Neural Basis of Motor Control
... Without a synapse there is no communication between neurons and target site such as muscles* There is not an all or none transmission at the junction ...
... Without a synapse there is no communication between neurons and target site such as muscles* There is not an all or none transmission at the junction ...
Nervous System and Mental Health
... – Surround neurons and hold them in place – Supply nutrients/oxygen to neurons – Insulate one neuron from another – Destroy and remove dead neurons ...
... – Surround neurons and hold them in place – Supply nutrients/oxygen to neurons – Insulate one neuron from another – Destroy and remove dead neurons ...
T A BOLD window into brain waves
... there are distinct modes of neuronal activity, such as a READY mode and a GO mode (and possibly an inhibited, STOP mode). Spontaneous activity would then be the READY mode of neuronal firing signaling the absence of preferred stimuli (an ongoing, low-level buzz). By contrast, in the GO mode, neurons ...
... there are distinct modes of neuronal activity, such as a READY mode and a GO mode (and possibly an inhibited, STOP mode). Spontaneous activity would then be the READY mode of neuronal firing signaling the absence of preferred stimuli (an ongoing, low-level buzz). By contrast, in the GO mode, neurons ...
Brain Plasticity and Emotional Regulation
... Long after the probability of danger has decreased, the person is unable to inhibit the expression of the latent fear associations. This may be associated with pathology in the prefrontalamygdala system. Specifically, inhibition of the amygdala by the vmPFC has been associated with anxiety and m ...
... Long after the probability of danger has decreased, the person is unable to inhibit the expression of the latent fear associations. This may be associated with pathology in the prefrontalamygdala system. Specifically, inhibition of the amygdala by the vmPFC has been associated with anxiety and m ...
Slide () - AccessAnesthesiology
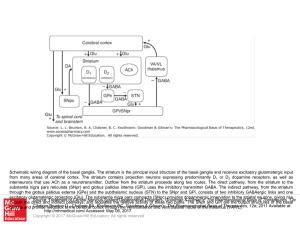
... Schematic wiring diagram of the basal ganglia. The striatum is the principal input structure of the basal ganglia and receives excitatory glutamatergic input from many areas of cerebral cortex. The striatum contains projection neurons expressing predominantly D1 or D2 dopamine receptors, as well as ...
... Schematic wiring diagram of the basal ganglia. The striatum is the principal input structure of the basal ganglia and receives excitatory glutamatergic input from many areas of cerebral cortex. The striatum contains projection neurons expressing predominantly D1 or D2 dopamine receptors, as well as ...
INTEGUMENTARY SYSTEM
... “Relay station” for all sensory impulses to cerebral cortex Consists of 2 lobes (may be joined by “Intermediate Mass” (a bridge of gray matter) Third ventricle is superior & medial to thalamus ...
... “Relay station” for all sensory impulses to cerebral cortex Consists of 2 lobes (may be joined by “Intermediate Mass” (a bridge of gray matter) Third ventricle is superior & medial to thalamus ...
Development of CNS
... Different neural tube defects are caused when various parts of the neural tube fail to close. Failure to close the human posterior neural tube at day 27 results in spina bifida. Failure to close the anterior neural tube results in a lethal condition, anencephaly. In this condition, the forebrain rem ...
... Different neural tube defects are caused when various parts of the neural tube fail to close. Failure to close the human posterior neural tube at day 27 results in spina bifida. Failure to close the anterior neural tube results in a lethal condition, anencephaly. In this condition, the forebrain rem ...
Aging and Anxiety: Intrusive Thoughts as a Barrier to Healthy Aging
... Intrusive thoughts are unpleasant but familiar visitors to the minds of most adults. From nagging worries about one’s health to jarring thoughts about a partner being in a car accident, these thoughts encompass a broad range of life concerns. This collaborative study examines age differences in intr ...
... Intrusive thoughts are unpleasant but familiar visitors to the minds of most adults. From nagging worries about one’s health to jarring thoughts about a partner being in a car accident, these thoughts encompass a broad range of life concerns. This collaborative study examines age differences in intr ...
U3 Neurobiology Summary
... Myelination is the development of myelin round axon fibres of individual neurons. Myelination is not complete at birth and so nervous control increases over the first two years as many more neurons are myelinated. Myelination continues from birth to adolescence. As a result responses to stimuli in t ...
... Myelination is the development of myelin round axon fibres of individual neurons. Myelination is not complete at birth and so nervous control increases over the first two years as many more neurons are myelinated. Myelination continues from birth to adolescence. As a result responses to stimuli in t ...
charting the brain`s networks
... the institute’s chief technology officer (see ‘Neuroscience goes industrial’). Large-scale efforts at a number of other labs take on circuits in big ways. At Harvard Medical School, Reid and his colleagues have been mapping and studying neural connections in the mouse visual cortex. To do this, they ...
... the institute’s chief technology officer (see ‘Neuroscience goes industrial’). Large-scale efforts at a number of other labs take on circuits in big ways. At Harvard Medical School, Reid and his colleagues have been mapping and studying neural connections in the mouse visual cortex. To do this, they ...
General Senses Complete
... tendons, joints, ligaments, and connective tissue coverings Provide information on the position and degree of stretch Structure of General Sensory Receptors Sensory receptors are modified dendritic nerve endings React to stimuli by initiating a nerve impulse There is controversy over precise functio ...
