Datasheet - Santa Cruz Biotechnology
... MND1 (meiotic nuclear division protein 1 homolog), also known as GAJ, is a 205 amino acid nuclear protein required for proper homologous chromosome pairing and meiotic double-strand break repair. Belonging to the MND1 family, MND1 localizes to chromatin during meiotic prophase and preferentially bin ...
... MND1 (meiotic nuclear division protein 1 homolog), also known as GAJ, is a 205 amino acid nuclear protein required for proper homologous chromosome pairing and meiotic double-strand break repair. Belonging to the MND1 family, MND1 localizes to chromatin during meiotic prophase and preferentially bin ...
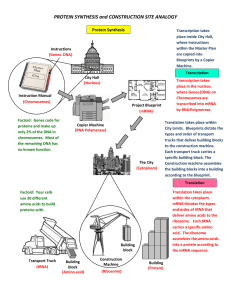
PROTEIN SYNTHESIS and CONSTRUCTION SITE ANALOGY
... Factoid: Genes code for proteins and make up only 2% of the DNA in chromosomes. Most of the remaining DNA has no known function. ...
... Factoid: Genes code for proteins and make up only 2% of the DNA in chromosomes. Most of the remaining DNA has no known function. ...
Viruses
... 2. Viruses require a host organism, or living cell, to reproduce. 3. Viruses are parasites because they harm living cells. A virus has two basic parts: 1. a core of hereditary material 2. an outer coat of protein Viral Host Cell Infection 1. After a cell attaches to its host cell, it injects its her ...
... 2. Viruses require a host organism, or living cell, to reproduce. 3. Viruses are parasites because they harm living cells. A virus has two basic parts: 1. a core of hereditary material 2. an outer coat of protein Viral Host Cell Infection 1. After a cell attaches to its host cell, it injects its her ...
Detecting and Modeling Long Range Correlation in Genomic
... A genome encodes information that is needed to create complex machineries combining DNA, RNA and proteins. However, this structure has evolved by certain basic biological processes that modify the genome in a specific but stochastic manner, and has been shaped by selection pressure. With complete se ...
... A genome encodes information that is needed to create complex machineries combining DNA, RNA and proteins. However, this structure has evolved by certain basic biological processes that modify the genome in a specific but stochastic manner, and has been shaped by selection pressure. With complete se ...
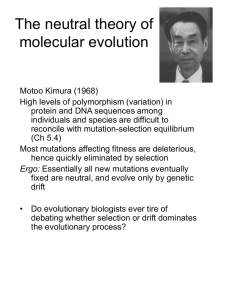
Null hypotheses in evolutionary biology
... individuals and species are difficult to reconcile with mutation-selection equilibrium (Ch 5.4) Most mutations affecting fitness are deleterious, hence quickly eliminated by selection Ergo: Essentially all new mutations eventually fixed are neutral, and evolve only by genetic drift • Do evolutionary ...
... individuals and species are difficult to reconcile with mutation-selection equilibrium (Ch 5.4) Most mutations affecting fitness are deleterious, hence quickly eliminated by selection Ergo: Essentially all new mutations eventually fixed are neutral, and evolve only by genetic drift • Do evolutionary ...
SoonChunHyang University: SoonChunHyang Institute of Medi
... Course Description : The course objective is to consider both principles and current topics in Molecular Biology in depth. This course primarily deals with nucleic acids and proteins and how these molecules interact within the cell to promote proper growth, division, and development. Especially this ...
... Course Description : The course objective is to consider both principles and current topics in Molecular Biology in depth. This course primarily deals with nucleic acids and proteins and how these molecules interact within the cell to promote proper growth, division, and development. Especially this ...
Inquiry into Life Twelfth Edition
... product of a gene – usually more is better • For this reason, expression vectors have very strong promoters • Prefer keep a cloned gene repressed until time to express – Large quantities of eukaryotic protein in bacteria are ...
... product of a gene – usually more is better • For this reason, expression vectors have very strong promoters • Prefer keep a cloned gene repressed until time to express – Large quantities of eukaryotic protein in bacteria are ...
