Exam 2 Student Key
... d. (2pts) In which of the cells below would you likely find active telomerase? (Circle ALL correct) ...
... d. (2pts) In which of the cells below would you likely find active telomerase? (Circle ALL correct) ...
Unit-1-Match-Up - Lesmahagow High School
... P. Formed when cancerous cells lose the surface molecules that hold them together and detach and spread through the body. Q. Cells that do not respond to normal regulatory signals. R. Stem cells found in locations such as red bone marrow. S. Differentiated cells that have been reprogrammed to turn s ...
... P. Formed when cancerous cells lose the surface molecules that hold them together and detach and spread through the body. Q. Cells that do not respond to normal regulatory signals. R. Stem cells found in locations such as red bone marrow. S. Differentiated cells that have been reprogrammed to turn s ...
The exploitation of chromosome recombination between Lolium and
... medicines. Human proteins can even be made in bacteria, and this process is at present the simplest, cheapest and quickest means of doing so. However, not all proteins can be obtained in this way. This is why higher organisms – fungi, plants and animals – are also used in such processes. In these sy ...
... medicines. Human proteins can even be made in bacteria, and this process is at present the simplest, cheapest and quickest means of doing so. However, not all proteins can be obtained in this way. This is why higher organisms – fungi, plants and animals – are also used in such processes. In these sy ...
Transcription Regulation And Gene Expression in Eukaryotes (Cycle
... in chromatin, the compact form of genomic DNA – histone N-term „tails“ modification, eg H3K9 methylation, mediate interactions with regulatory proteins, such as repressors, and assemble into heterochromatin, the silenced form of chromatin ...
... in chromatin, the compact form of genomic DNA – histone N-term „tails“ modification, eg H3K9 methylation, mediate interactions with regulatory proteins, such as repressors, and assemble into heterochromatin, the silenced form of chromatin ...
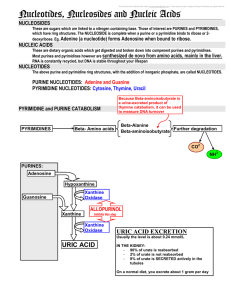
3 Nucleosides nucleotides and nucleic acids
... - EXONS are portions of genes which encode protens; - INTRONS are portions of the gene which are not encoded into proteins - PROMOTER regions are near the transcription start of the gene, and this is where RNA polymerase binds to start the encryption of RNA; it usually includes a TATA (thymine-adeni ...
... - EXONS are portions of genes which encode protens; - INTRONS are portions of the gene which are not encoded into proteins - PROMOTER regions are near the transcription start of the gene, and this is where RNA polymerase binds to start the encryption of RNA; it usually includes a TATA (thymine-adeni ...
T Dx test II
... a. their target cells must formulate new proteins before an effect can take place b. second messengers act slowly c. they are large molecules and move slowly through the blood d. because they are large polar molecules, they do not enter cells easily e. they are synthesized in very small quantities b ...
... a. their target cells must formulate new proteins before an effect can take place b. second messengers act slowly c. they are large molecules and move slowly through the blood d. because they are large polar molecules, they do not enter cells easily e. they are synthesized in very small quantities b ...
Lecture 5
... •Depends on transfer of energy from one molecule to another. (1-10 nm) •Requires two proteins to be modified and then expressed inside cells. •cyan fluorescent protein and yellow fluorescent protein are commonly used. • Comment on green fluorescent protein. •Detect by microscopy-makes pretty images. ...
... •Depends on transfer of energy from one molecule to another. (1-10 nm) •Requires two proteins to be modified and then expressed inside cells. •cyan fluorescent protein and yellow fluorescent protein are commonly used. • Comment on green fluorescent protein. •Detect by microscopy-makes pretty images. ...
Lecture 7
... • Purpose is to create new DNA strand, so that upon binary fission, each of the 2 cells receives a complete copy of DNA • Bidirectional- from distinct starting pointproceeds in both directions • Semi- conservative- each of the 2 DNA helix’s generated contains 1 new strand and 1 old strand ...
... • Purpose is to create new DNA strand, so that upon binary fission, each of the 2 cells receives a complete copy of DNA • Bidirectional- from distinct starting pointproceeds in both directions • Semi- conservative- each of the 2 DNA helix’s generated contains 1 new strand and 1 old strand ...
