Chapter 2: Brain and Behavior
... hemispheres and makes possible the transfer of information and the synchronization of activity between them ...
... hemispheres and makes possible the transfer of information and the synchronization of activity between them ...
Aotearoa Neuroscience Postdoctoral Fellow Projects
... subunits and scaffolding proteins such as gephyrin as well as other important receptors such as dopaminergic receptors in post-mortem adult human brain and spinal cord. To date few studies have reported on the presence of inhibitory receptor proteins in the neurogenic and high plasticity areas of th ...
... subunits and scaffolding proteins such as gephyrin as well as other important receptors such as dopaminergic receptors in post-mortem adult human brain and spinal cord. To date few studies have reported on the presence of inhibitory receptor proteins in the neurogenic and high plasticity areas of th ...
Anatomy and Physiology
... The division of the nervous system into say the CNS and the PNS is really about anatomy Nothing wrong with this, but the distinction is not as much about physiology Physiologically we can talk about the cranial nervous system and the spinal nervous system ...
... The division of the nervous system into say the CNS and the PNS is really about anatomy Nothing wrong with this, but the distinction is not as much about physiology Physiologically we can talk about the cranial nervous system and the spinal nervous system ...
______ 1
... _____________________ 3. The difference in electrical charge across a membrane _____________________ 4. Another name for a receiving neuron _____________________ 5. Another name for a transmitting neuron _____________________ 6. Is generated when a dendrite or cell body is stimulated _______________ ...
... _____________________ 3. The difference in electrical charge across a membrane _____________________ 4. Another name for a receiving neuron _____________________ 5. Another name for a transmitting neuron _____________________ 6. Is generated when a dendrite or cell body is stimulated _______________ ...
1. The left and right hemispheres communicate with each other
... a. It accounts for why forgetting is often temporary rather than permanent b. The detrimental effects of a change in physical context from study to test can be offset by mentally recreating the original physical context c. It may explain why childhood experiences before the age of three or four are ...
... a. It accounts for why forgetting is often temporary rather than permanent b. The detrimental effects of a change in physical context from study to test can be offset by mentally recreating the original physical context c. It may explain why childhood experiences before the age of three or four are ...
Mind, Brain & Behavior
... Brightness, not color, is important to motion detection, perspective, relative sizes, depth perception, figure-ground relations, visual illusions. Motion is a cue for distinguishing among objects. ...
... Brightness, not color, is important to motion detection, perspective, relative sizes, depth perception, figure-ground relations, visual illusions. Motion is a cue for distinguishing among objects. ...
NEUROSCIENCE FOR HUMANITIES HESP SYLLABUS
... select a topic from a list of offered articles, or they may propose their own before week 5. They have to deliver an abstract by week 8, when presentations begin. The activity includes: 1) One page abstract of no more than 550 words (Arial 10) containing the relevant information and three references ...
... select a topic from a list of offered articles, or they may propose their own before week 5. They have to deliver an abstract by week 8, when presentations begin. The activity includes: 1) One page abstract of no more than 550 words (Arial 10) containing the relevant information and three references ...
lecture9
... Initially use the trunk & shoulder (proximal joints) to reach for objects; use elbow less frequently. When babies do make large movements, can’t control inter-segmental dynamics. So hand oscillates. ...
... Initially use the trunk & shoulder (proximal joints) to reach for objects; use elbow less frequently. When babies do make large movements, can’t control inter-segmental dynamics. So hand oscillates. ...
Chapter 2—Biological Bases of Behavior I. Neuroanatomy-
... III. The Endocrine System—our body’s chemical messenger system that interacts with the nervous system to regulate behavior and bodily functions Consists of glands that secrete Hormones travel to target organs where Some glands located in the brain (hypothalamus, pituitary, pineal), some in the ...
... III. The Endocrine System—our body’s chemical messenger system that interacts with the nervous system to regulate behavior and bodily functions Consists of glands that secrete Hormones travel to target organs where Some glands located in the brain (hypothalamus, pituitary, pineal), some in the ...
Unit 5: Study Guide Biological Bases of Behavior (Neuroscience)
... C. Reward Centers in our brains? Cool because I’m just a rat. D. You can comprehend me because of your left temporal lobe (named after me) E. Cut my corpus callosum and I’ll have two separate minds F. Show a picture to my right hemisphere and my left hand will draw a picture of it ...
... C. Reward Centers in our brains? Cool because I’m just a rat. D. You can comprehend me because of your left temporal lobe (named after me) E. Cut my corpus callosum and I’ll have two separate minds F. Show a picture to my right hemisphere and my left hand will draw a picture of it ...
Review #2 - Course Notes
... 27. With regard to the process of neural transmission, a refractory period refers to a time interval in which: a. chemical messengers traverse the synaptic gaps between neurons. b. positively charged atoms are pumped back outside a neural membrane. c. a brief electrical charge travels down an axon. ...
... 27. With regard to the process of neural transmission, a refractory period refers to a time interval in which: a. chemical messengers traverse the synaptic gaps between neurons. b. positively charged atoms are pumped back outside a neural membrane. c. a brief electrical charge travels down an axon. ...
Practice Test #2
... 23. Sir Charles Sherrington observed that impulses took more time to travel a neural pathway than he might have anticipated. His observation provided evidence for the existence of: a. association areas. b. the limbic system. c. interneurons. d. synaptic gaps. e. neural networks. 24. Epinephrine and ...
... 23. Sir Charles Sherrington observed that impulses took more time to travel a neural pathway than he might have anticipated. His observation provided evidence for the existence of: a. association areas. b. the limbic system. c. interneurons. d. synaptic gaps. e. neural networks. 24. Epinephrine and ...
