Neuron Structure and Function
... Contains sensors, integrating centers, and output pathways More interneurons in a pathways greater ability to integrate information ...
... Contains sensors, integrating centers, and output pathways More interneurons in a pathways greater ability to integrate information ...
Lecture 4 ppt
... MOMENT AND VANIHES. WHEN CENTER SPOT DISAPPEARS EYES TURN TO POSITION WHERE THE TARGET WAS. THERE ARE NEURONS WHICH KEEP INFORMATION WHERE THE ...
... MOMENT AND VANIHES. WHEN CENTER SPOT DISAPPEARS EYES TURN TO POSITION WHERE THE TARGET WAS. THERE ARE NEURONS WHICH KEEP INFORMATION WHERE THE ...
A1987K582900002
... in the rat visual cortex. His findings utilized a combined Golgi electron-microscopic method that revealed valuable new information about the synaptic relationships of the local circuit neurons of the cerebral cortex. The results of my study showed that the basket plexus that surrounds virtually eve ...
... in the rat visual cortex. His findings utilized a combined Golgi electron-microscopic method that revealed valuable new information about the synaptic relationships of the local circuit neurons of the cerebral cortex. The results of my study showed that the basket plexus that surrounds virtually eve ...
Central Nervous System Functional Anatomy of the Brain
... brain stem and is enclosed by the cerebral hemispheres (see Figure 7.12). The major structures of the diencephalon are the thalamus, hypothalamus, and epithalamus (see Figure 7.15). The thalamus, which encloses the shallow third ventricle of the brain, is a relay station for sensory impulses passing ...
... brain stem and is enclosed by the cerebral hemispheres (see Figure 7.12). The major structures of the diencephalon are the thalamus, hypothalamus, and epithalamus (see Figure 7.15). The thalamus, which encloses the shallow third ventricle of the brain, is a relay station for sensory impulses passing ...
RHCh2 - HomePage Server for UT Psychology
... All-or-None Response: A strong stimulus can trigger more neurons to fire, and to fire more often, but it does not affect the action potentials strength or speed. Intensity of an action potential remains the same throughout the length of the axon. ...
... All-or-None Response: A strong stimulus can trigger more neurons to fire, and to fire more often, but it does not affect the action potentials strength or speed. Intensity of an action potential remains the same throughout the length of the axon. ...
123COM.CHP:Corel VENTURA
... f low within the vascular network. These findings have notable implications for functional brain mapping using hemodynamic changes as a ‘proxy’ for neural activity. On the one hand, the finding that intrinsic signals identif y reasonably well the area of activation, assessed by electrophysiological ...
... f low within the vascular network. These findings have notable implications for functional brain mapping using hemodynamic changes as a ‘proxy’ for neural activity. On the one hand, the finding that intrinsic signals identif y reasonably well the area of activation, assessed by electrophysiological ...
Review
... the nervous system and the brain, and genetic contributions to behavior—is an important element in the AP course. Identify basic processes and systems in the biological bases of behavior, including parts of the neuron and the process of transmission of a signal between neurons. Discuss the influ ...
... the nervous system and the brain, and genetic contributions to behavior—is an important element in the AP course. Identify basic processes and systems in the biological bases of behavior, including parts of the neuron and the process of transmission of a signal between neurons. Discuss the influ ...
AP Psychology - cloudfront.net
... The cortex is divided into two cerebral hemispheres. The two hemispheres are connected by a band of neural fibers called the corpus callosum, which allows each side to communicate with the other. The occipital lobe is located in the rear base and processes information from the eyes. The pari ...
... The cortex is divided into two cerebral hemispheres. The two hemispheres are connected by a band of neural fibers called the corpus callosum, which allows each side to communicate with the other. The occipital lobe is located in the rear base and processes information from the eyes. The pari ...
Nervous and Endocrine Systems
... Aggression; Serial killers low levels; important for sleep and low levels assoc with depression ...
... Aggression; Serial killers low levels; important for sleep and low levels assoc with depression ...
Nervous System
... Actions/Effects: LSD alters the action of the neurotransmitters serotonin, norepinephrine, and dopamine, triggering extreme changes in brain function. Physical effects include increased body temperature, heart rate, and blood pressure. Psychological effects include perceptual and thought distortions ...
... Actions/Effects: LSD alters the action of the neurotransmitters serotonin, norepinephrine, and dopamine, triggering extreme changes in brain function. Physical effects include increased body temperature, heart rate, and blood pressure. Psychological effects include perceptual and thought distortions ...
Class X Episode 5 A. P State HUMAN NERVOUS SYSTEM The
... The wall of cerebrum has two regions the outer region is called Cortex. The cortex has bodies of neurons and is grayish in colour. In view of the gray colour it is known as Gray Matter. The gray matter is highly convoluted with ridges. Due to this several ridges or elevations called Gyri and groves ...
... The wall of cerebrum has two regions the outer region is called Cortex. The cortex has bodies of neurons and is grayish in colour. In view of the gray colour it is known as Gray Matter. The gray matter is highly convoluted with ridges. Due to this several ridges or elevations called Gyri and groves ...
