Neural Coalition and Main Theorem
... • Can the max information rate hypothesis be proved by appealing to a least action principal in chemical statistical mechanics? (Perhaps this can be approached via the fact that the solution of multiphase chemical equilibrium problems is obtained by solving for the minimum of the Gibbs/Helmholtz Fre ...
... • Can the max information rate hypothesis be proved by appealing to a least action principal in chemical statistical mechanics? (Perhaps this can be approached via the fact that the solution of multiphase chemical equilibrium problems is obtained by solving for the minimum of the Gibbs/Helmholtz Fre ...
ANPS 019 Beneyto-Santonja 10-24
... Inferior Colliculi – play a role in sound localization Substantia nigra – neurons die in Parkinson’s disease Brainstem: Pons Also called metencephalon Connects cerebellum to brainstem Controls sensory and motor function for the face Brainstem: Medulla Oblongata Also called myelencephalon ...
... Inferior Colliculi – play a role in sound localization Substantia nigra – neurons die in Parkinson’s disease Brainstem: Pons Also called metencephalon Connects cerebellum to brainstem Controls sensory and motor function for the face Brainstem: Medulla Oblongata Also called myelencephalon ...
Unit 2 - Monroe Community College
... line tracings called brain waves different patterns associated with different states of mental activity patterns of brain activity for specific behaviors and specific emotions (e.g. anxiety) studying stages of sleep ...
... line tracings called brain waves different patterns associated with different states of mental activity patterns of brain activity for specific behaviors and specific emotions (e.g. anxiety) studying stages of sleep ...
Biological of Behavior
... Researchers use case studies to analyze the effects of brain damage on behavior and cognition. One of the most famous case studies is the story of Phineas Gage. In 1848, Gage (a railway worker) was injured by a spike driving itself through his left cheek out the top of his skull, leaving the frontal ...
... Researchers use case studies to analyze the effects of brain damage on behavior and cognition. One of the most famous case studies is the story of Phineas Gage. In 1848, Gage (a railway worker) was injured by a spike driving itself through his left cheek out the top of his skull, leaving the frontal ...
Answer Key
... 12. With regard to the process of neural transmission, a refractory period refers to a time interval in which A) a neuron fires more rapidly than usual. B) an electrical charge travels from a sensory neuron to a motor neuron. C) positively charged ions are pumped back outside a neural membrane. D) a ...
... 12. With regard to the process of neural transmission, a refractory period refers to a time interval in which A) a neuron fires more rapidly than usual. B) an electrical charge travels from a sensory neuron to a motor neuron. C) positively charged ions are pumped back outside a neural membrane. D) a ...
Arithmetic
... animals, and injured human beings. But brain injuries are imprecise, damaged areas are hard to locate, and often observed post-mortem (as in case of Broca’s and Wernicke’s patients). Brain also compensates for the damage, lesions change over time, adaptation occurs, so that post mortem examinati ...
... animals, and injured human beings. But brain injuries are imprecise, damaged areas are hard to locate, and often observed post-mortem (as in case of Broca’s and Wernicke’s patients). Brain also compensates for the damage, lesions change over time, adaptation occurs, so that post mortem examinati ...
Name
... 4. How do nerve impulses travel from one neuron to another? 5. What are the structure and functions of the central nervous system? 6. What are the structures and functions of the peripheral nervous system? 7. What is a reflex? Give examples 8. What are two ways in which the nervous system can be inj ...
... 4. How do nerve impulses travel from one neuron to another? 5. What are the structure and functions of the central nervous system? 6. What are the structures and functions of the peripheral nervous system? 7. What is a reflex? Give examples 8. What are two ways in which the nervous system can be inj ...
Food for Thought: What Fuels Brain Cells?
... Further analyses of the cell-specific metabolic fluxes in the brain have shown the existence of an “à la carte” delivery of energy substrates. Thus, neurons predominantly use lactate as a fuel, and restrict the use of glucose to predominantly produce a form of energy called reducing power. This allo ...
... Further analyses of the cell-specific metabolic fluxes in the brain have shown the existence of an “à la carte” delivery of energy substrates. Thus, neurons predominantly use lactate as a fuel, and restrict the use of glucose to predominantly produce a form of energy called reducing power. This allo ...
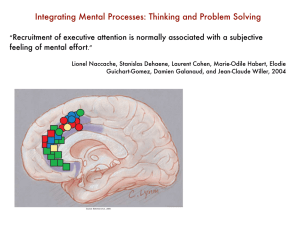
Integrating Mental Processes: Thinking and Problem Solving
... information is acquired about categories and concepts as the result of encounters with specifi c instances. We describe a profoundly amnesic patient (E.P.) who cannot learn and remember specifi c instances-i.e., he has no detectable declarative memory. Yet after inspecting a series of 40 training st ...
... information is acquired about categories and concepts as the result of encounters with specifi c instances. We describe a profoundly amnesic patient (E.P.) who cannot learn and remember specifi c instances-i.e., he has no detectable declarative memory. Yet after inspecting a series of 40 training st ...
Chapter Outlines - Cengage Learning
... 1. The spinal cord carries messages to and from the brain. Reflexes—quick, involuntary muscular responses (through efferent neurons) that are initiated on the basis of incoming sensory information (through afferent neurons)—occur in the spinal cord without instruction from the brain. The brain is in ...
... 1. The spinal cord carries messages to and from the brain. Reflexes—quick, involuntary muscular responses (through efferent neurons) that are initiated on the basis of incoming sensory information (through afferent neurons)—occur in the spinal cord without instruction from the brain. The brain is in ...
