Electronic Structures and Chemical Bonding of Minerals and
... If atoms have similar electronegativities, they adopt closed-shell configurations by sharing electrons with each other; the atoms are held together by covalent bonds. The chemical bond between two different elements is intermediate between the ionic and covalent extremes. The %ionic character is det ...
... If atoms have similar electronegativities, they adopt closed-shell configurations by sharing electrons with each other; the atoms are held together by covalent bonds. The chemical bond between two different elements is intermediate between the ionic and covalent extremes. The %ionic character is det ...
Use of the Jahn-Teller Theorem in Inorganic Chemistry
... two e, components and involving lengthening and shortening of various bonds, is possible and is described by the traditional "Mexican hat" potential-energy surface, shown in ref 8 for example. (Le., the Jahn-Teller theorem gives the symmetry species of the distortion, but there is an ambiguity as to ...
... two e, components and involving lengthening and shortening of various bonds, is possible and is described by the traditional "Mexican hat" potential-energy surface, shown in ref 8 for example. (Le., the Jahn-Teller theorem gives the symmetry species of the distortion, but there is an ambiguity as to ...
Answer - Assignment Expert
... For example, Fe(CN)63- and Fe(CN)64- are named ferricyanide and ferrocyanide respectively, and Fe(CO)5 is called iron carbonyl. Examples 1. [Cr(NH3)3(H2O)3]Cl3 Name: triamminetriaquachromium(III) chloride Solution: The complex ion is inside the parentheses, which is a cation. The ammine ligands are ...
... For example, Fe(CN)63- and Fe(CN)64- are named ferricyanide and ferrocyanide respectively, and Fe(CO)5 is called iron carbonyl. Examples 1. [Cr(NH3)3(H2O)3]Cl3 Name: triamminetriaquachromium(III) chloride Solution: The complex ion is inside the parentheses, which is a cation. The ammine ligands are ...
Document
... In the MO approach, the molecular wavefunctions are a combination of the atomic orbitals, wherein the latter can physically overlap with each other. In particular, the orbitals of the ligands overlap with those of the metal to generate the coordination bonds. Since the MOs are irreducible representa ...
... In the MO approach, the molecular wavefunctions are a combination of the atomic orbitals, wherein the latter can physically overlap with each other. In particular, the orbitals of the ligands overlap with those of the metal to generate the coordination bonds. Since the MOs are irreducible representa ...
Inorganic concepts relevant to metal binding, activity
... dxz, dyz; Fig. 2). The availability of d electrons can stabilize the system by preferential rather than random filling of the low lying levels (t2g). The gain in bond energy by preferential filling is called the "crystal field stabilization energy" (CFSE). Referring to the crystal field splitting di ...
... dxz, dyz; Fig. 2). The availability of d electrons can stabilize the system by preferential rather than random filling of the low lying levels (t2g). The gain in bond energy by preferential filling is called the "crystal field stabilization energy" (CFSE). Referring to the crystal field splitting di ...
ch22_lecture_6e_final
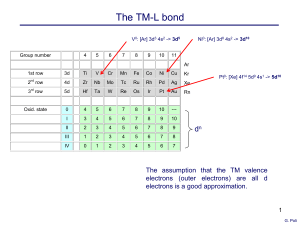
... The abundance of an element is the amount of that element in a particular region of the natural world. Elements are not equally abundant in all regions – abundances differ due to the differences in physical and chemical behavior of the elements. - The core of the Earth is rich in dense Group 8B(8) t ...
... The abundance of an element is the amount of that element in a particular region of the natural world. Elements are not equally abundant in all regions – abundances differ due to the differences in physical and chemical behavior of the elements. - The core of the Earth is rich in dense Group 8B(8) t ...
Chapter 24 Organometallic d
... •Valid for middle d-block metals, and there are exceptions for early and late d-block metals. •16 electron complexes common for Rh(I), Ir(I), Pd(0) and Pt(0) Rules •Treat all ligands as neutral species to avoid assigning oxidation state to metal center. •The number of valence electrons for a zero ox ...