Chapter 3: The Biological Bases of Behavior
... magnetic resonance imaging: Transcranial magnetic stimulation (TMS) ...
... magnetic resonance imaging: Transcranial magnetic stimulation (TMS) ...
The Nervous System - Practicum-Health-II-2011-2012
... brain is a mass of nerve tissue well protected by membranes and the cranium. It is made up of several sections. ...
... brain is a mass of nerve tissue well protected by membranes and the cranium. It is made up of several sections. ...
ACP Level 2 Lesson Twelve
... This part, I love. Mater, of course is mother. The names of the layers of protection demonstrate each facet of the mother’s personality. On the outside you have the Dura mater which is the strong mother. A double thickness wraps around the outside of the brain and then a single thickness around the ...
... This part, I love. Mater, of course is mother. The names of the layers of protection demonstrate each facet of the mother’s personality. On the outside you have the Dura mater which is the strong mother. A double thickness wraps around the outside of the brain and then a single thickness around the ...
Sensory Cortex
... “gray matter” • Glial Cells: support brain cells. • Wrinkles are called fissures. • If you lay brain out flat it would be as big as an extra-large pizza. • It’s divided into 2 hemispheres and 4 lobes! ...
... “gray matter” • Glial Cells: support brain cells. • Wrinkles are called fissures. • If you lay brain out flat it would be as big as an extra-large pizza. • It’s divided into 2 hemispheres and 4 lobes! ...
Peripheral Nervous System - UBC Psychology`s Research Labs
... distinct brain regions (i.e., functional localization). Involves artificially stimulating distinct regions and assessing changes in behaviour. Electrical stimulation is delivered through electrodes; the electrical current increases the firing of neurons at the tip of the electrode. ...
... distinct brain regions (i.e., functional localization). Involves artificially stimulating distinct regions and assessing changes in behaviour. Electrical stimulation is delivered through electrodes; the electrical current increases the firing of neurons at the tip of the electrode. ...
Human brain
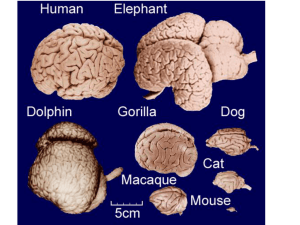
The human brain is the main organ of the human nervous system. It is located in the head, protected by the skull. It has the same general structure as the brains of other mammals, but with a more developed cerebral cortex. Large animals such as whales and elephants have larger brains in absolute terms, but when measured using a measure of relative brain size, which compensates for body size, the quotient for the human brain is almost twice as large as that of a bottlenose dolphin, and three times as large as that of a chimpanzee. Much of the size of the human brain comes from the cerebral cortex, especially the frontal lobes, which are associated with executive functions such as self-control, planning, reasoning, and abstract thought. The area of the cerebral cortex devoted to vision, the visual cortex, is also greatly enlarged in humans compared to other animals.The human cerebral cortex is a thick layer of neural tissue that covers most of the brain. This layer is folded in a way that increases the amount of surface that can fit into the volume available. The pattern of folds is similar across individuals, although there are many small variations. The cortex is divided into four lobes – the frontal lobe, parietal lobe, temporal lobe, and occipital lobe. (Some classification systems also include a limbic lobe and treat the insular cortex as a lobe.) Within each lobe are numerous cortical areas, each associated with a particular function, including vision, motor control, and language. The left and right sides of the cortex are broadly similar in shape, and most cortical areas are replicated on both sides. Some areas, though, show strong lateralization, particularly areas that are involved in language. In most people, the left hemisphere is dominant for language, with the right hemisphere playing only a minor role. There are other functions, such as visual-spatial ability, for which the right hemisphere is usually dominant.Despite being protected by the thick bones of the skull, suspended in cerebrospinal fluid, and isolated from the bloodstream by the blood–brain barrier, the human brain is susceptible to damage and disease. The most common forms of physical damage are closed head injuries such as a blow to the head, a stroke, or poisoning by a variety of chemicals which can act as neurotoxins, such as ethanol alcohol. Infection of the brain, though serious, is rare because of the biological barriers which protect it. The human brain is also susceptible to degenerative disorders, such as Parkinson's disease, and Alzheimer's disease, (mostly as the result of aging) and multiple sclerosis. A number of psychiatric conditions, such as schizophrenia and clinical depression, are thought to be associated with brain dysfunctions, although the nature of these is not well understood. The brain can also be the site of brain tumors and these can be benign or malignant.There are some techniques for studying the brain that are used in other animals that are just not suitable for use in humans and vice versa. It is easier to obtain individual brain cells taken from other animals, for study. It is also possible to use invasive techniques in other animals such as inserting electrodes into the brain or disabling certains parts of the brain in order to examine the effects on behaviour – techniques that are not possible to be used in humans. However, only humans can respond to complex verbal instructions or be of use in the study of important brain functions such as language and other complex cognitive tasks, but studies from humans and from other animals, can be of mutual help. Medical imaging technologies such as functional neuroimaging and EEG recordings are important techniques in studying the brain. The complete functional understanding of the human brain is an ongoing challenge for neuroscience.