Chapter 15 - Nervous System Brain & Cranial Nerves
... blood vascular system. CSF provides protection and nourishment to the brain and spinal cord. Has higher levels of Na and K than blood. CSF reduces weight of brain (1400 gm to 50 gm). ...
... blood vascular system. CSF provides protection and nourishment to the brain and spinal cord. Has higher levels of Na and K than blood. CSF reduces weight of brain (1400 gm to 50 gm). ...
ANATOMY NEURO REVALIDA QUESTIONS
... Give me the difference between the left and right cerebral hemispheres A patient sustains a complete spinal cord transection at the L2 level. Give a description of simple things that he can or cannot do. In simple terms, explain hydrocephalus, cerebrovascular accident (CVA) and transient ischemic at ...
... Give me the difference between the left and right cerebral hemispheres A patient sustains a complete spinal cord transection at the L2 level. Give a description of simple things that he can or cannot do. In simple terms, explain hydrocephalus, cerebrovascular accident (CVA) and transient ischemic at ...
Brain & Behavior
... The Brain, Function & Form • Limbic System • Hippocampus • memory • Amygdala • emotion • Hypothalamus • Motivation; biological drives ...
... The Brain, Function & Form • Limbic System • Hippocampus • memory • Amygdala • emotion • Hypothalamus • Motivation; biological drives ...
Nervous System - Science
... 1. Stimuli comes into the brain through the five senses. The nerves that bring stimuli into the body are SENSORY neurons. 2. The impulse travels through INTERNEURONS. 3. When the impulse reaches the MOTOR neuron, the response occurs. ...
... 1. Stimuli comes into the brain through the five senses. The nerves that bring stimuli into the body are SENSORY neurons. 2. The impulse travels through INTERNEURONS. 3. When the impulse reaches the MOTOR neuron, the response occurs. ...
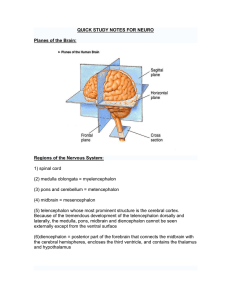
quick study notes for neuro
... - located beneath the grey matter, in the internal regions of the cerebrum and cerebellum - white matter consists of myelinated fibre tracts or neuronal axons - In contrast with the neurons of the white matter, grey matter neurons do not contain long axons that transmit the nerve impulses to more di ...
... - located beneath the grey matter, in the internal regions of the cerebrum and cerebellum - white matter consists of myelinated fibre tracts or neuronal axons - In contrast with the neurons of the white matter, grey matter neurons do not contain long axons that transmit the nerve impulses to more di ...
Cerebral cortex and thalamus lecture
... The basal ganglia • Strongly connected with cortex, thalamus and other brain areas • Involved in movements disorders, including Parkinson’s disease (substantia nigra) and Huntington’s disease (striatum) ...
... The basal ganglia • Strongly connected with cortex, thalamus and other brain areas • Involved in movements disorders, including Parkinson’s disease (substantia nigra) and Huntington’s disease (striatum) ...
The Brain and The Nervous System
... the corpus callosum? • A. The corpus callosum transfers information between the cerebral hemispheres of the brain. • B. Patients with brain damage are unable to send neural information through the corpus callosum. • C. The corpus callosum ensures that each hemisphere of the brain is able to function ...
... the corpus callosum? • A. The corpus callosum transfers information between the cerebral hemispheres of the brain. • B. Patients with brain damage are unable to send neural information through the corpus callosum. • C. The corpus callosum ensures that each hemisphere of the brain is able to function ...
Central Nervous System
... The junction between 2 neurons or between a neuron and a receptor is the synapse. ...
... The junction between 2 neurons or between a neuron and a receptor is the synapse. ...
Harnessing Plasticity to Reset Dysfunctional Neurons
... Plastic changes, however, can also harbor potential danger. The new pattern of neural activation may in itself lead to reorganization and new behaviors that are maladaptive and that not only lack an obvious protective or reparative benefit but, in fact, make matters worse. Examples of this “dark sid ...