... •Valid for middle d-block metals, and there are exceptions for early and late d-block metals. •16 electron complexes common for Rh(I), Ir(I), Pd(0) and Pt(0) Rules •Treat all ligands as neutral species to avoid assigning oxidation state to metal center. •The number of valence electrons for a zero ox ...
Chapter 23
... align opposite each other, but the spins are not equal, so there is a net magnetic field. • This can occur because magnetic centers have different numbers of unpaired electrons; more sites align in one direction than the other; both of these conditions apply. • Examples are NiMnO3, Y3Fe5O12, a ...
... align opposite each other, but the spins are not equal, so there is a net magnetic field. • This can occur because magnetic centers have different numbers of unpaired electrons; more sites align in one direction than the other; both of these conditions apply. • Examples are NiMnO3, Y3Fe5O12, a ...
Nomenclature of Coordination Complexes Rule 1
... Geometrical isomers are designated by cis- or trans- and mer- or fac- , the latter two standing for meridional or facial, respectively. Rule 9: Bridging ligands are designated with the prefix - . When there are two bridging ligands of the same kind, the prefix di-- is used. Bridging ligands are l ...
... Geometrical isomers are designated by cis- or trans- and mer- or fac- , the latter two standing for meridional or facial, respectively. Rule 9: Bridging ligands are designated with the prefix - . When there are two bridging ligands of the same kind, the prefix di-- is used. Bridging ligands are l ...
MOLECULAR NITRIDES CONTAINING TITANIUM AND GROUP 1, 2
... The preorganized ligand 1 reacts with one equivalent of magnesium amido-, alkyl- and cyclopentadienyl compounds [MgR2(thf)n] to give single cubetype molecular nitrides [RMg{(µ3-N)(µ3-NH)2Ti3Cp*3(µ3-N)}] (R = N(SiMe3)2 (11), CH2CMe3 (12), CH2Ph (13), Cp (14)). Analogous reactions with the heavier alk ...
... The preorganized ligand 1 reacts with one equivalent of magnesium amido-, alkyl- and cyclopentadienyl compounds [MgR2(thf)n] to give single cubetype molecular nitrides [RMg{(µ3-N)(µ3-NH)2Ti3Cp*3(µ3-N)}] (R = N(SiMe3)2 (11), CH2CMe3 (12), CH2Ph (13), Cp (14)). Analogous reactions with the heavier alk ...
and Platinum(1V) Compounds
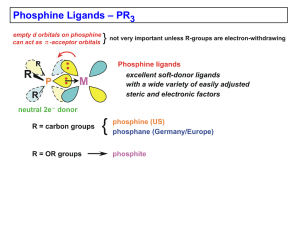
... describe the use of photoelectron spectroscopy to investigate the a-acceptor character of ligands in coordination compound^.^ In our first study1 we found that the 2p binding energy of phosphorus in triphenylphosphine does not increase upon coordination of the triphenylphosphine to nickel, palladium ...
... describe the use of photoelectron spectroscopy to investigate the a-acceptor character of ligands in coordination compound^.^ In our first study1 we found that the 2p binding energy of phosphorus in triphenylphosphine does not increase upon coordination of the triphenylphosphine to nickel, palladium ...
Sample Chem 111 Final
... a) All particles moving with the same velocity have the same kinetic energy. b) All particles at the same temperature have the same kinetic energy. c) All particles having the same kinetic energy have the same mass. d) As the kinetic energy of a particle is halved its velocity is also halved. e) As ...
... a) All particles moving with the same velocity have the same kinetic energy. b) All particles at the same temperature have the same kinetic energy. c) All particles having the same kinetic energy have the same mass. d) As the kinetic energy of a particle is halved its velocity is also halved. e) As ...
Synthesis and Properties of a New Kind of One
... nitride, as well. But in the proposed new structure there are not so many restrictions limiting the number of possible compounds with good conductivity. Because much more metal atoms prefer an octahedral coordination as there are suitable atoms with a ds configuration available. In addition a greate ...
