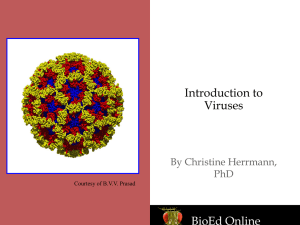
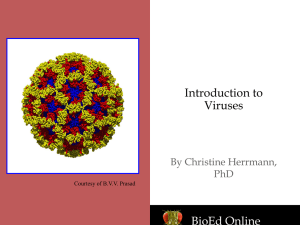
Viruses & Bacteria
... a) RNA b) Protein 6) Later, scientists were able to separate the RNA from the protein. When they reassembled the two components, the reconstructed TMV particles were fully able to infect healthy tobacco plants. ...
... a) RNA b) Protein 6) Later, scientists were able to separate the RNA from the protein. When they reassembled the two components, the reconstructed TMV particles were fully able to infect healthy tobacco plants. ...
Red Nose in Calves - Prevention and Control
... Bovine Rhinotracheitis (IBR) virus and Bovine Parainfluenza (PI-3) virus. Both of these viruses are common in cattle populations and can be isolated from normal healthy cattle. When cattle are stressed and/or their immunity is low, they may develop disease related to infection of "Red Nose". Most ca ...
... Bovine Rhinotracheitis (IBR) virus and Bovine Parainfluenza (PI-3) virus. Both of these viruses are common in cattle populations and can be isolated from normal healthy cattle. When cattle are stressed and/or their immunity is low, they may develop disease related to infection of "Red Nose". Most ca ...
Since just about everything comes in a range of sizes, numbers
... machinery of its own, it invades other organisms and, like a very bad house guest, it sponges off the reproductive resources of its host. Viral genomes are made of DNA or RNA and encode for the proteins needed to make more virions. There are an incredible variety of strategies that different viruses ...
... machinery of its own, it invades other organisms and, like a very bad house guest, it sponges off the reproductive resources of its host. Viral genomes are made of DNA or RNA and encode for the proteins needed to make more virions. There are an incredible variety of strategies that different viruses ...
Life Size Scaling
... machinery of its own, it invades other organisms and, like a very bad house guest, it sponges off the reproductive resources of its host. Viral genomes are made of DNA or RNA and encode for the proteins needed to make more virions. There are an incredible variety of strategies that different viruses ...
... machinery of its own, it invades other organisms and, like a very bad house guest, it sponges off the reproductive resources of its host. Viral genomes are made of DNA or RNA and encode for the proteins needed to make more virions. There are an incredible variety of strategies that different viruses ...
1. Is a virus ALIVE?
... 2. Penetration — The cell wall is weakened by the viral enzymes, and the deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) of the virus is injected into the host cell. 3. Synthesis — The DNA of the host cell is inactivated, and the viral DNA takes over making viral proteins and viral nucleic acid. 4. Assembly — Viral coa ...
... 2. Penetration — The cell wall is weakened by the viral enzymes, and the deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) of the virus is injected into the host cell. 3. Synthesis — The DNA of the host cell is inactivated, and the viral DNA takes over making viral proteins and viral nucleic acid. 4. Assembly — Viral coa ...
Welcome to the Hannover Medical School
... ohuman influenza preferentially bind to sialic acid that is linked to galactose by an a2,6linkage (SAa2,6Gal) othis preference is matched by SAa2,6Gal on epithelial cells in the human trachea oin contrast, avian influenza viruses preferentially recognize SAa2,3Gal that is matched by SAa2,3Gal on epi ...
... ohuman influenza preferentially bind to sialic acid that is linked to galactose by an a2,6linkage (SAa2,6Gal) othis preference is matched by SAa2,6Gal on epithelial cells in the human trachea oin contrast, avian influenza viruses preferentially recognize SAa2,3Gal that is matched by SAa2,3Gal on epi ...
chapt17b_lecture
... It’s nucleic acid hijacks a cells machinery for making nucleic acids and proteins. ...
... It’s nucleic acid hijacks a cells machinery for making nucleic acids and proteins. ...
Viruses - Emerald Meadow Stables
... Viruses • Virus – non-cellular particle made up of genetic material and protein. Reproduce only by infecting living cells. • TMV – tobacco mosaic virus – first heavily studied virus • Dmitri Ivanovski – 1892, cause of TMV – juice extracted from infected plants • Martinus Beijerinck – 1897, named TM ...
... Viruses • Virus – non-cellular particle made up of genetic material and protein. Reproduce only by infecting living cells. • TMV – tobacco mosaic virus – first heavily studied virus • Dmitri Ivanovski – 1892, cause of TMV – juice extracted from infected plants • Martinus Beijerinck – 1897, named TM ...