... Plastic changes, however, can also harbor potential danger. The new pattern of neural activation may in itself lead to reorganization and new behaviors that are maladaptive and that not only lack an obvious protective or reparative benefit but, in fact, make matters worse. Examples of this “dark sid ...
It`s All About Relationships
... Teens and Alcohol Teens and Nicotine Myelination Increases in certain parts of the brain100% during adolescence. ...
... Teens and Alcohol Teens and Nicotine Myelination Increases in certain parts of the brain100% during adolescence. ...
The Central Nervous System
... Sensory Areas of the Cerebrum • Primary Sensory Cortex - Homunculus Man – The body is represented spatially and upside-down according to the site of stimulus – The right hemisphere receives input from the left side of the body – The amount of sensory cortex devoted to a body region is related to th ...
... Sensory Areas of the Cerebrum • Primary Sensory Cortex - Homunculus Man – The body is represented spatially and upside-down according to the site of stimulus – The right hemisphere receives input from the left side of the body – The amount of sensory cortex devoted to a body region is related to th ...
BIOL241brain12aAUG2012
... • Alpha waves – regular and rhythmic, lowamplitude, slow, synchronous waves indicating an “idling” brain (drifting off) • Beta waves – rhythmic, more irregular waves occurring during the awake and ...
... • Alpha waves – regular and rhythmic, lowamplitude, slow, synchronous waves indicating an “idling” brain (drifting off) • Beta waves – rhythmic, more irregular waves occurring during the awake and ...
BIOL241brain12aAUG2012
... • Alpha waves – regular and rhythmic, lowamplitude, slow, synchronous waves indicating an “idling” brain (drifting off) • Beta waves – rhythmic, more irregular waves occurring during the awake and ...
... • Alpha waves – regular and rhythmic, lowamplitude, slow, synchronous waves indicating an “idling” brain (drifting off) • Beta waves – rhythmic, more irregular waves occurring during the awake and ...
biophysiology show 1
... The nervous system has two parts: • The Central Nervous System – the brain and spinal cord. The spinal cord consists of a large bundle of nerve fibres that run down the back and transmit signals between the body and the brain. • The Peripheral Nervous System – includes the smaller nerves that branc ...
... The nervous system has two parts: • The Central Nervous System – the brain and spinal cord. The spinal cord consists of a large bundle of nerve fibres that run down the back and transmit signals between the body and the brain. • The Peripheral Nervous System – includes the smaller nerves that branc ...
AHISA PASTORAL CARE CONFERENCE, 2006
... • It contains about 100 billion neurons (nerve cells) which are responsible for all our mental activity. These make up the grey matter of the brain ...
... • It contains about 100 billion neurons (nerve cells) which are responsible for all our mental activity. These make up the grey matter of the brain ...
Nervous system part 2
... faces and localizing us in space, involved in understanding written and spoken language (Wernicke’s area) ...
... faces and localizing us in space, involved in understanding written and spoken language (Wernicke’s area) ...
Chapter 7 Body Systems
... voluntary movements on opposite side of the body voluntary movements on same side of body maintain posture during movement transmit impulses that coordinate body movements and maintenance of posture head and neck movements during visual reflexes coordination of posture and balance ...
... voluntary movements on opposite side of the body voluntary movements on same side of body maintain posture during movement transmit impulses that coordinate body movements and maintenance of posture head and neck movements during visual reflexes coordination of posture and balance ...
Robin Balbernie
... Experience-expectant brain growth. • This take place when the brain is primed to receive particular classes of information from the ...
... Experience-expectant brain growth. • This take place when the brain is primed to receive particular classes of information from the ...
Body Systems: Nervous and Sensory Systems
... result of their inability to deal with the stimuli they take in (i.e. a bright light causes a spastic tantrum), generally caused by the brain’s misinterpretation of stimuli (part neurological, part sensory), cannot be treated, but kept under control with hyperactivity and sensitivity drugs like thos ...
... result of their inability to deal with the stimuli they take in (i.e. a bright light causes a spastic tantrum), generally caused by the brain’s misinterpretation of stimuli (part neurological, part sensory), cannot be treated, but kept under control with hyperactivity and sensitivity drugs like thos ...