... nitride, as well. But in the proposed new structure there are not so many restrictions limiting the number of possible compounds with good conductivity. Because much more metal atoms prefer an octahedral coordination as there are suitable atoms with a ds configuration available. In addition a greate ...
Axial Ligation Equilibria as Probes of the Effective Steric Bulk of
... Recently, we used octasubstituted tetraarylporphyrins to establish that the alkyl exchange reaction of alkyl-cobalt(III) porphyrin complexes with cobalt(II) porphyrin complexes proceeds via a bimolecular, SH2 mechanism. However, our results suggested that the relationship between the effective steri ...
... Recently, we used octasubstituted tetraarylporphyrins to establish that the alkyl exchange reaction of alkyl-cobalt(III) porphyrin complexes with cobalt(II) porphyrin complexes proceeds via a bimolecular, SH2 mechanism. However, our results suggested that the relationship between the effective steri ...
Spin crossover

Spin Crossover (SCO), sometimes referred to as spin transition or spin equilibrium behavior, is a phenomenon that occurs in some metal complexes wherein the spin state of the complex changes due to external stimuli such as a variation of temperature, pressure, light irradiation or an influence of a magnetic field.With regard to a ligand field and ligand field theory, the change in spin state is a transition from a low spin (LS) ground state electron configuration to a high spin (HS) ground state electron configuration of the metal’s d atomic orbitals (AOs), or vice versa. The magnitude of the ligand field splitting along with the pairing energy of the complex determines whether it will have a LS or HS electron configuration. A LS state occurs because the ligand field splitting (Δ) is greater than the pairing energy of the complex (which is an unfavorable process).Figure 1 is a simplified illustration of the metal’s d orbital splitting in the presence of an octahedral ligand field. A large splitting between the t2g and eg AOs requires a substantial amount of energy for the electrons to overcome the energy gap (Δ) to comply with Hund’s Rule. Therefore, electrons will fill the lower energy t2g orbitals completely before populating the higher energy eg orbitals. Conversely, a HS state occurs with weaker ligand fields and smaller orbital splitting. In this case the energy required to populate the higher levels is substantially less than the pairing energy and the electrons fill the orbitals according to Hund’s Rule by populating the higher energy orbitals before pairing with electrons in the lower lying orbitals. An example of a metal ion that can exist in either a LS or HS state is Fe3+ in an octahedral ligand field. Depending on the ligands that are coordinated to this complex the Fe3+ can attain a LS or a HS state, as in Figure 1.Spin crossover refers to the transitions between high to low, or low to high, spin states. This phenomenon is commonly observed with some first row transition metal complexes with a d4 through d7 electron configuration in an octahedral ligand geometry. Spin transition curves are a common representation of SCO phenomenon with the most commonly observed types depicted in Figure 2 in which γHS (the high-spin molar fraction) is plotted vs. T. The figure shows a gradual spin transition (left), an abrupt transition with hysteresis (middle) and a two-step transition (right). For a transition to be considered gradual, it typically takes place over a large temperature range, even up to several hundred K, whereas for a transition to be considered abrupt, it should take place within 10 K or less.These curves indicate that a spin transition has occurred in a metal complex as temperature changed. The gradual transition curve is an indication that not all metal centers within the complex are undergoing the transition at the same temperature. The abrupt spin change with hysteresis indicates a strong cooperativity, or “communication”, between neighboring metal complexes. In the latter case, the material is bistable and can exist in the two different spin states with a different range of external stimuli (temperature in this case) for the two phenomena, namely LS → HS and HS → LS. The two-step transition is relatively rare but is observed, for example, with dinuclear SCO complexes for which the spin transition in one metal center renders the transition in the second metal center less favorable.There are several types of spin crossover that can occur in a complex; some of them are light induced excited state spin trapping (LIESST), ligand-driven light induced spin change (LD-LISC), and charge transfer induced spin transition (CTIST).