e , E0 , a0 , etc.) (b) (10) Calculate the 4 energy eigenstates as superpositions of the original unperturbed states 200 , 210 , 211 , and 21, !1 . (I.e., if the new states are labeled 1 , 2 , 3 , 4 , you might obtain solutions ...
Physics 722, Spring 2007 Final Exam Due Friday, May 11, 5pm
... iΠµν (k), where k is the (off-shell) photon momentum flowing through the diagram. Show that the loop integral is convergent (or more precisely, the divergent parts cancel), and express it in the form, i Πµν (k) = g µν F (k 2 ) + k µ k ν G(k 2 ). You may leave F (k 2 ) and G(k 2 ) as integrals over a ...
... iΠµν (k), where k is the (off-shell) photon momentum flowing through the diagram. Show that the loop integral is convergent (or more precisely, the divergent parts cancel), and express it in the form, i Πµν (k) = g µν F (k 2 ) + k µ k ν G(k 2 ). You may leave F (k 2 ) and G(k 2 ) as integrals over a ...
Note 1
... and so they are not physical observables.7 On the other hand, di↵eomorphisms that reach infinity (like, say, a global translation) are physical symmetries — taking states in the Hilbert space to di↵erent states in the Hilbert space — so we get a physical observable by taking the insertion points to ...
... and so they are not physical observables.7 On the other hand, di↵eomorphisms that reach infinity (like, say, a global translation) are physical symmetries — taking states in the Hilbert space to di↵erent states in the Hilbert space — so we get a physical observable by taking the insertion points to ...
Lecture6.QM.to.Lagrangian.Densities
... Just as there is no “derivation” of quantum mechanics from classical mechanics, there is no derivation of relativistic field theory from quantum mechanics. The “route” from one to the other is based on physically reasonable postulates and the imposition of Lorentz invariance and relativistic kinemat ...
... Just as there is no “derivation” of quantum mechanics from classical mechanics, there is no derivation of relativistic field theory from quantum mechanics. The “route” from one to the other is based on physically reasonable postulates and the imposition of Lorentz invariance and relativistic kinemat ...
Is there a preferred canonical quantum gauge?
... which produces a magnetic field analogous to a long solenoid, and a particle with charge e outside it. For simplicity, the electrostatic interaction is removed by putting a uniform stationary line charge inside the cylinder with its linear charge density opposite to that of the cylinder so that the ...
... which produces a magnetic field analogous to a long solenoid, and a particle with charge e outside it. For simplicity, the electrostatic interaction is removed by putting a uniform stationary line charge inside the cylinder with its linear charge density opposite to that of the cylinder so that the ...
Quantum Mechanics Lecture Course for 4 Semester Students by W.B. von Schlippe
... (i) Newton’s 1st law of mechanics, the relativity principle, remains in force; (ii) Newton’s 3rd law of mechanics, “action equals reaction”, also remains in force. The first one of these was later extended to electromagnetism: it is one of the postulates of Einstein’s (special) theory of relativity. ...
... (i) Newton’s 1st law of mechanics, the relativity principle, remains in force; (ii) Newton’s 3rd law of mechanics, “action equals reaction”, also remains in force. The first one of these was later extended to electromagnetism: it is one of the postulates of Einstein’s (special) theory of relativity. ...
LOYOLA COLLEGE (AUTONOMOUS), CHENNAI – 600 034
... 2. Prove explicitly that the momentum operator is a self-adjoint operator. 3. Write down the ground state energy eigenfunction of a simple harmonic oscillator? Sketch its graph. 4. Define the parity operator by its effect on a wave function. What are its eigenvalues? 5. If A is any Hermitian operato ...
... 2. Prove explicitly that the momentum operator is a self-adjoint operator. 3. Write down the ground state energy eigenfunction of a simple harmonic oscillator? Sketch its graph. 4. Define the parity operator by its effect on a wave function. What are its eigenvalues? 5. If A is any Hermitian operato ...