BIOL260Exam2 review
... 3. What do transformation, conjugation, and transduction have in common? What is different? 4. What do you need to have transformation occur? What about conjugation? What about transduction? 5. Understand conjugation between the following cells: F+ and F-. 6. What is the definition of the following ...
... 3. What do transformation, conjugation, and transduction have in common? What is different? 4. What do you need to have transformation occur? What about conjugation? What about transduction? 5. Understand conjugation between the following cells: F+ and F-. 6. What is the definition of the following ...
Viral Pathogens
... • icosahedral protein coat (capsid) – 4 capsid proteins: VP1, VP2, VP3, VP4 (all cleaved from VP0) • >71 antigenically distinct human types ...
... • icosahedral protein coat (capsid) – 4 capsid proteins: VP1, VP2, VP3, VP4 (all cleaved from VP0) • >71 antigenically distinct human types ...
VIRUS STRUCTURE
... Secondary characteristics Replication strategy Sometimes a group of viruses that seems to be a single group by the above criteria is found to contain a subgroup of viruses which have a fundamentally different replication strategy – ...
... Secondary characteristics Replication strategy Sometimes a group of viruses that seems to be a single group by the above criteria is found to contain a subgroup of viruses which have a fundamentally different replication strategy – ...
virus
... Plant viruses • Plant viruses face special problems initiating an infection. - The outer surfaces of plants are composed of protective layers of waxes and pectin, but more significantly, each cell is surrounded by a thick wall of cellulose overlying the cytoplasmic membrane. - no plant virus is kno ...
... Plant viruses • Plant viruses face special problems initiating an infection. - The outer surfaces of plants are composed of protective layers of waxes and pectin, but more significantly, each cell is surrounded by a thick wall of cellulose overlying the cytoplasmic membrane. - no plant virus is kno ...
Enter Topic Title in each section above
... A. Non-cellular; One nucleic acid; Polio; ‘Flu; Common cold; Leaf Obligate parasite; No metabolism; mosaic; AIDS or HIV; Mumps; Do not possess organelles Rubella; Rabies Q. What is meant by the term Q. Give a role of memory T-cells. immunity? A. The ability of the body to resist infection ...
... A. Non-cellular; One nucleic acid; Polio; ‘Flu; Common cold; Leaf Obligate parasite; No metabolism; mosaic; AIDS or HIV; Mumps; Do not possess organelles Rubella; Rabies Q. What is meant by the term Q. Give a role of memory T-cells. immunity? A. The ability of the body to resist infection ...
Document
... How Do Viruses Reproduce? Viruses reproduce via three basic steps. 1. Viruses deliver their genomes into a host cell. 2. Viruses commandeer the host cell transcription and translation machineries and utilize host cell building blocks to copy viral genomes and synthesize viral proteins. 3. Viral gen ...
... How Do Viruses Reproduce? Viruses reproduce via three basic steps. 1. Viruses deliver their genomes into a host cell. 2. Viruses commandeer the host cell transcription and translation machineries and utilize host cell building blocks to copy viral genomes and synthesize viral proteins. 3. Viral gen ...
Infectious diseases DNA viruses
... How Do Viruses Reproduce? Viruses reproduce via three basic steps. 1. Viruses deliver their genomes into a host cell. 2. Viruses commandeer the host cell transcription and translation machineries and utilize host cell building blocks to copy viral genomes and synthesize viral proteins. 3. Viral gen ...
... How Do Viruses Reproduce? Viruses reproduce via three basic steps. 1. Viruses deliver their genomes into a host cell. 2. Viruses commandeer the host cell transcription and translation machineries and utilize host cell building blocks to copy viral genomes and synthesize viral proteins. 3. Viral gen ...
learning outcomes - McGraw Hill Higher Education
... list organisms that are hosts to viruses state the size range of virions identify the parts of a virion and describe their function distinguish enveloped from noneveloped viruses describe the types of capsid symmetry describe the five steps common to the life cycles of all viruses discuss the roles ...
... list organisms that are hosts to viruses state the size range of virions identify the parts of a virion and describe their function distinguish enveloped from noneveloped viruses describe the types of capsid symmetry describe the five steps common to the life cycles of all viruses discuss the roles ...
Threat of Mosquito-Borne Human Viral Diseases
... The initial clinical manifestations are very similar among mosquito-borne viral diseases; with a short incubation period, symptoms that may begin three to six days after infection, and fever, arthralgia, headache, shivers, anorexia,nausea and vomiting during acute phase. Majority of inflicting patie ...