The Cerebral Cortex
... • If a body part is amputated, the surrounding neurons in the somatosensory cortex rewire themselves to other areas in the body. • Example: The hand is between the face and are regions on the sensory cortex thus when stroking the face of someone whose hand was amputated, the person felt the sensatio ...
... • If a body part is amputated, the surrounding neurons in the somatosensory cortex rewire themselves to other areas in the body. • Example: The hand is between the face and are regions on the sensory cortex thus when stroking the face of someone whose hand was amputated, the person felt the sensatio ...
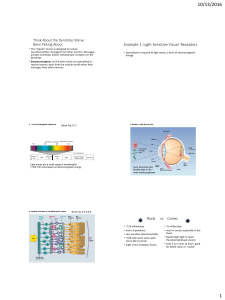
Think About the Dendrites We`ve Been Talking About
... Primary visual cortex is just the first level of cortical processing Damage here”cortical blindness” Secondary “visual cortex” has parallel pathways to separate regions devoted to shape, color, location, & movement that extend beyond occipital lobe. ...
... Primary visual cortex is just the first level of cortical processing Damage here”cortical blindness” Secondary “visual cortex” has parallel pathways to separate regions devoted to shape, color, location, & movement that extend beyond occipital lobe. ...
Sam Wangdescribes some of the physics of our most complex organ
... pink mushy “hardware” and “software” generated by life experiences. However, any comparison with computers misses a messy truth. Because the brain arose through natural selection, it contains layers of systems that arose for one function and then were adopted for another (even though they do not wor ...
... pink mushy “hardware” and “software” generated by life experiences. However, any comparison with computers misses a messy truth. Because the brain arose through natural selection, it contains layers of systems that arose for one function and then were adopted for another (even though they do not wor ...
Learning and the Brain - Santa Clara County Office of
... parts of speech. It is also involved in purposeful acts such as creativity, judgment, problem solving, and ...
... parts of speech. It is also involved in purposeful acts such as creativity, judgment, problem solving, and ...
Lecture 12
... THE BRAIN Overview Neurons within the nervous system link to form circuits with specific functions. In the brain, neural networks create affective and cognitive behaviors. Signaling within these pathways creates thinking, language, feeling, learning, and memory. The brain exhibits plasticity, the ab ...
... THE BRAIN Overview Neurons within the nervous system link to form circuits with specific functions. In the brain, neural networks create affective and cognitive behaviors. Signaling within these pathways creates thinking, language, feeling, learning, and memory. The brain exhibits plasticity, the ab ...
BIOLOGY AND BEHAVIOR
... • Neurotransmitters: the chemicals that propel the message across the synapse from the end of the axon to the awaiting dendrite. Discovered 20 years ago. Die off in adulthood. • Myelin: grease coating on the axon - speeds up message. Not much in the digestive track. ...
... • Neurotransmitters: the chemicals that propel the message across the synapse from the end of the axon to the awaiting dendrite. Discovered 20 years ago. Die off in adulthood. • Myelin: grease coating on the axon - speeds up message. Not much in the digestive track. ...
Visual vs. Language-based Thinking
... by the mirror neuron system. From a cognitive load perspective, this might benefit learning by leaving more working memory capacity available for processes such as elaboration or reflection on intentions of actions, compared to static visualizations. However, we do not know whether and how the mirro ...
... by the mirror neuron system. From a cognitive load perspective, this might benefit learning by leaving more working memory capacity available for processes such as elaboration or reflection on intentions of actions, compared to static visualizations. However, we do not know whether and how the mirro ...
Study Guide Solutions - Elsevier: Baars and Gage
... The brain constantly generates expectations about the world it encounters. Walking downstairs in the dark, we have expectations about every step we take. In dealing with ambiguities like the figures shown here, we constantly make predictions about which of two perceptual interpretations is the best ...
... The brain constantly generates expectations about the world it encounters. Walking downstairs in the dark, we have expectations about every step we take. In dealing with ambiguities like the figures shown here, we constantly make predictions about which of two perceptual interpretations is the best ...
The left hemisphere
... Brain power evolves because there is a need for it. Some environments require all of it for us to survive and reproduce. Evolutionary changes are constrained by physical and temporal factors. Going up the evolutionary chain, we see more bumps or convolutions (folds) on the brains of the “higher” ev ...
... Brain power evolves because there is a need for it. Some environments require all of it for us to survive and reproduce. Evolutionary changes are constrained by physical and temporal factors. Going up the evolutionary chain, we see more bumps or convolutions (folds) on the brains of the “higher” ev ...
answers - UCSD Cognitive Science
... are filled with CSF. (lateral, third, fourth, choroid plexus creastes CSF) Evolution 1. View 1: Quantitative difference a. There are just more neurons in a human brain. The increase in the number of neurons is what gives us added capabilities. ...
... are filled with CSF. (lateral, third, fourth, choroid plexus creastes CSF) Evolution 1. View 1: Quantitative difference a. There are just more neurons in a human brain. The increase in the number of neurons is what gives us added capabilities. ...
Neuroesthetics

Neuroesthetics (or neuroaesthetics) is a relatively recent sub-discipline of empirical aesthetics. Empirical aesthetics takes a scientific approach to the study of aesthetic perceptions of art and music. Neuroesthetics received its formal definition in 2002 as the scientific study of the neural bases for the contemplation and creation of a work of art. Neuroesthetics uses neuroscience to explain and understand the aesthetic experiences at the neurological level. The topic attracts scholars from many disciplines including neuroscientists, art historians, artists, and psychologists.