TRANSGENIC ANIMALS
... o Rabbits are quite promising for gene farming or molecular farming, which aims at the production of recoverable quantities of biologically important proteins encoded by the transgenes. o Transgenic animals used for this purpose are popularly called bioreactors. o These transgenes are expressed in m ...
... o Rabbits are quite promising for gene farming or molecular farming, which aims at the production of recoverable quantities of biologically important proteins encoded by the transgenes. o Transgenic animals used for this purpose are popularly called bioreactors. o These transgenes are expressed in m ...
$doc.title
... Interactions between Mediterranean diet, MTHFR and MTR genes influence breast cancer risk among Cypriot women ...
... Interactions between Mediterranean diet, MTHFR and MTR genes influence breast cancer risk among Cypriot women ...
Ph.D. position
... A role of blue light, anion channels and 7B-1 gene in plant tolerance to abiotic stress We are looking for a friendly and dynamic Ph.D. student for Laboratory of Molecular Physiology. The doctoral study focuses on determination of mechanisms whereby blue light alters plant ability to withstand abiot ...
... A role of blue light, anion channels and 7B-1 gene in plant tolerance to abiotic stress We are looking for a friendly and dynamic Ph.D. student for Laboratory of Molecular Physiology. The doctoral study focuses on determination of mechanisms whereby blue light alters plant ability to withstand abiot ...
Semester 2 review sheet - Summit School District
... -Explain the theory of evolution using Darwin’s original ideas of decent with modification, genetic variation, natural selection. -Explain how scientists use the 4 main bodies of evidence to support the current theory of evolution and give examples of each. Essential Vocab: a. Fossils/The Fossil Rec ...
... -Explain the theory of evolution using Darwin’s original ideas of decent with modification, genetic variation, natural selection. -Explain how scientists use the 4 main bodies of evidence to support the current theory of evolution and give examples of each. Essential Vocab: a. Fossils/The Fossil Rec ...
More Exam Practice - Iowa State University
... their bundle sheath cells as an adaption to hot, dry climates. If they were to open their stomata to take in CO2 during the day, they would also lose too much water. This way, they can keep their stomata partially closed during the day and use CO2 that is concentrated in bundle-sheath cells to gener ...
... their bundle sheath cells as an adaption to hot, dry climates. If they were to open their stomata to take in CO2 during the day, they would also lose too much water. This way, they can keep their stomata partially closed during the day and use CO2 that is concentrated in bundle-sheath cells to gener ...
Large Scale expression Profiling to find transcription
... Selection bias in gene extraction on the basis of microarray geneexpression data Christphe Ambroise, and Geoffrey J. McLachlan ...
... Selection bias in gene extraction on the basis of microarray geneexpression data Christphe Ambroise, and Geoffrey J. McLachlan ...
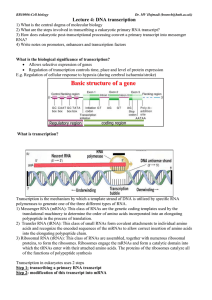
Lecture 4: DNA transcription
... A) Initiation by RNA polymerase holoenzyme (an agglomeration of many different factors that together direct the synthesis of mRNA on a DNA template and which has a natural affinity for DNA) binding to specific DNA sequences called promoters that drive transcription (region where RNA polymerase binds ...
... A) Initiation by RNA polymerase holoenzyme (an agglomeration of many different factors that together direct the synthesis of mRNA on a DNA template and which has a natural affinity for DNA) binding to specific DNA sequences called promoters that drive transcription (region where RNA polymerase binds ...
1.3.6 Structural Role of Biomolecules Worksheet
... Meetabolic Role of Biomolecules = the function / job / involvement of carbohydrates, fats, proteins in the chemical reactions in cells making various substances for living things ...
... Meetabolic Role of Biomolecules = the function / job / involvement of carbohydrates, fats, proteins in the chemical reactions in cells making various substances for living things ...
File - Ms. Poole`s Biology
... sequence of DNA molecules that can direct the synthesis of a molecule product. • Genes do not all code for a protein, but all do code for an RNA molecule. • Some of those RNAs are translated into ...
... sequence of DNA molecules that can direct the synthesis of a molecule product. • Genes do not all code for a protein, but all do code for an RNA molecule. • Some of those RNAs are translated into ...
BIOL 3010
... Colegio de Artes y Ciencias Departamento de Biología Programa de Biología, Pre-médica, Microbiología Industrial ...
... Colegio de Artes y Ciencias Departamento de Biología Programa de Biología, Pre-médica, Microbiología Industrial ...