Diapositiva 1 - Laboratorio de Genómica Viral y Humana
... – Most ERVs appear to be defective, containing nonsense mutations or major deletions which prevent them from producing infectious virus particles. – However, there is one family of viruses that have been active since the divergence of humans and chimpanzees [ hERV-K(HML2)]. ...
... – Most ERVs appear to be defective, containing nonsense mutations or major deletions which prevent them from producing infectious virus particles. – However, there is one family of viruses that have been active since the divergence of humans and chimpanzees [ hERV-K(HML2)]. ...
Genetic engineering methods
... limit growth to engineered cells Other kinds of genes can also be used to favor transgenic cells (e.g., sugar uptake, herbicide resistance, hormone sensitivity) ...
... limit growth to engineered cells Other kinds of genes can also be used to favor transgenic cells (e.g., sugar uptake, herbicide resistance, hormone sensitivity) ...
Topic 4.4 genetic engineering
... The outcomes include the knowledge of how many genes code for humans. We thought there could be as many as 100,000 genes, turns out to be around 25,000 genes. The complete genome allows for evolutionary comparisons of humans to other organisms. The project included mapping the genomes of other spec ...
... The outcomes include the knowledge of how many genes code for humans. We thought there could be as many as 100,000 genes, turns out to be around 25,000 genes. The complete genome allows for evolutionary comparisons of humans to other organisms. The project included mapping the genomes of other spec ...
RNA and Protein Synthesis Notes Organizer
... 9. A ____________________ is a 3 base mRNA sequence that codes for a particular ________________________. a. There are _______________ different amino acids. b. Amino acids join together to form _________________________________. 10. Translation: ______________ ______________ 11. What is translat ...
... 9. A ____________________ is a 3 base mRNA sequence that codes for a particular ________________________. a. There are _______________ different amino acids. b. Amino acids join together to form _________________________________. 10. Translation: ______________ ______________ 11. What is translat ...
Our Time To Lead
... • Evidently there is still a lot more to be learned about the how genes determine characteristics and how gene expression is controlled… ...
... • Evidently there is still a lot more to be learned about the how genes determine characteristics and how gene expression is controlled… ...
NF1X - BioMed Central
... Nuclear factor 1 X-type (NF1X) is a transcription factor known to bind the palindromic consensus sequence TTGGC(N)5GCCAA [1], and has been shown to activate replication of adenoviral DNA [2]. It is highly conserved in vertebrates, with chicken and hamster orthologs showing 92% amino acid sequence id ...
... Nuclear factor 1 X-type (NF1X) is a transcription factor known to bind the palindromic consensus sequence TTGGC(N)5GCCAA [1], and has been shown to activate replication of adenoviral DNA [2]. It is highly conserved in vertebrates, with chicken and hamster orthologs showing 92% amino acid sequence id ...
Concept checks - WordPress.com
... Explain the relationship between the number of amino acid residues in the enzyme and the number of nucleotide pairs in its gene ...
... Explain the relationship between the number of amino acid residues in the enzyme and the number of nucleotide pairs in its gene ...
Lecture Slides - METU Computer Engineering
... terms of molecules (in the sense of physicalchemistry) and then applying “informatics” techniques (derived from disciplines such as applied math, CS, and statistics) to understand and organize the information associated with these molecules, on a large-scale. • Bioinformatics is a practical discipli ...
... terms of molecules (in the sense of physicalchemistry) and then applying “informatics” techniques (derived from disciplines such as applied math, CS, and statistics) to understand and organize the information associated with these molecules, on a large-scale. • Bioinformatics is a practical discipli ...
Pdf Version - Fondazione Diritti Genetici
... hereditary characteristics made up of four NITROUS chemicals : adenine (A), cytosine (C), guanine (G) and tyrosine (T) (substituted by uracile in the case of RNA). A minimum number of nucleotide particle sequences (genes) make up the basis of the hereditary character code while the majority of genet ...
... hereditary characteristics made up of four NITROUS chemicals : adenine (A), cytosine (C), guanine (G) and tyrosine (T) (substituted by uracile in the case of RNA). A minimum number of nucleotide particle sequences (genes) make up the basis of the hereditary character code while the majority of genet ...
Mendelian Genetics
... – The last relay molecule activates a transcription factor that causes the transcription of a specific gene in the DNA of the nucleus. – This leads to the production of a protein that may act as an enzyme or structural element needed to effect a change in the cell. ...
