The Problem of Consciousness by Francis Crick and
... agrees that what we know as mind is closely related to certain aspects of the behavior of the brain, not to the heart, as Aristotle thought. Its most mysterious aspect is consciousness or awareness, which can take many forms, from the experience of pain to self-consciousness. In the past the mind (o ...
... agrees that what we know as mind is closely related to certain aspects of the behavior of the brain, not to the heart, as Aristotle thought. Its most mysterious aspect is consciousness or awareness, which can take many forms, from the experience of pain to self-consciousness. In the past the mind (o ...
Dynamic functional reorganization of the motor execution network
... and Hilgetag, 2006). In addition, graph theoretical methods also allow one to evaluate regional centrality in a graph using measures of centrality in contrast to the connectivity methods mentioned above. So far, graph theoretical approaches have been applied to study development (Fair et al., 2009; ...
... and Hilgetag, 2006). In addition, graph theoretical methods also allow one to evaluate regional centrality in a graph using measures of centrality in contrast to the connectivity methods mentioned above. So far, graph theoretical approaches have been applied to study development (Fair et al., 2009; ...
THE TELL-TALE BRAIN:
... feels like it is moving—sometimes for the first time in years. In many patients this exercise relieves the phantom cramp and associated pain. In clinical trials, mirror visual feedback has also been shown to be more effective than conventional treatments for chronic regional pain syndrome and paraly ...
... feels like it is moving—sometimes for the first time in years. In many patients this exercise relieves the phantom cramp and associated pain. In clinical trials, mirror visual feedback has also been shown to be more effective than conventional treatments for chronic regional pain syndrome and paraly ...
Nervous_system_Tissue_Overview
... Have 3 specialized characteristics Longevity: with nutrition, can live as long as you do Amitotic: unable to reproduce themselves (so cannot be replaced) ...
... Have 3 specialized characteristics Longevity: with nutrition, can live as long as you do Amitotic: unable to reproduce themselves (so cannot be replaced) ...
Fluid-Attenuated Inversion Recovery MR Imaging and Subarachnoid
... readily available than are CT scanners. Often, unstable or irritable patients do not readily/easily undergo MR imaging. In cases in which the patient is more stable, MR imaging may be superior to CT in detecting blood in the CSF because the attenuation changes shown on CT scans resolve more rapidly ...
... readily available than are CT scanners. Often, unstable or irritable patients do not readily/easily undergo MR imaging. In cases in which the patient is more stable, MR imaging may be superior to CT in detecting blood in the CSF because the attenuation changes shown on CT scans resolve more rapidly ...
brain –computer interface - Nexus Academic Publishers
... The brain is incredibly complex. To say that all thoughts or actions are the result of simple electric signals in the brain is a gross understatement. There are about 100 billion neurons in a human brain. Each neuron is constantly sending and receiving signals through a complex web of connections. T ...
... The brain is incredibly complex. To say that all thoughts or actions are the result of simple electric signals in the brain is a gross understatement. There are about 100 billion neurons in a human brain. Each neuron is constantly sending and receiving signals through a complex web of connections. T ...
The Biology
... discussion on how the different areas work to control voluntary and involuntary behaviours. The chapter also examines how the various parts of the nervous system operate together in emergency situations to produce lifesaving responses to danger. Next, the brain itself will be considered by examining ...
... discussion on how the different areas work to control voluntary and involuntary behaviours. The chapter also examines how the various parts of the nervous system operate together in emergency situations to produce lifesaving responses to danger. Next, the brain itself will be considered by examining ...
Bioinspired Computing Lecture 5
... Thus, we would expect to find very few ‘redundant’ neurons with co-varying outputs in that network. Accordingly, an optimal temporal coding circuit might tend to eliminate redundancy in the pattern of inputs to different neurons. On the other hand, if neural information is carried by a noisy rate-ba ...
... Thus, we would expect to find very few ‘redundant’ neurons with co-varying outputs in that network. Accordingly, an optimal temporal coding circuit might tend to eliminate redundancy in the pattern of inputs to different neurons. On the other hand, if neural information is carried by a noisy rate-ba ...
