Consciousness, Literature and the Arts
... philosophies that engage with the disturbances of the Modern and PostModern, in profoundly thoughtful ways, as a poetics of science as well as a science of poetics, bodies and languages in complex syntheses, as liquidities, differences, assemblages, or rhizomes. Here I might be thinking, as a single ...
... philosophies that engage with the disturbances of the Modern and PostModern, in profoundly thoughtful ways, as a poetics of science as well as a science of poetics, bodies and languages in complex syntheses, as liquidities, differences, assemblages, or rhizomes. Here I might be thinking, as a single ...
Document
... – damage to a brain area (electrical or chemical) • Ablation – removal of brain area • Stereotaxic instrument – a device that allows for precise neurosurgical procedures • Sham lesion – performing identical procedures except for damaging the brain – produced by an experimenter in a control subject ...
... – damage to a brain area (electrical or chemical) • Ablation – removal of brain area • Stereotaxic instrument – a device that allows for precise neurosurgical procedures • Sham lesion – performing identical procedures except for damaging the brain – produced by an experimenter in a control subject ...
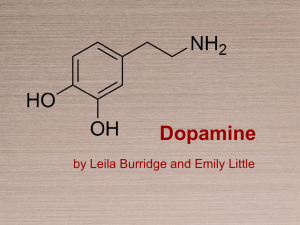
Dopamine 2013
... brain and not just a precursor of norepinephrine. ● Discovered that a lack of dopamine in some areas of the brain could disrupt pathways among nerves that control movement and motor functions. ● This causes Parkinson’s disease. ● Parkinson’s disease symptoms: tremors, rigid muscles, speech changes, ...
... brain and not just a precursor of norepinephrine. ● Discovered that a lack of dopamine in some areas of the brain could disrupt pathways among nerves that control movement and motor functions. ● This causes Parkinson’s disease. ● Parkinson’s disease symptoms: tremors, rigid muscles, speech changes, ...
Bringing the Brain of the Child with Autism Back on Track
... living subjects at such a fine level behavioral effects. Although these studies of detail allows greater understand- have been invaluable in understanding more about the disorder, it is research at a more ing of the processes that underlie basic level that may provide the start for normal brain func ...
... living subjects at such a fine level behavioral effects. Although these studies of detail allows greater understand- have been invaluable in understanding more about the disorder, it is research at a more ing of the processes that underlie basic level that may provide the start for normal brain func ...
Abnormal Magnetic Resonance Imaging and Hemichorea
... also proposed as a potential pathological mechanism explaining the CT and MRI changes associated with non-ketotic hyperglycemia [7]. Complete or partial resolution of the basal ganglia hyperintensity, as was seen in both our cases, refutes this theory and suggests an alternative mechanism(s). In the ...
... also proposed as a potential pathological mechanism explaining the CT and MRI changes associated with non-ketotic hyperglycemia [7]. Complete or partial resolution of the basal ganglia hyperintensity, as was seen in both our cases, refutes this theory and suggests an alternative mechanism(s). In the ...
Chapter 12: The Central Nervous System
... a. Two categories of memory are fact memory and skill memory b. Fact (declarative) memory: 1) Entails learning explicit information 2) Related to our conscious thoughts and our language ability 3) Stored with the context in which it was learned c. Skill Memory 1) Skill memory is less conscious than ...
... a. Two categories of memory are fact memory and skill memory b. Fact (declarative) memory: 1) Entails learning explicit information 2) Related to our conscious thoughts and our language ability 3) Stored with the context in which it was learned c. Skill Memory 1) Skill memory is less conscious than ...
VNS Worksheet - Rice CAAM Department
... information toward the brain? 2. How can touching someone's ear make them cough? 3. How can someone "naturally" stimulate their vagus nerve? 4. Why is the locus coeruleus (LC) called the "blue spot." 5. How many neurons are contained in the blue spot. 6. If the volume of a typical LC neuron is 50,00 ...
... information toward the brain? 2. How can touching someone's ear make them cough? 3. How can someone "naturally" stimulate their vagus nerve? 4. Why is the locus coeruleus (LC) called the "blue spot." 5. How many neurons are contained in the blue spot. 6. If the volume of a typical LC neuron is 50,00 ...
