International Baccalaureate Biology Option
... The visceral system is largely subconscious and deals with systems such as heart, gut, breathing. The motor neurons of the visceral system form the ANS. In general these are antagonistic, e.g. for the heart, sympathetic impulses speed it up and parasympathetic impulses slow it down. (See core guide ...
... The visceral system is largely subconscious and deals with systems such as heart, gut, breathing. The motor neurons of the visceral system form the ANS. In general these are antagonistic, e.g. for the heart, sympathetic impulses speed it up and parasympathetic impulses slow it down. (See core guide ...
unit 2: biological bases of behavior
... Summarize the criticisms of evolutionary explanations of human behaviors, and describe the evolutionary psychologists’ responses to those criticisms. ...
... Summarize the criticisms of evolutionary explanations of human behaviors, and describe the evolutionary psychologists’ responses to those criticisms. ...
D. Eisenhower Polio Myelitis: A Virus which caused Nerve cell
... Axon takes message from one nerve to another. Dendrites receives the messages from an axon from another cell. Nota Bene: The axon and dendrite do not touch there is a gap between them. this gap is a bridged by a synapse facilitated by a chemical known as Acetyicholine which is active in the tr ...
... Axon takes message from one nerve to another. Dendrites receives the messages from an axon from another cell. Nota Bene: The axon and dendrite do not touch there is a gap between them. this gap is a bridged by a synapse facilitated by a chemical known as Acetyicholine which is active in the tr ...
Basic Brain Facts - The Practice of Parenting
... • By the age of three, we have 1,000 trillion (a quadrillion) connections between neurons. • By the age of three, the connections that are the weakest start to get pruned. This allows the brain to operate more efficiently. The strongest connections, those associated with emotion and repetition, remain ...
... • By the age of three, we have 1,000 trillion (a quadrillion) connections between neurons. • By the age of three, the connections that are the weakest start to get pruned. This allows the brain to operate more efficiently. The strongest connections, those associated with emotion and repetition, remain ...
Unit 4: Neuroscience The Neuron Soma (cell body): Contains
... planning, and language. About 75-80% of the brain is composed of association areas. Hemispheres of the Brain Virtually all activities require BOTH hemispheres. However, the Left Hemisphere receives sensory information from the right side of the body and controls movement of the right side of the bod ...
... planning, and language. About 75-80% of the brain is composed of association areas. Hemispheres of the Brain Virtually all activities require BOTH hemispheres. However, the Left Hemisphere receives sensory information from the right side of the body and controls movement of the right side of the bod ...
Cerebrospinal Fluid
... Cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) is a clear bodily fluid that occupies the subarachnoid space and the ventricular system around and inside the brain and spinal cord. The CSF occupies the space between the Arachnoid and the Pia . It constitutes the content of all intra-cerebral, cisterns, and Sulci as well ...
... Cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) is a clear bodily fluid that occupies the subarachnoid space and the ventricular system around and inside the brain and spinal cord. The CSF occupies the space between the Arachnoid and the Pia . It constitutes the content of all intra-cerebral, cisterns, and Sulci as well ...
Long Term effects of drugs on the brain
... specific brain areas: the mammillary bodies (important for memory) the cerebral cortex (controls mental functions) ...
... specific brain areas: the mammillary bodies (important for memory) the cerebral cortex (controls mental functions) ...
Module 4 Notes
... 6. Describe research on the split brain, and discuss what it reveals regarding normal brain functioning. A split brain is one whose corpus callosum, the wide band of axon fibers that connects the two brain hemispheres, has been severed. Experiments on split-brain patients have refined our knowledge ...
... 6. Describe research on the split brain, and discuss what it reveals regarding normal brain functioning. A split brain is one whose corpus callosum, the wide band of axon fibers that connects the two brain hemispheres, has been severed. Experiments on split-brain patients have refined our knowledge ...
The body`s information system is built from billions of interconnected
... More intelligent animals have increased “uncommitted” or association areas of the cortex. The Brain’s Plasticity The brain is sculpted by our genes but also by our experiences. Plasticity refers to the brain’s ability to modify itself after some types of injury or illness. the brain is capable of ch ...
... More intelligent animals have increased “uncommitted” or association areas of the cortex. The Brain’s Plasticity The brain is sculpted by our genes but also by our experiences. Plasticity refers to the brain’s ability to modify itself after some types of injury or illness. the brain is capable of ch ...
Neuron and Brain Review Handout
... 2. Reticular Formation: A neural network within the brainstem; important in arousal including sleep. Thalamus: Sits on top of the brainstem; received all incoming sensory information (except smell) and sends it to the appropriate part of the brain for further processing. Cerebellum: The "little brai ...
... 2. Reticular Formation: A neural network within the brainstem; important in arousal including sleep. Thalamus: Sits on top of the brainstem; received all incoming sensory information (except smell) and sends it to the appropriate part of the brain for further processing. Cerebellum: The "little brai ...
Module 07_lecture
... Medulla • Located at the base of the brainstem • Controls life-supporting functions like heartbeat and breathing • Damage to this area can lead to death. ...