HUMAN BRAIN EVOLUTION IN AN ECOLOGICAL CONTEXT^
... on the best-fit line (Jerison. 973). In practice, there is little difference between the encephalization index of Bauchot and Stephan (Stephan, ...
... on the best-fit line (Jerison. 973). In practice, there is little difference between the encephalization index of Bauchot and Stephan (Stephan, ...
Neural plasticity and recovery of function
... • How does learning change the structure and function of neuron in the brain? – CNS structural changes occur because of the interaction between both genetic and experiential factors – There appears to be use-dependent competitions among neurons for synaptic connections (transient and long term modif ...
... • How does learning change the structure and function of neuron in the brain? – CNS structural changes occur because of the interaction between both genetic and experiential factors – There appears to be use-dependent competitions among neurons for synaptic connections (transient and long term modif ...
Morphomechanics: transforming tubes into organs
... simple tubes. Some of these organs (e.g., lungs and kidneys) eventually become a network of branched tubes, while others (e.g., heart and brain) develop into complex structures that no longer bear much resemblance to tubes. Although much is now known about the physical mechanisms that drive many of ...
... simple tubes. Some of these organs (e.g., lungs and kidneys) eventually become a network of branched tubes, while others (e.g., heart and brain) develop into complex structures that no longer bear much resemblance to tubes. Although much is now known about the physical mechanisms that drive many of ...
Introduction to the Self
... processes: physical objects, light, sound, and other persons’ bodies; (2) the out-of-body mind entity can apparently be “seen” by animals; (3) phantom limb “touch” on another person’s head in the region of the brain can elicit visual and other sensations similar to electrical brain stimulation (Mays ...
... processes: physical objects, light, sound, and other persons’ bodies; (2) the out-of-body mind entity can apparently be “seen” by animals; (3) phantom limb “touch” on another person’s head in the region of the brain can elicit visual and other sensations similar to electrical brain stimulation (Mays ...
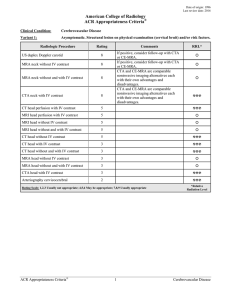
American College of Radiology ACR Appropriateness Criteria
... vascular brain imaging should be considered. MRI preferred over CT due to greater range of soft-tissue contrast and superior anatomic detail. Contrast is useful to evaluate for underlying enhancing mass or vascular malformation. Parenchymal imaging and MR or CT vascular brain imaging should be consi ...
... vascular brain imaging should be considered. MRI preferred over CT due to greater range of soft-tissue contrast and superior anatomic detail. Contrast is useful to evaluate for underlying enhancing mass or vascular malformation. Parenchymal imaging and MR or CT vascular brain imaging should be consi ...
The Nervous System
... tions, some better understood than others. The nervous system is used to communicate from one end of the body to another. The nervous system receives and integrates stimuli, and formulates an appropriate response. The stimulus can be an external change, such as a shift in temperature or sound, or it ...
... tions, some better understood than others. The nervous system is used to communicate from one end of the body to another. The nervous system receives and integrates stimuli, and formulates an appropriate response. The stimulus can be an external change, such as a shift in temperature or sound, or it ...
Learning pattern recognition and decision making in the insect brain
... where one can discriminate objects much more easily. The theoretical basis for discrimination on a large screen to discriminate more easily was already proposed by Thomas Cover [140] and later within the framework of support vector machines [141]. In addition, sparse code is a very useful component ...
... where one can discriminate objects much more easily. The theoretical basis for discrimination on a large screen to discriminate more easily was already proposed by Thomas Cover [140] and later within the framework of support vector machines [141]. In addition, sparse code is a very useful component ...
Richard J. Wurtman by Thomas A. Ban
... eosinophilia myalgia syndrome. And I felt a little bit responsible; if I’d done what I should have done, if my university had patented tryptophan for insomnia and controlled its use by companies that licensed the patent, this wouldn’t have happened. Anyhow, I’d discovered the need to patent discover ...