Слайд 1 - Polymer
... each other. • Collections of individuals become increasingly “group like” when they: –Are interdependent –Share a common identity –Have a group structure ...
... each other. • Collections of individuals become increasingly “group like” when they: –Are interdependent –Share a common identity –Have a group structure ...
The Nervous System - Hastings High School
... CSF samples are sometimes taken using a procedure called a lumbar puncture to see if the fluid around the brain is functioning normally. ...
... CSF samples are sometimes taken using a procedure called a lumbar puncture to see if the fluid around the brain is functioning normally. ...
The Neural Control of Movement
... cells involved in skilled movement, particularly in the outer layer of the cerebellum called cerebellum cortex Purkinje cell in cerebellar cortex has a cell body with a large number of denrites The dendritic spines contain small processes called dendritic spines ...
... cells involved in skilled movement, particularly in the outer layer of the cerebellum called cerebellum cortex Purkinje cell in cerebellar cortex has a cell body with a large number of denrites The dendritic spines contain small processes called dendritic spines ...
Brain Areas and Topography
... • MT receives direct input from V1 – largely from the “fast” magno pathway cells ...
... • MT receives direct input from V1 – largely from the “fast” magno pathway cells ...
Addiction - Biological, Not Sociological
... abuser. Genetic factors do not ensure addiction; just as lack of them does not prevent addiction. Certain genes make it harder for a user to stop using drugs. Similarly, certain genes can “protect” from addiction by causing uncomfortable or even painful side effects. An example of this is the ALDH1 ...
... abuser. Genetic factors do not ensure addiction; just as lack of them does not prevent addiction. Certain genes make it harder for a user to stop using drugs. Similarly, certain genes can “protect” from addiction by causing uncomfortable or even painful side effects. An example of this is the ALDH1 ...
I. Global ischemia
... - Neuronal loss in transient global ischemia is due to excitotoxicity - The susceptible neurons have many receptors to the excitatory neurotransmitter glutamate - So in transient global ischemia, the astrocytes release glutamate that binds to its neuronal receptors NMDA (N-methyl D-aspartate) leadin ...
... - Neuronal loss in transient global ischemia is due to excitotoxicity - The susceptible neurons have many receptors to the excitatory neurotransmitter glutamate - So in transient global ischemia, the astrocytes release glutamate that binds to its neuronal receptors NMDA (N-methyl D-aspartate) leadin ...
Biopsychology – Paper 2
... Sensory neurons are also known as afferent neurons, meaning moving towards a central organ or point, that is they move impulses towards the CNS . This type of neuron receives information or stimuli from sensory receptors found in various locations in the body, for example the eyes, ears, tongue, sk ...
... Sensory neurons are also known as afferent neurons, meaning moving towards a central organ or point, that is they move impulses towards the CNS . This type of neuron receives information or stimuli from sensory receptors found in various locations in the body, for example the eyes, ears, tongue, sk ...
Intro-ANN - Computer Science
... – Modeling the brain – “Just” representation of complex functions (Continuous; contrast decision trees) Much progress on both fronts. Drawn interest from: Neuroscience, Cognitive science, AI, Physics, Statistics, and CS/EE. Carla P. Gomes CS4700 ...
... – Modeling the brain – “Just” representation of complex functions (Continuous; contrast decision trees) Much progress on both fronts. Drawn interest from: Neuroscience, Cognitive science, AI, Physics, Statistics, and CS/EE. Carla P. Gomes CS4700 ...
Document
... 2. Procedure may involve injection of a contrast dye, but involves shorter period of scanning than MRI and can be used with patients who have pacemakers or metallic implants B. MRI--magnetic resonance imaging 1. Magnetic field causes usually random spin of hydrogen nuclei in water of cells to orient ...
... 2. Procedure may involve injection of a contrast dye, but involves shorter period of scanning than MRI and can be used with patients who have pacemakers or metallic implants B. MRI--magnetic resonance imaging 1. Magnetic field causes usually random spin of hydrogen nuclei in water of cells to orient ...