Human Genetics
... AAs to ribosomes. The AA’s join in cytoplasm to form proteins. 20 types. Loop structure – Ribosomal RNA: (rRNA) Joins with proteins made in cytoplasm to form the subunits of ribosomes. Linear ...
... AAs to ribosomes. The AA’s join in cytoplasm to form proteins. 20 types. Loop structure – Ribosomal RNA: (rRNA) Joins with proteins made in cytoplasm to form the subunits of ribosomes. Linear ...
Biochemistry and Molecular Biology
... function) and optimal control of living matter (animal, plant and microorganism). After a survey of the molecular building blocks and of the macromolecules of the living cell, the properties and kinetics of enzymes as biocatalysts are covered. Finally, the principles and major pathways of the centra ...
... function) and optimal control of living matter (animal, plant and microorganism). After a survey of the molecular building blocks and of the macromolecules of the living cell, the properties and kinetics of enzymes as biocatalysts are covered. Finally, the principles and major pathways of the centra ...
Mutations - No Brain Too Small
... Describe the changes to both the mRNA codon and the DNA base sequence as a result of this mutation. Discuss the effect of this mutation on the red blood cell, through the mutation’s effect on: ...
... Describe the changes to both the mRNA codon and the DNA base sequence as a result of this mutation. Discuss the effect of this mutation on the red blood cell, through the mutation’s effect on: ...
Engineered Communications for Microbial Robotics
... • Ring Oscillator implementation [Elowitz & Leibler, ’00] ...
... • Ring Oscillator implementation [Elowitz & Leibler, ’00] ...
Biotechnology PP
... can be a treatment for heart disease, Alzheimer's, cancer, and other diseases. ...
... can be a treatment for heart disease, Alzheimer's, cancer, and other diseases. ...
Gene regulatory network

A gene regulatory network or genetic regulatory network (GRN) is a collection of regulators thatinteract with each other and with other substances in the cell to govern the gene expression levels of mRNA and proteins.The regulator can be DNA, RNA, protein and their complex. The interaction can be direct or indirect (through their transcribed RNA or translated protein).In general, each mRNA molecule goes on to make a specific protein (or set of proteins). In some cases this protein will be structural, and will accumulate at the cell membrane or within the cell to give it particular structural properties. In other cases the protein will be an enzyme, i.e., a micro-machine that catalyses a certain reaction, such as the breakdown of a food source or toxin. Some proteins though serve only to activate other genes, and these are the transcription factors that are the main players in regulatory networks or cascades. By binding to the promoter region at the start of other genes they turn them on, initiating the production of another protein, and so on. Some transcription factors are inhibitory.In single-celled organisms, regulatory networks respond to the external environment, optimising the cell at a given time for survival in this environment. Thus a yeast cell, finding itself in a sugar solution, will turn on genes to make enzymes that process the sugar to alcohol. This process, which we associate with wine-making, is how the yeast cell makes its living, gaining energy to multiply, which under normal circumstances would enhance its survival prospects.In multicellular animals the same principle has been put in the service of gene cascades that control body-shape. Each time a cell divides, two cells result which, although they contain the same genome in full, can differ in which genes are turned on and making proteins. Sometimes a 'self-sustaining feedback loop' ensures that a cell maintains its identity and passes it on. Less understood is the mechanism of epigenetics by which chromatin modification may provide cellular memory by blocking or allowing transcription. A major feature of multicellular animals is the use of morphogen gradients, which in effect provide a positioning system that tells a cell where in the body it is, and hence what sort of cell to become. A gene that is turned on in one cell may make a product that leaves the cell and diffuses through adjacent cells, entering them and turning on genes only when it is present above a certain threshold level. These cells are thus induced into a new fate, and may even generate other morphogens that signal back to the original cell. Over longer distances morphogens may use the active process of signal transduction. Such signalling controls embryogenesis, the building of a body plan from scratch through a series of sequential steps. They also control and maintain adult bodies through feedback processes, and the loss of such feedback because of a mutation can be responsible for the cell proliferation that is seen in cancer. In parallel with this process of building structure, the gene cascade turns on genes that make structural proteins that give each cell the physical properties it needs.It has been suggested that, because biological molecular interactions are intrinsically stochastic, gene networks are the result of cellular processes and not their cause (i.e. cellular Darwinism). However, recent experimental evidence has favored the attractor view of cell fates.