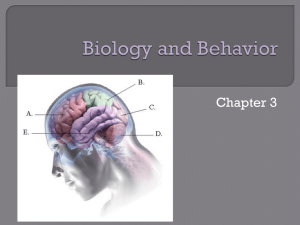
Chapter 3 Section 2 - 6th
... Four key areas of the Forebrain 1. Thalamus- “inner chamber”, critical structure that serves as relay station for sensory stimulation 2. Hypothalamus- extremely important to behavior and physiological aspects Also vital for regulation of body temperature, storage of nutrients and motivation/emotion ...
... Four key areas of the Forebrain 1. Thalamus- “inner chamber”, critical structure that serves as relay station for sensory stimulation 2. Hypothalamus- extremely important to behavior and physiological aspects Also vital for regulation of body temperature, storage of nutrients and motivation/emotion ...
HW CH 5 PSY 2513 Submit your answers on canvas
... In a highly plastic cerebral cortex, a. the areas of the brain are strongly committed to specific functions, and there is a high capacity for learning. b. if a part of the cortex is damaged, other parts can take over the tasks it would have handled. c. spatial skills develop more rapidly than langua ...
... In a highly plastic cerebral cortex, a. the areas of the brain are strongly committed to specific functions, and there is a high capacity for learning. b. if a part of the cortex is damaged, other parts can take over the tasks it would have handled. c. spatial skills develop more rapidly than langua ...
Biosocial Development - Austin Community College District
... children to gain increasing neurological control over their motor functions and sensory abilities and facilitates their intellectual functioning as well. ...
... children to gain increasing neurological control over their motor functions and sensory abilities and facilitates their intellectual functioning as well. ...
Unit 4: Neuroscience The Neuron Soma (cell body): Contains
... Association Areas: Areas of the cortex not involved in sensory or motor functions. They are involved in higher mental functions such as learning, remembering, thinking, planning, and language. About 75-80% of the brain is composed of association areas. Hemispheres of the Brain Virtually all activiti ...
... Association Areas: Areas of the cortex not involved in sensory or motor functions. They are involved in higher mental functions such as learning, remembering, thinking, planning, and language. About 75-80% of the brain is composed of association areas. Hemispheres of the Brain Virtually all activiti ...
Limbic System - WordPress.com
... computer chip) that would restore movement to a limb that was paralyzed due to a brain injury. The device would work by stimulating existing nerves to send messages to cause contraction of the non-functioning limb muscles. Which part of the brain would be the best place to implant this device? ...
... computer chip) that would restore movement to a limb that was paralyzed due to a brain injury. The device would work by stimulating existing nerves to send messages to cause contraction of the non-functioning limb muscles. Which part of the brain would be the best place to implant this device? ...
File
... • They can change their size, shape, function and connections with other neurons • They are influenced by biological processes and environmental experiences ...
... • They can change their size, shape, function and connections with other neurons • They are influenced by biological processes and environmental experiences ...
VISION John Gabrieli Melissa Troyer 9.00
... • A piano can only emit its own notes – it can’t sound like a clarinet. Similarly perceptions are evoked by the world, but they generate experiences limited by the neural structures of our brain. • Our percepts are evoked by nature; but they are personal and not a copy of nature. ...
... • A piano can only emit its own notes – it can’t sound like a clarinet. Similarly perceptions are evoked by the world, but they generate experiences limited by the neural structures of our brain. • Our percepts are evoked by nature; but they are personal and not a copy of nature. ...
File - firestone falcons
... • The absolute threshold for vision was assessed in a landmark experiment by Hecht, Shlaer and Pirenne in 1942. • Vision The amount of light present if someone held up a single candle 30 mi (48 km) away from us, if our eyes were used to the dark. If a person in front of you held up a candle and bega ...
... • The absolute threshold for vision was assessed in a landmark experiment by Hecht, Shlaer and Pirenne in 1942. • Vision The amount of light present if someone held up a single candle 30 mi (48 km) away from us, if our eyes were used to the dark. If a person in front of you held up a candle and bega ...
Ch 3 biology and Behavioir Notes
... The information is processed and place in a “file” in the cortex. Your state of mind activates these networks of connections. When you are in a clear thinking, comfortable and safe frame of mind, you will learn and recall more ...
... The information is processed and place in a “file” in the cortex. Your state of mind activates these networks of connections. When you are in a clear thinking, comfortable and safe frame of mind, you will learn and recall more ...
123COM.CHP:Corel VENTURA
... f low within the vascular network. These findings have notable implications for functional brain mapping using hemodynamic changes as a ‘proxy’ for neural activity. On the one hand, the finding that intrinsic signals identif y reasonably well the area of activation, assessed by electrophysiological ...
... f low within the vascular network. These findings have notable implications for functional brain mapping using hemodynamic changes as a ‘proxy’ for neural activity. On the one hand, the finding that intrinsic signals identif y reasonably well the area of activation, assessed by electrophysiological ...
The Brain, Biology, and Behavior Neuron
... shown, the hippocampus and the amygdala extend out into the temporal lobes at each side of the brain. The limbic system is a sort of “primitive core” of the brain strongly associated with emotion. ...
... shown, the hippocampus and the amygdala extend out into the temporal lobes at each side of the brain. The limbic system is a sort of “primitive core” of the brain strongly associated with emotion. ...