... Medulla • Located at the base of the brainstem • Controls life-supporting functions like heartbeat and breathing • Damage to this area can lead to death. ...
The human brain
... The secret of the brain lies in the vast number of neurons (tens of billions) and the complicated way they are connected. ...
... The secret of the brain lies in the vast number of neurons (tens of billions) and the complicated way they are connected. ...
______ 1
... _____________________44. Associated with movement, orientation, recognition, & perception of stimuli _____________________45. Associated with visual processing _____________________46. Four lobes of the brain _____________________ _____________________ _____________________ _____________________47. ...
... _____________________44. Associated with movement, orientation, recognition, & perception of stimuli _____________________45. Associated with visual processing _____________________46. Four lobes of the brain _____________________ _____________________ _____________________ _____________________47. ...
Chapter-5-Sources-of-Energy
... • To examine the structure of lipids and their various roles in cells and organisms • To study protein degradation and their use as an alternative respiratory ...
... • To examine the structure of lipids and their various roles in cells and organisms • To study protein degradation and their use as an alternative respiratory ...
Brain Cell or Neuron
... part of PNS consisting of motor neurons that control internal organs. controls muscles in the heart, the smooth muscle in internal organs such as the intestine, bladder, and uterus. two subsystems. o Sympathetic Nervous System involved in the fight or flight response. o Parasympathetic Nervous Syste ...
... part of PNS consisting of motor neurons that control internal organs. controls muscles in the heart, the smooth muscle in internal organs such as the intestine, bladder, and uterus. two subsystems. o Sympathetic Nervous System involved in the fight or flight response. o Parasympathetic Nervous Syste ...
Brain
... 2. Despite the specialization, no brain area performs only one function. 3. The brain represents the world in maps. 4. All incoming sensory information goes through a switchboard first. ...
... 2. Despite the specialization, no brain area performs only one function. 3. The brain represents the world in maps. 4. All incoming sensory information goes through a switchboard first. ...
The Brain Summary Notes
... If there is damage to #1- one cannot see, #2- one cannot read, #3- one cannot understand, and #4- one cannot physically speak. 75% of the brain is not committed to motor or sensory functions. Theses brain regions are calledAssociation Areas areas that are involved in thinking, remembering, and speak ...
... If there is damage to #1- one cannot see, #2- one cannot read, #3- one cannot understand, and #4- one cannot physically speak. 75% of the brain is not committed to motor or sensory functions. Theses brain regions are calledAssociation Areas areas that are involved in thinking, remembering, and speak ...
Nervous System
... Lies below and behind the cerebral hemispheres Its surface is highly folded It helps coordinate muscle action It receives sensory impulses from muscles, tendons, joints, eyes and ears, as well as input from other brain centers • It processes information about body position • Controls posture by keep ...
... Lies below and behind the cerebral hemispheres Its surface is highly folded It helps coordinate muscle action It receives sensory impulses from muscles, tendons, joints, eyes and ears, as well as input from other brain centers • It processes information about body position • Controls posture by keep ...
Language and the brain
... Language and the brain When we see an object – like a red apple, we recognise its shape and its colour and other things about it. Surprisingly, perhaps, different parts of the brain deal with different aspects of the same thing. So the colour – the redness – registers in one place in the brain and t ...
... Language and the brain When we see an object – like a red apple, we recognise its shape and its colour and other things about it. Surprisingly, perhaps, different parts of the brain deal with different aspects of the same thing. So the colour – the redness – registers in one place in the brain and t ...
File
... – 3 layers of tough, elastic type tissue within the skull and the spinal column – Prevent direct blood flow through the brain and spinal cord – Blood brain barrier (BBB) ...
... – 3 layers of tough, elastic type tissue within the skull and the spinal column – Prevent direct blood flow through the brain and spinal cord – Blood brain barrier (BBB) ...
Nervous System
... – The size and weight of the brain decreases – The senses gradually decline because the number of neurons in this area declines – The functions of all other neurons decreases because the number of neurons decline as well ...
... – The size and weight of the brain decreases – The senses gradually decline because the number of neurons in this area declines – The functions of all other neurons decreases because the number of neurons decline as well ...
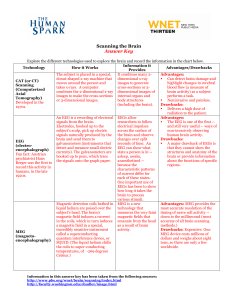
Scanning the Brain AK.rtf
... (electrodetect and measure small electric EEG can show what that they cannot show the encephalograph) currents). The galvanometers are state a person is in -structures and anatomy of the Fun fact: Austrian hooked up to pens, which trace asleep, awake, brain or provide information psychiatrist Hans t ...
... (electrodetect and measure small electric EEG can show what that they cannot show the encephalograph) currents). The galvanometers are state a person is in -structures and anatomy of the Fun fact: Austrian hooked up to pens, which trace asleep, awake, brain or provide information psychiatrist Hans t ...