Introduction to Psychology - Ms. Kelly's AP Psychology Website
... the autonomic control system of the body (the peripheral nervous system) It regulates breathing, heartbeat & digestion. It sometimes can be overridden by the brain. It is a dual system composed of: ...
... the autonomic control system of the body (the peripheral nervous system) It regulates breathing, heartbeat & digestion. It sometimes can be overridden by the brain. It is a dual system composed of: ...
Unit 2 bio-behavior review guide
... c. help bridge the gap between two neurons d. include all of the above 12. The neurotransmitter dopamine primarily affects a. movement b. sleepiness c. sense of well-being d. aggression e. all of the above 13. The spaces between neurons are called a. axons b. dendrites c. synapses d. neurotransmitte ...
... c. help bridge the gap between two neurons d. include all of the above 12. The neurotransmitter dopamine primarily affects a. movement b. sleepiness c. sense of well-being d. aggression e. all of the above 13. The spaces between neurons are called a. axons b. dendrites c. synapses d. neurotransmitte ...
4Central Nervous System (CNS)
... Helps ______________________________ from the cortex and the cerebellum Midbrain Associated with ____________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________________ Brain – Cerebellum Second largest part of the human brain ...
... Helps ______________________________ from the cortex and the cerebellum Midbrain Associated with ____________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________________ Brain – Cerebellum Second largest part of the human brain ...
Human brain
The human brain is the main organ of the human nervous system. It is located in the head, protected by the skull. It has the same general structure as the brains of other mammals, but with a more developed cerebral cortex. Large animals such as whales and elephants have larger brains in absolute terms, but when measured using a measure of relative brain size, which compensates for body size, the quotient for the human brain is almost twice as large as that of a bottlenose dolphin, and three times as large as that of a chimpanzee. Much of the size of the human brain comes from the cerebral cortex, especially the frontal lobes, which are associated with executive functions such as self-control, planning, reasoning, and abstract thought. The area of the cerebral cortex devoted to vision, the visual cortex, is also greatly enlarged in humans compared to other animals.The human cerebral cortex is a thick layer of neural tissue that covers most of the brain. This layer is folded in a way that increases the amount of surface that can fit into the volume available. The pattern of folds is similar across individuals, although there are many small variations. The cortex is divided into four lobes – the frontal lobe, parietal lobe, temporal lobe, and occipital lobe. (Some classification systems also include a limbic lobe and treat the insular cortex as a lobe.) Within each lobe are numerous cortical areas, each associated with a particular function, including vision, motor control, and language. The left and right sides of the cortex are broadly similar in shape, and most cortical areas are replicated on both sides. Some areas, though, show strong lateralization, particularly areas that are involved in language. In most people, the left hemisphere is dominant for language, with the right hemisphere playing only a minor role. There are other functions, such as visual-spatial ability, for which the right hemisphere is usually dominant.Despite being protected by the thick bones of the skull, suspended in cerebrospinal fluid, and isolated from the bloodstream by the blood–brain barrier, the human brain is susceptible to damage and disease. The most common forms of physical damage are closed head injuries such as a blow to the head, a stroke, or poisoning by a variety of chemicals which can act as neurotoxins, such as ethanol alcohol. Infection of the brain, though serious, is rare because of the biological barriers which protect it. The human brain is also susceptible to degenerative disorders, such as Parkinson's disease, and Alzheimer's disease, (mostly as the result of aging) and multiple sclerosis. A number of psychiatric conditions, such as schizophrenia and clinical depression, are thought to be associated with brain dysfunctions, although the nature of these is not well understood. The brain can also be the site of brain tumors and these can be benign or malignant.There are some techniques for studying the brain that are used in other animals that are just not suitable for use in humans and vice versa. It is easier to obtain individual brain cells taken from other animals, for study. It is also possible to use invasive techniques in other animals such as inserting electrodes into the brain or disabling certains parts of the brain in order to examine the effects on behaviour – techniques that are not possible to be used in humans. However, only humans can respond to complex verbal instructions or be of use in the study of important brain functions such as language and other complex cognitive tasks, but studies from humans and from other animals, can be of mutual help. Medical imaging technologies such as functional neuroimaging and EEG recordings are important techniques in studying the brain. The complete functional understanding of the human brain is an ongoing challenge for neuroscience.