... – The last relay molecule activates a transcription factor that causes the transcription of a specific gene in the DNA of the nucleus. – This leads to the production of a protein that may act as an enzyme or structural element needed to effect a change in the cell. ...
THE GENETICS OF VIRUSES
... o “lock-and-key” fit between virus proteins and receptor on cell surface o some are broad enough for several species, some can only infect single species Eukaryotic viruses are tissue specific Steps of a viral infection 1- genome of a virus enters host cell-(entrance mechanism differs by type) 2- Vi ...
... o “lock-and-key” fit between virus proteins and receptor on cell surface o some are broad enough for several species, some can only infect single species Eukaryotic viruses are tissue specific Steps of a viral infection 1- genome of a virus enters host cell-(entrance mechanism differs by type) 2- Vi ...
RNA Viruses
... site and share 3’ end of genome • May be produced by jumping polymerase - 7 base sequence in various parts of genome – Get recombinant viruses with mixed infections – DI particles are common ...
... site and share 3’ end of genome • May be produced by jumping polymerase - 7 base sequence in various parts of genome – Get recombinant viruses with mixed infections – DI particles are common ...
Ecology Pre
... SC.912.L.16.3 Describe the basic process of DNA replication and how it relates to the transmission and conservation of the genetic information. SC.912.L.16.10 Evaluate the impact of biotechnology on the individual, society and the environment, including medical and ethical issues. SC.912.L.16.4 Expl ...
... SC.912.L.16.3 Describe the basic process of DNA replication and how it relates to the transmission and conservation of the genetic information. SC.912.L.16.10 Evaluate the impact of biotechnology on the individual, society and the environment, including medical and ethical issues. SC.912.L.16.4 Expl ...
Mitochondrial Genome Evolution
... genome of Chara vulgaris: insights into the mitochondrial DNA of the last common ancestor of green algae and land plants” Plant Cell 15: 1888-1903 ...
... genome of Chara vulgaris: insights into the mitochondrial DNA of the last common ancestor of green algae and land plants” Plant Cell 15: 1888-1903 ...
Some Products Made Using Biotechnology
... DNA profiles can be used to determine whether a particular person is the parent of a child. A childs paternity (father) and maternity(mother) can be determined. This information can be used in ...
... DNA profiles can be used to determine whether a particular person is the parent of a child. A childs paternity (father) and maternity(mother) can be determined. This information can be used in ...
Lecture, Gene Expression
... After DNA Replication, there is enough DNA make 2 new cells… and then again, and again until the organism stops performing cell division (i.e., never, really). Once a new cell is made, it can begin to use the DNA to create phenotypes. We call this next part Gene Expression, or the production of a ph ...
... After DNA Replication, there is enough DNA make 2 new cells… and then again, and again until the organism stops performing cell division (i.e., never, really). Once a new cell is made, it can begin to use the DNA to create phenotypes. We call this next part Gene Expression, or the production of a ph ...
Reading Guide for Week 5
... acids, nucleotides, fatty acids, glycerol, and monosaccharides). In this reading guide we’ll put those subunits together to make macromolecules through the processes of DNA replication, transcription, and translation, and put those macromolecules together to make cellular structures (for example: pr ...
... acids, nucleotides, fatty acids, glycerol, and monosaccharides). In this reading guide we’ll put those subunits together to make macromolecules through the processes of DNA replication, transcription, and translation, and put those macromolecules together to make cellular structures (for example: pr ...
Endogenous retrovirus
Endogenous retroviruses (ERVs) are endogenous viral elements in the genome that closely resemble and can be derived from retroviruses. They are abundant in the genomes of jawed vertebrates, and they comprise up to 5–8% of the human genome (lower estimates of ~1%). ERVs are a subclass of a type of gene called a transposon, which can be packaged and moved within the genome to serve a vital role in gene expression and in regulation. Researchers have suggested that retroviruses evolved from a type of transposable gene called a retrotransposon, which includes ERVs; these genes can mutate and instead of moving to another location in the genome they can become exogenous or pathogenic. This means that all ERVs may not have originated as an insertion by a retrovirus but that some may have been the source for the genetic information in the retroviruses they resemble.