... tendons, joints, ligaments, and connective tissue coverings Provide information on the position and degree of stretch Structure of General Sensory Receptors Sensory receptors are modified dendritic nerve endings React to stimuli by initiating a nerve impulse There is controversy over precise functio ...
Nervous System PPT
... may be incorrect • The anatomical basis for sophisticated information processing in birds (without a highly convoluted neocortex) appears to be the clustering of nuclei in the top or outer portion of the brain (pallium) ...
... may be incorrect • The anatomical basis for sophisticated information processing in birds (without a highly convoluted neocortex) appears to be the clustering of nuclei in the top or outer portion of the brain (pallium) ...
Ch 2 The Biological Basis of Behavior
... 3. Dopamine – involved in motor behavior (Parkinson's disease-too little; Schizophrenia – too much) 4. noradrenalin – prepares body for action 5. serotonin – emotional arousal and sleep (too little – depression) http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=bkwyLOZD9FE ...
... 3. Dopamine – involved in motor behavior (Parkinson's disease-too little; Schizophrenia – too much) 4. noradrenalin – prepares body for action 5. serotonin – emotional arousal and sleep (too little – depression) http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=bkwyLOZD9FE ...
Modeling large cortical networks with growing self
... RF-LISSOM focuses on the two-dimensional topographic organization of the cortex, modeling a cortical area as an N × N sheet of neurons and the retina as an R × R sheet of ganglion cells. Neurons receive afferent connections from broad patches of radius rA on the retina, and receive lateral excitator ...
... RF-LISSOM focuses on the two-dimensional topographic organization of the cortex, modeling a cortical area as an N × N sheet of neurons and the retina as an R × R sheet of ganglion cells. Neurons receive afferent connections from broad patches of radius rA on the retina, and receive lateral excitator ...
49_Lecture_Presentation
... may be incorrect • The anatomical basis for sophisticated information processing in birds (without a highly convoluted neocortex) appears to be the clustering of nuclei in the top or outer portion of the brain (pallium) ...
... may be incorrect • The anatomical basis for sophisticated information processing in birds (without a highly convoluted neocortex) appears to be the clustering of nuclei in the top or outer portion of the brain (pallium) ...
neurology_lab6_13_4_2011 - Post-it
... anterior horn{ Fastigeal reticular pathway} -C-intermedeat zone to interposed nuclei{ Globose and emboliform in cerebllum}then to Contralateral red nucleus in brain stem → rubrospinal tract →motor neurons of anterior horn{ Globoseemboliform-rubral pathway} ...
... anterior horn{ Fastigeal reticular pathway} -C-intermedeat zone to interposed nuclei{ Globose and emboliform in cerebllum}then to Contralateral red nucleus in brain stem → rubrospinal tract →motor neurons of anterior horn{ Globoseemboliform-rubral pathway} ...
3-As.Tracts 2015 (final).
... • Some of this information eventually reaches a conscious level (the cerebral cortex), • while some is destined for subconscious centers (e.g. the cerebellum). ...
... • Some of this information eventually reaches a conscious level (the cerebral cortex), • while some is destined for subconscious centers (e.g. the cerebellum). ...
Nervous System = communication conduit b/w brain
... Some axons have myelin sheath (insulating layer) Myelin sheath has gaps (nodes of Ranvier) along axon Na+/K+ cannot diffuse through myelin but they can reach plasma membrane at these nodes This allows action potential to jump from node to node, increasing speed of impulse as it travels lengt ...
... Some axons have myelin sheath (insulating layer) Myelin sheath has gaps (nodes of Ranvier) along axon Na+/K+ cannot diffuse through myelin but they can reach plasma membrane at these nodes This allows action potential to jump from node to node, increasing speed of impulse as it travels lengt ...
File - LC Biology 2012-2013
... seen in older people, in which muscles become rigid and movement is slow and difficult, with persistent tremors [shaking]. It is caused by the brain reducing the normal amount of dopamine that it makes. There is at present no means of preventing it, but giving L-dopa (which the body changes into d ...
... seen in older people, in which muscles become rigid and movement is slow and difficult, with persistent tremors [shaking]. It is caused by the brain reducing the normal amount of dopamine that it makes. There is at present no means of preventing it, but giving L-dopa (which the body changes into d ...
Descending Spinal Tracts
... Receptors - also called hair cells encode location and movement relative to gravity ...
... Receptors - also called hair cells encode location and movement relative to gravity ...
BRAINS OF NORWAY
... — humans as well as rats — are born with a very primitive sense of where they are in space, and that this sense develops as their brains adapt to the world. The Mosers are also planning to test how the hexagonal pattern would be modified in the brain of a rat that has been reared from birth in a per ...
... — humans as well as rats — are born with a very primitive sense of where they are in space, and that this sense develops as their brains adapt to the world. The Mosers are also planning to test how the hexagonal pattern would be modified in the brain of a rat that has been reared from birth in a per ...
Chapter 1 - Beulah School District 27
... • State protect children from the results of their own lack of judgment • Cannot make a contract • Treated differently in court than adults • Local laws can be enacted also ...
... • State protect children from the results of their own lack of judgment • Cannot make a contract • Treated differently in court than adults • Local laws can be enacted also ...