... eosinophilia myalgia syndrome. And I felt a little bit responsible; if I’d done what I should have done, if my university had patented tryptophan for insomnia and controlled its use by companies that licensed the patent, this wouldn’t have happened. Anyhow, I’d discovered the need to patent discover ...
Methods of Studying The Nervous System
... of the waves emitted by hydrogen atoms when they are placed in a magnetic field • Its clarity stems from the fact that neural structures differ considerably in their density of hydrogen atoms Pinel's Biopsychology, 5th Ed. ...
... of the waves emitted by hydrogen atoms when they are placed in a magnetic field • Its clarity stems from the fact that neural structures differ considerably in their density of hydrogen atoms Pinel's Biopsychology, 5th Ed. ...
FREE Sample Here
... Each technique has strengths and weaknesses. II. Three Layers of the Brain The most primitive layer of the brain is the brain stem, an extension of the spinal cord, which regulates most instinctual responses and basic life processes. Located on top of the brain stem are the limbic system and t ...
... Each technique has strengths and weaknesses. II. Three Layers of the Brain The most primitive layer of the brain is the brain stem, an extension of the spinal cord, which regulates most instinctual responses and basic life processes. Located on top of the brain stem are the limbic system and t ...
Chapter 11
... • The left hemisphere is dominant is most individuals • Dominant hemisphere controls • speech • writing • reading • verbal skills • analytical skills • computational skills ...
... • The left hemisphere is dominant is most individuals • Dominant hemisphere controls • speech • writing • reading • verbal skills • analytical skills • computational skills ...
This file has Chapter II: Structural differentiation of the brain • Neural
... regressive phenomena such as neuronal cell death and axonal pruning (see Cowan 1978). Insightful work on mechanism underlying these processes is now advancing rapidly, but is beyond the scope of the present volume. How can a purely descriptive account of brain structure differentiation be justified ...
... regressive phenomena such as neuronal cell death and axonal pruning (see Cowan 1978). Insightful work on mechanism underlying these processes is now advancing rapidly, but is beyond the scope of the present volume. How can a purely descriptive account of brain structure differentiation be justified ...
Materials - Web Adventures
... body to the synapse. Brain: located in the skull, it is the organ that controls all body activities through the spinal cord and peripheral nerves of the nervous system. Codeine: a naturally occurring component (alkaloid) of opium. It is capable of inducing sleep, relieving pain, and causing addictio ...
... body to the synapse. Brain: located in the skull, it is the organ that controls all body activities through the spinal cord and peripheral nerves of the nervous system. Codeine: a naturally occurring component (alkaloid) of opium. It is capable of inducing sleep, relieving pain, and causing addictio ...
asgn2a -- NERVOUS SYSTEM - Indiana University Bloomington
... The list is as long as the list of things people do and feel. The nervous system uses two basic codes: 1. place codes: where activity is in the brain; This works as a code because different parts of the brain do different things. Such codes are usually called labeled line codes or anatomical codes. ...
... The list is as long as the list of things people do and feel. The nervous system uses two basic codes: 1. place codes: where activity is in the brain; This works as a code because different parts of the brain do different things. Such codes are usually called labeled line codes or anatomical codes. ...
The Neurobiology of Opioid Dependence
... well understood by science, appear to resolve after detoxification, within days or weeks after opioid use stops. The abnormalities that produce addiction, however, are more wide-ranging, complex, and long-lasting. They may involve an interac tion of environmental effects—for example, stress, the so ...
... well understood by science, appear to resolve after detoxification, within days or weeks after opioid use stops. The abnormalities that produce addiction, however, are more wide-ranging, complex, and long-lasting. They may involve an interac tion of environmental effects—for example, stress, the so ...
Nervous System
... What is its FUNCTION? • Receives information about what’s happening inside and outside the body. • Directs the way your body responds to this info. • Helps maintain homeostasis. ...
... What is its FUNCTION? • Receives information about what’s happening inside and outside the body. • Directs the way your body responds to this info. • Helps maintain homeostasis. ...