Chapter Three - New Providence School District
... Unlike CT and MRI scans, which can only show the structure of the brain, the positron emission tomogacross time. The images produced by this raphy scanner can portray the brain6s actual scans. Newer variations of MRI scans can also monitor brain activity, procedure are called such as blood and oxyge ...
... Unlike CT and MRI scans, which can only show the structure of the brain, the positron emission tomogacross time. The images produced by this raphy scanner can portray the brain6s actual scans. Newer variations of MRI scans can also monitor brain activity, procedure are called such as blood and oxyge ...
BRAIN
... signals that correspond with different parts of the body Used in various fields of study to reflect the relative space that human body parts occupy on the somatosensory cortex (sensory homunculus) and the motor cortex (motor homunculus) Sensory and motor areas for the hands and face are especially l ...
... signals that correspond with different parts of the body Used in various fields of study to reflect the relative space that human body parts occupy on the somatosensory cortex (sensory homunculus) and the motor cortex (motor homunculus) Sensory and motor areas for the hands and face are especially l ...
The BRAIN - davis.k12.ut.us
... Formation of CSF by the choroid plexus is facilitated by the very high rates of blood flow to the choroid plexus Covered with ependymal cells that form the cerebrospinal fluid In the choroid plexus the ependymal cells are, in contrast to elsewhere in the brain, tightly bound by tight junctions That ...
... Formation of CSF by the choroid plexus is facilitated by the very high rates of blood flow to the choroid plexus Covered with ependymal cells that form the cerebrospinal fluid In the choroid plexus the ependymal cells are, in contrast to elsewhere in the brain, tightly bound by tight junctions That ...
references - Academic Science,International Journal of Computer
... Here we use brain wave stimulator which controls the car by detecting the brain wave signals like alpha waves are one type of brain waves predominantly originate from the occipital lobe during wakeful relaxation with closed eyes. Alpha waves are reduced with open eyes, drowsiness and sleep. Beta wav ...
... Here we use brain wave stimulator which controls the car by detecting the brain wave signals like alpha waves are one type of brain waves predominantly originate from the occipital lobe during wakeful relaxation with closed eyes. Alpha waves are reduced with open eyes, drowsiness and sleep. Beta wav ...
Wrap your head around head injuries
... PMBs include the medical and surgical management of all head injuries. People with serious head injuries are always admitted to hospital for observation. The Regulations in the Medical Schemes Act do not restrict the setting in which head injuries may be treated. Relevant treatment and care may be p ...
... PMBs include the medical and surgical management of all head injuries. People with serious head injuries are always admitted to hospital for observation. The Regulations in the Medical Schemes Act do not restrict the setting in which head injuries may be treated. Relevant treatment and care may be p ...
A1980JG24200001
... is simply that in man you must employ techniques that are essentially atraumatic. “The data collected in the 1959 review also included several series of studies in patients with essential hypertension. They were ...
... is simply that in man you must employ techniques that are essentially atraumatic. “The data collected in the 1959 review also included several series of studies in patients with essential hypertension. They were ...
Unit Outline_Ch17 - Westgate Mennonite Collegiate
... The spinal cord and the brain make up the central nervous system (CNS). The Spinal Cord The spinal cord extends from the base of the brain through a large opening in the skull and into the vertebral canal. Structure of the Spinal Cord The spinal nerves project from the cord between the vertebrae. Fl ...
... The spinal cord and the brain make up the central nervous system (CNS). The Spinal Cord The spinal cord extends from the base of the brain through a large opening in the skull and into the vertebral canal. Structure of the Spinal Cord The spinal nerves project from the cord between the vertebrae. Fl ...
module 6: the nervous system and the endocrine system
... Many students have encountered the material in this unit before, either in biology or in high school psychology. The trick, then, is to make this material clear but also different enough in orientation from what they have learned earlier so that it will engage their interest. To the extent that you ...
... Many students have encountered the material in this unit before, either in biology or in high school psychology. The trick, then, is to make this material clear but also different enough in orientation from what they have learned earlier so that it will engage their interest. To the extent that you ...