Neuroscience
... cerebral cortex for non-automatic human responses The Thalamus – acts as a sensory relay station sending and receiving information to other parts of the brain (vision, hearing, taste & touch) damage can cause blindness, deafness, etc (not smell) The Cerebellum – primarily regulates posture, muscle ...
... cerebral cortex for non-automatic human responses The Thalamus – acts as a sensory relay station sending and receiving information to other parts of the brain (vision, hearing, taste & touch) damage can cause blindness, deafness, etc (not smell) The Cerebellum – primarily regulates posture, muscle ...
FIGURE LEGENDS FIGURE 22.1 An example of a figure that can
... FIGURE 22.1 An example of a figure that can elicit different perceptions (faces or vase) even though stimulus and sensation remain constant. The mind can “see” purple figures against a blue background or a blue figure against a purple background. FIGURE 22.2 Receptor morphology and relationship to g ...
... FIGURE 22.1 An example of a figure that can elicit different perceptions (faces or vase) even though stimulus and sensation remain constant. The mind can “see” purple figures against a blue background or a blue figure against a purple background. FIGURE 22.2 Receptor morphology and relationship to g ...
Chapter 8: Sensation and Perception
... What types of automatic survival functions are controlled by the brainstem? ...
... What types of automatic survival functions are controlled by the brainstem? ...
nervous system B
... Strange perceptions Which one of these, if any, is the right color for this letter? ...
... Strange perceptions Which one of these, if any, is the right color for this letter? ...
The Nervous System - Centennial Christian School
... • Includes the brain and spinal cord • Is where sensory information is received and motor (movement) control is initiated • Protected by – bone • Brain – skull • Spinal cord – vertebrae ...
... • Includes the brain and spinal cord • Is where sensory information is received and motor (movement) control is initiated • Protected by – bone • Brain – skull • Spinal cord – vertebrae ...
Older Brain Structures
... What types of automatic survival functions are controlled by the brainstem? ...
... What types of automatic survival functions are controlled by the brainstem? ...
MARIJUANA - ctclearinghouse.org
... binds to and activates specific receptors, known as cannabinoid receptors. There are many of these receptors in parts of the brain that control memory, thought, concentration, time and depth perception, and coordinated movement. By activating these receptors, THC interferes with the normal functioni ...
... binds to and activates specific receptors, known as cannabinoid receptors. There are many of these receptors in parts of the brain that control memory, thought, concentration, time and depth perception, and coordinated movement. By activating these receptors, THC interferes with the normal functioni ...
The Brain and Cranial Nerves
... • They have sensory, motor, or both sensory and motor functions • Each nerve is identified by a number (I through XII) and a name ...
... • They have sensory, motor, or both sensory and motor functions • Each nerve is identified by a number (I through XII) and a name ...
Defining the Self: The Orientation Association Area
... OAA so that we can experience a rich sense of the self. iii. The prefrontal cortex actually has many different complex functions. However, for the purposes of this book, we will focus primarily on its ability to help us to focus attention. iv. In terms of the attention association areas function, a ...
... OAA so that we can experience a rich sense of the self. iii. The prefrontal cortex actually has many different complex functions. However, for the purposes of this book, we will focus primarily on its ability to help us to focus attention. iv. In terms of the attention association areas function, a ...
Cognitive Development - Oakland Schools Moodle
... Extremely important medical research area Research continues to show that a baby’s brain capacity is even greater than we ever imagined Our brains are stimulated through our senses Brain function is due to the brain’s capabilities as well as outside experiences ...
... Extremely important medical research area Research continues to show that a baby’s brain capacity is even greater than we ever imagined Our brains are stimulated through our senses Brain function is due to the brain’s capabilities as well as outside experiences ...
primary visual cortex
... central region of its receptive field by firing more rapidly, and illumination in the peripheral region of its receptive field by firing less rapidly. Off-center cells respond to illumination in the peripheral region of its receptive field by firing more rapidly, and illumination in the central re ...
... central region of its receptive field by firing more rapidly, and illumination in the peripheral region of its receptive field by firing less rapidly. Off-center cells respond to illumination in the peripheral region of its receptive field by firing more rapidly, and illumination in the central re ...
Central Nervous System
... body • Sensory – Sensations from the body come here to be processed • Association Areas – where incoming information from the body is processed ...
... body • Sensory – Sensations from the body come here to be processed • Association Areas – where incoming information from the body is processed ...
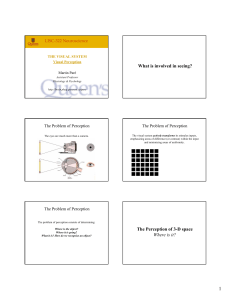
Visual Perception
... These perceptual grouping principles can all be united under a single general rule: the principle of maximum likelihood. The knowledge about which configurations are likely and which are not guides us whenever we seek to determine what is the relationship between neighboring stimuli. ...
... These perceptual grouping principles can all be united under a single general rule: the principle of maximum likelihood. The knowledge about which configurations are likely and which are not guides us whenever we seek to determine what is the relationship between neighboring stimuli. ...
Neuroesthetics

Neuroesthetics (or neuroaesthetics) is a relatively recent sub-discipline of empirical aesthetics. Empirical aesthetics takes a scientific approach to the study of aesthetic perceptions of art and music. Neuroesthetics received its formal definition in 2002 as the scientific study of the neural bases for the contemplation and creation of a work of art. Neuroesthetics uses neuroscience to explain and understand the aesthetic experiences at the neurological level. The topic attracts scholars from many disciplines including neuroscientists, art historians, artists, and psychologists.