... The initial clinical manifestations are very similar among mosquito-borne viral diseases; with a short incubation period, symptoms that may begin three to six days after infection, and fever, arthralgia, headache, shivers, anorexia,nausea and vomiting during acute phase. Majority of inflicting patie ...
Lytic Cycle
... • Viruses cannot reproduce on their own—they REPLICATE by using a HOST cell • Infects a host cell • HOST: A living organism in which a virus is found ...
... • Viruses cannot reproduce on their own—they REPLICATE by using a HOST cell • Infects a host cell • HOST: A living organism in which a virus is found ...
2016-2017 micro virus to fungi
... • Protists are eukaryotes that cannot be classified as animals, plants, or fungi. They are unicellular. • Animal-like protists are heterotrophs and are able to move from place to place to obtain food. ...
... • Protists are eukaryotes that cannot be classified as animals, plants, or fungi. They are unicellular. • Animal-like protists are heterotrophs and are able to move from place to place to obtain food. ...
Lesson Plan BISP Characterisation Clothes
... What diseases do viruses cause? – Ask class for answers. Write on the board How are viruses transmitted? – Ask class for answers. Write on board Very small so can spread in all sorts of ways: airborne, contaminated food or water, vectors (mosquitoes) or infected animal bite, sexual contact, contamin ...
... What diseases do viruses cause? – Ask class for answers. Write on the board How are viruses transmitted? – Ask class for answers. Write on board Very small so can spread in all sorts of ways: airborne, contaminated food or water, vectors (mosquitoes) or infected animal bite, sexual contact, contamin ...
QE GenKnowl Topics
... What are points of connection between antibodies and aspects of innate immunity? In structural and functional terms, how does Ag recognition by B cells differ from that of T cells [put a different way, how does each class “see” antigen]? For both of these classes of lymphocyte (B cells and T cells) ...
... What are points of connection between antibodies and aspects of innate immunity? In structural and functional terms, how does Ag recognition by B cells differ from that of T cells [put a different way, how does each class “see” antigen]? For both of these classes of lymphocyte (B cells and T cells) ...
Introduction to Google Adwords
... Only one type of nucleic acid Viruses contain either DNA or RNA (never both) as their genetic material. The nucleic acid can be single-stranded or double stranded. Do not grow in size Unlike cells, viruses do not grow in size and mass leading to a division process. Rather viruses grow by separate sy ...
... Only one type of nucleic acid Viruses contain either DNA or RNA (never both) as their genetic material. The nucleic acid can be single-stranded or double stranded. Do not grow in size Unlike cells, viruses do not grow in size and mass leading to a division process. Rather viruses grow by separate sy ...
BIOI 121 cell and tissues
... Viruses can do all of the following EXCEPT: A. alter transcription and translation in a host cell. B. carry genes coding for specific proteins. C. cause cellular ribosomes to produce viral proteins. D. code for enzymes different from those of the host. E. grow and replicate on their own. ...
... Viruses can do all of the following EXCEPT: A. alter transcription and translation in a host cell. B. carry genes coding for specific proteins. C. cause cellular ribosomes to produce viral proteins. D. code for enzymes different from those of the host. E. grow and replicate on their own. ...
Virus Notes
... capsid, of an individual virus particle, or virion, is composed of multiple copies of one or several types of protein subunits, or capsomeres. Some viruses contain enzymes, and some have an outer membranous envelope. Many viruses have striking geometrically regular shapes ...
... capsid, of an individual virus particle, or virion, is composed of multiple copies of one or several types of protein subunits, or capsomeres. Some viruses contain enzymes, and some have an outer membranous envelope. Many viruses have striking geometrically regular shapes ...
March 27-31 and April 3-7
... Infections caused by harmful bacteria can almost always be cured with antibiotics. While some viruses can be vaccinated against, most, such as HIV and the viruses which cause the common cold, are incurable, even if their symptoms can be treated, meaning the living host must have a strong enough immu ...
... Infections caused by harmful bacteria can almost always be cured with antibiotics. While some viruses can be vaccinated against, most, such as HIV and the viruses which cause the common cold, are incurable, even if their symptoms can be treated, meaning the living host must have a strong enough immu ...
Plant virus

Plant viruses are viruses that affect plants. Like all other viruses, plant viruses are obligate intracellular parasites that do not have the molecular machinery to replicate without a host. Plant viruses are pathogenic to higher plants. While this article does not intend to list all plant viruses, it discusses some important viruses as well as their uses in plant molecular biology.