Introduction to Brain Structure - Center for Behavioral Neuroscience
... so is involved in all the bodily functions such as digestion (getting nutrients from food), respiration (bringing in oxygen to the lungs), and circulation (having the heart beat and bringing nutrients and oxygen to all the cells of the body through the blood). Additionally, the brain allows one to d ...
... so is involved in all the bodily functions such as digestion (getting nutrients from food), respiration (bringing in oxygen to the lungs), and circulation (having the heart beat and bringing nutrients and oxygen to all the cells of the body through the blood). Additionally, the brain allows one to d ...
Test Question 1 Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS) is a progressive
... a) Assume that the effects of rTMS in ALS patients are the same as in healthy subjects. Which rTMS protocol(s) can then potentially be beneficial for ALS patients? Explain your answer. AW: rTMS with inhibitory effects (e.g. rTMS with 1 HZ or cTBS) b) rTMS is ethically acceptable for neuroscientific ...
... a) Assume that the effects of rTMS in ALS patients are the same as in healthy subjects. Which rTMS protocol(s) can then potentially be beneficial for ALS patients? Explain your answer. AW: rTMS with inhibitory effects (e.g. rTMS with 1 HZ or cTBS) b) rTMS is ethically acceptable for neuroscientific ...
Chapter
... the retina is upside-down. • Here at the retina, the light rays are converted to electrical impulses which are then transmitted through the optic nerve, to the brain, where the image is translated and perceived in an upright position! ...
... the retina is upside-down. • Here at the retina, the light rays are converted to electrical impulses which are then transmitted through the optic nerve, to the brain, where the image is translated and perceived in an upright position! ...
Nervous System
... The brain is organized in ventricles. The Cerebrum is in the two lateral ventricles, the diencephalon is in the third ventricle, and the brain stem is in the fourth ventricle. Cerebrum: largest portion; last to receive sensory input and integrate it before commanding voluntary motor response; coordi ...
... The brain is organized in ventricles. The Cerebrum is in the two lateral ventricles, the diencephalon is in the third ventricle, and the brain stem is in the fourth ventricle. Cerebrum: largest portion; last to receive sensory input and integrate it before commanding voluntary motor response; coordi ...
Understanding Traumatic Brain Injury
... carbon monoxide poisoning, near drowning, choking, and cardiac arrest. ...
... carbon monoxide poisoning, near drowning, choking, and cardiac arrest. ...
Biology
... Sensory- carry messages from sense organs to spinal cord or brain Motor- carry messages from spinal cord or brain to muscles or glands Interneurons- carry messages from one neuron to another and do most of the work of the nervous system ...
... Sensory- carry messages from sense organs to spinal cord or brain Motor- carry messages from spinal cord or brain to muscles or glands Interneurons- carry messages from one neuron to another and do most of the work of the nervous system ...
Biology The Nervous System
... information from other neurons and pass the message through the cell body Axon- carries messages away from the neuron, single fiber Myelin- covering of the axon, insulates and protects the axon, helps to speed up the transmission of the message Axon terminal- small fibers branching out from an axon ...
... information from other neurons and pass the message through the cell body Axon- carries messages away from the neuron, single fiber Myelin- covering of the axon, insulates and protects the axon, helps to speed up the transmission of the message Axon terminal- small fibers branching out from an axon ...
Medical Science/ Neuroscience
... the progressive dysfunction and death of neurons that are responsible for learning and memory processes. Accumulation of amyloid- peptide (A) in the brain is a triggering event leading to the pathological cascade of AD, including dementia. It is necessary for overcoming AD to inhibit A production ...
... the progressive dysfunction and death of neurons that are responsible for learning and memory processes. Accumulation of amyloid- peptide (A) in the brain is a triggering event leading to the pathological cascade of AD, including dementia. It is necessary for overcoming AD to inhibit A production ...
Nervous system and senses
... The axon carries messages away from the cell body. 1. What do Neurons do? ________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________ ...
... The axon carries messages away from the cell body. 1. What do Neurons do? ________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________ ...
A nerve cell
... rats, and leads to increased formation of new granule cells in the dentate gyrus, while the dendrites grow and get more spines, ie more synapses (Eadie et al. 2005 J Comp Neurol) New neurons continue to be formed in the dentate gyrus of hippocampus in mammals including man. The newly formed neurons ...
... rats, and leads to increased formation of new granule cells in the dentate gyrus, while the dendrites grow and get more spines, ie more synapses (Eadie et al. 2005 J Comp Neurol) New neurons continue to be formed in the dentate gyrus of hippocampus in mammals including man. The newly formed neurons ...
The Nervous System - Marblehead High School
... Peripheral Nervous System (PNS) receives information from the environment and sends commands from the CNS to the organs and glands ...
... Peripheral Nervous System (PNS) receives information from the environment and sends commands from the CNS to the organs and glands ...
Psychology 101 Exam 1
... 20) The part of the neuron that sends information is called the _________. a. Dendrite b. Axon c. Myelin sheath d. Terminal button 21) The two halves of the brain are connected by the __________. a. Cerebral hemisphere b. Sulcus c. Corpus callosum d. Gyrus 22) According to lecture, two sources of th ...
... 20) The part of the neuron that sends information is called the _________. a. Dendrite b. Axon c. Myelin sheath d. Terminal button 21) The two halves of the brain are connected by the __________. a. Cerebral hemisphere b. Sulcus c. Corpus callosum d. Gyrus 22) According to lecture, two sources of th ...